Business Strategy Assignment: Strategic Issues Encounter By Bunnings Warehouse
Question
Task:
Business Strategy Assignment Scenario: You are a consultant hired to analyze the strategic issues facing the company. To do so, you will need to conduct an internal analysis of the company, and complete a SWOT to identify strategic issues.
You should apply relevant strategic concepts, frameworks and models from the course, to identify Strategic issues facing the company.
Answer
Executive Summary
The purpose of this business strategy assignment paper is to make an organisational analysis of Bunnings Warehouse. The paper will include an external analysis. The external analysis has two parts, one is the macro environmental analysis which will be conducted using the PESTEL method; the other is the industrial analysis which will be based on Porter’s five forces. The external environmental analysis is like an early warning for the organisation, based on which it can make its strategic plans. The paper also includes an industry profile which will highlight the name of the industry, its growth prospect, key customers, etc. The competitors’ profile is like a comparative study of Bunnings Warehouse with respect to its competitors in the market. The internal analysis of the company will be based on SWOT analysis. The SWOT analysis will focus on the strength, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of Bunnings Warehouse. The business as well as corporate strategies has been discussed. The core competencies have been highlighted and a VRIO analysis is prepared. The paper also includes a strategic mapping along with value chain analysis which will provide deeper insight into the organisational structure, its operations and environment.
1. Introduction
The purpose of this paper is to conduct an internal as well as external analysis for Bunnings Warehouse. This paper is written from the perspective of an organisational consultant of Bunnings Warehouse. A clear understanding of the internal and external business environment is important for strategic planning. The various strategic issues that Bunnings Warehouse is facing will be discussed in this paper. The internal analysis of the company will be based on VRIO and SWOT, while for external analysis PESTEL and Porter’s model will be referred to. The identification of the strategic issues will facilitate resolving the problems, hence fostering company growth.
2. External Analysis
The external analysis refers to the environmental analysis or assessment in which the changing business environment and the factors responsible for it are analysed. The enterprise here, Bunnings Warehouse, works in the hardware industry. Therefore, the external factors which affect the business of the hardware industry in New Zealand will be discussed in this section.
The external analysis will be conducted with the help of PESTEL (Appendix 5.3) and Porter’s five forcesmodel (Appendix 5.4). The external analysis facilitates getting a clearer picture of the potential threats and opportunities. This analysis could be an early warning system.
2.1. Industry Profile
- Industry Name : Bunnings Warehouse operates in the hardware industry (Tan et al, 2020).
- Size : The hardware andhome improvementretail sector is a substantially large industry in Australia and New Zealand.
- Growth rate : Bunnings Warehouse is operating in the growth stage of its life cycle. The rate of growth in the hardware industry is high considering the high and ever increasing demand for hardware, garden products and home improvement items. The industry promises high growth and good contribution to GDP. The industry exhibits high growth with annual value of 24 billion dollars (Tarrant, 2019).
- Competitors : The three major competitors of Bunnings Warehouse are Australian Outdoor Living, Home Hardware and Class Home Improvements. Besides, there are many small hardware companies in Australia and New Zealand.
- Geographic scope : The geographic area of Australia and New Zealand provides scope for growth of hardware and home improvement products’ business. The reason is the dry weather, large garden size and ownership of houses.Thus, Bunnings Warehouse can prosper in this environment (Nienaber et al, 2018).
- Key customers : The key customers of Bunnings Warehouse include the contractors, ‘do it yourself’ customers and builders.
2.2. Competitor Profiles
As per Feng et al (2020), the strategic group map as a tool will facilitate the business to visualise the position of its competitors in the industry. The rivals or competitors which have similar business models or strategies are referred to as strategic group. The strategic group mapping will help in identifying the scope of Bunnings Warehouse’s competitors. The major competitors of Bunnings Warehouse are True Value Hardware, Mitre 10, Australian Outdoor Living, Home Hardware and Class Home Improvements and Home Timer and Hardware. The competitor profile is presented in Appendix 5.1 and Strategic Group Mapping in Appendix 5.2.
2.3. Competitive Analysis (P5F)
As per Bruijl (2018), the Porter’s five forces model will provide an insight about the competitive analysis of the company within the hardware industry. The Porter’s five forces model facilitates analysis of the competition in the business. These five forces will determine the intensity of competition in the industry. This also suggests the attractiveness of a business in the particular industry.
Power of the suppliers: The power vested in the hands of the suppliers of the home improvement and hardware industry is a strong industrial force. This is because there is large number of suppliers in the industry. The business of Bunnings Warehouse is affected by this power of the suppliers.
Threat of Substitutes: The business of Bunnings Warehouse is moderately impacted by the threat of substitutes. The reason is that the customers will shift to other companies only when Bunnings Warehouse will increase their prices or their products will be defective (Cavagnino, 2019).
Threat of New Entrants: The impact or the threat of new threats is weak for Bunnings Warehouse. This is because of its strong brand image and the good share of market it has already captured. The new entrants will find it difficult to meet the standards of Bunnings Warehouse.
Power of Customers: The customers of the hardware industry are a strong force. The preferences of the customers drive the market demand. The customers affect the demand of Bunnings Warehouse.
Competitive rivalry: The competitive rivalry in the hardware industry is moderate. Bunnings Warehouse already has a good market share. They face least threat from competition. However, they constantly try to upgrade their products and process (Verma, 2018).
2.4. Driving Forces
The political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors affect the macro environment of Bunnings Warehouse. The business of hardware and home improvement products is affected by these factors. Thus, the analysis of these driving forces is required.
Macro-environmental analysis: PESTEL Analysis:
Political: The instability of the political situation in Australiaaffectsthe business of the hardware industry. The frequent amendments in the government regulations act as political barrier to the hardware business of Bunnings Warehouse. However, in Australia the governmental support fosters better growth of the local hardware companies. The government sometimes imposes tariffs on imports of the home improvement and building products. This could hinder the free business of hardware products. Thus, political factors impact the business of Bunnings Warehouse. (Ad?güzel, 2020)
Economic: In the Australian economy, the unstable prices, the economic instability andcrisis in the market has adverse effect on the business of Bunnings Warehouse. The global recession caused by Covid-19 pandemic affected the economy and hence the business of Bunnings Warehouse. The stores of Bunnings Warehouse have the home improvement and hardware which they retail. However, due to the recession the disposable income of the customers have reduced, which eventually lowers the sales of Bunnings Warehouse. The consumer behaviour has changed due to the pandemic. The customers focus on purchase of essentials over luxury, home décor items (Redman, Belleville & Dakin, 2019).
Social: The social environment and lifestyle of the people of Australia and New Zealand create demand for hardware and home improvement products. Thus, per capita consumption of hardware is high in Australia and New Zealand as they have large gardens, number of home ownerships is high and weather conditions are dry. The improvements in the social lifestyle of the people in Australia and New Zealand would increase the demand for Bunnings Warehouse’s products. The new tailored kitchen setup or the new air conditioners’ installation enhances the demand for the company’s products (Mapley et al, 2020).
Technological: The installation of hardware products and their designing requires innovation and technological advancement. Thus, technology highly impacts the business of Bunnings Warehouse. The quality of products and new materials’ development is affected by technological development. Technology facilitates better material and product utilisation.
Environmental: The government of Australia is showing its concern towards the protection of the environment. This has led to the imposition of restrictions and abandonment of various operations. Thus, to sustain in such regulated environment, Bunnings Warehouse has to improve its recycling operations. They should also consider finding ways of reducing the emission of carbon and lowering energy use while carrying out their production of home improvement and hardware products. The program of Bunnings Warehouse which aimed at achieving carbon neutrality by 2015 was designed to meet the environmental concerns of the government (Butters, 2019).
Legal: The legal restrictions which impact the business of Bunnings Warehouse are related to forest operation management. The company has to meet the compliance requirements, have proper license and adhere to the trade laws to operate legally in Australia and New Zealand.
3. Internal Analysis
3.1. Strategic Profile
The Bunnings Group trades under the name Bunnings Warehouse. They operate in the hardware industry. This Australian company has its stores in New Zealand and Australia. This household hardware chain is owned by Wesfarmers and the company has been operating since 1994. The companies deals inretail hardware and home improvement products in Australia and New Zealand. The target customers of Bunnings Warehouse include owner-builders, commercial businesses, SME builders, tradespersons and DIY enthusiasts. The company has 40,000 employees. They have 253 warehouses, 77 small format stores, 33 trade centres and 3 sites of frame and truss operating in Australia and New Zealand. The market share of Bunnings Warehouse accounts for almost 35.02 percent. The rivals of the company occupy only 5 percent of the market share in the hardware industry (May, 2019).
The strategic profile of Bunnings Warehouse includes its corporate as well as business strategies.
Business Strategy:
- Cost leadership is a significant business strategy of the company. The company offers lowest prices to its customers. Bunnings Warehouse offers the products at 10 percent lesser price than its competitors even when its competitors are offering cheaper items (Weaver, 2021).
- The other business strategy of Bunnings Warehouse is to attain a core position in the hardware market and a competitive advantage over its rivals by offering a wide range of affordable products.
Corporate Strategy:
- The corporate strategy of Bunnings Warehouse includes market penetration, domestic formulation, market development and execution of industrial focus.
- Bunnings Warehouse’s acquisition of various organisations is a significant corporate strategy. It also acquired its competitor Mitre 10 in the year 2013, which gives it a stronger brand position (Keil, 2019).
- The key corporate strategies of Bunnings Warehouse are based on diversified and vast product range, competitive prices and intensive services.
- The setting up of new warehouses is an implementation of Bunnings Warehouse’s corporate strategy of market penetration.
- The company is also planning gradual and steady geographical expansion for greater market share.
3.2. Value Chain
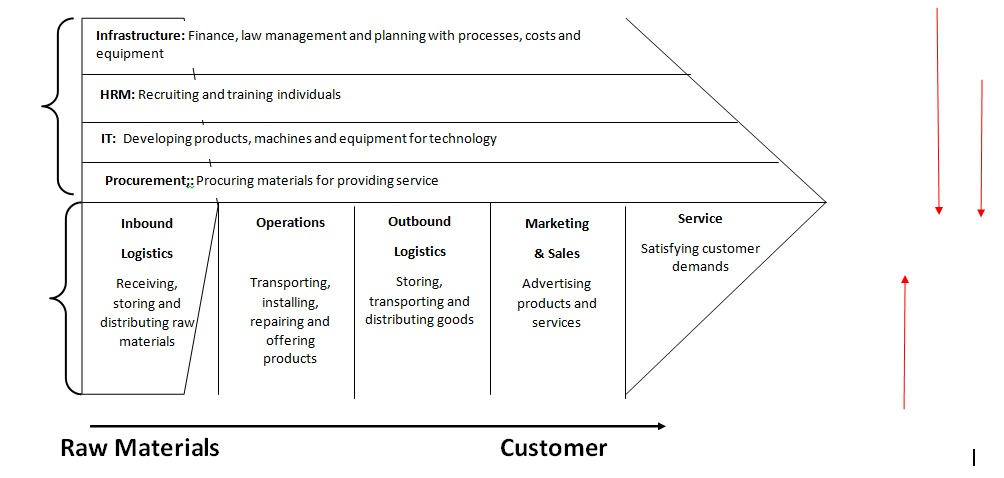
As per Straková et al (2020), the value chain is a very significant part of a business. The value chain of Bunnings Warehouse includes the various business activities as well as processes which are involved in the creation of a product or any service. There could be many stages in the value chain of a product’s lifecycle. These include sales, research and development, etc. The value chain has been presented in Appendix 5.5. The value chain will help in understanding the linkages between the various activities. It will also highlight the areas that are inconsistentin the value chain. The value chain of Bunnings Warehouse is linked to its business-level strategy.
3.3. Competitive Advantage (VRIO) Analysis
The core competencies of Bunnings Warehouse are seen in its system of freight delivery which fosters efficient deliveries. The company maintains abundant suppliers which is another core competency. The functional strategies of Bunnings Warehouse include areas like HRM, financial, marketing, distribution and information technology (Grimmer, 2017). Each of these areas has various drivers. Efficiency is the main driver in distribution area, quality in HRM and innovation in IT area.
The VRIO analysis will provide a better picture of competitive analysis of Bunnings Warehouse (Appendix 5.6).
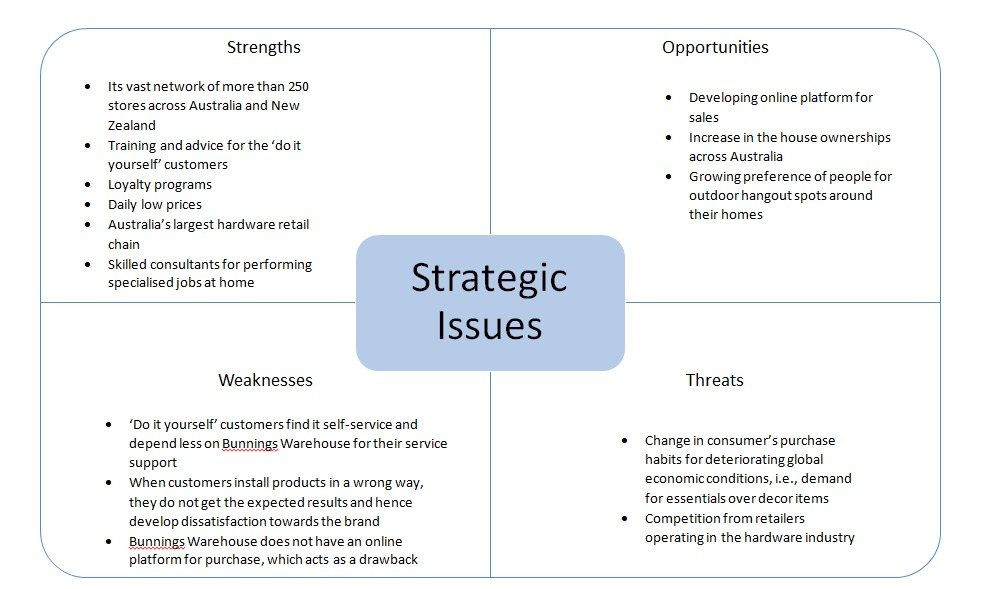
4. Strategic Issues: SWOT
Strengths:
The major strengths of Bunnings Warehouse are:
- Its vast network of more than 250 stores across Australia and New Zealand
- Training and advice for the ‘do it yourself’ customers
- Loyalty programs
- Daily low prices
- Australia’s largest hardware retail chain (Manassakis, 2019)
- Skilled consultants for performing specialised jobs at home
Weaknesses:
The major weaknesses of Bunnings Warehouse are:
- ‘Do it yourself’ customers find it self-service and depend less on Bunnings Warehouse for their service support (Boyd, 2018)
- When customers install products in a wrong way, they do not get the expected results and hence develop dissatisfaction towards the brand
- Bunnings Warehouse does not have an online platform for purchase, which acts as a drawback
Opportunities:
The opportunities that Bunnings Warehouse can reap include:
- Developing online platform for sales
- Increase in the house ownerships across Australia
- Growing preference of people for outdoor hangout spots around their homes (Mapley et al, 2020)
Threats:
The major threats of include:
- Change in consumer’s purchase habits for deteriorating global economic conditions, i.e., demand for essentials over decor items (Redman, Belleville & Dakin, 2019)
- Competition from retailers operating in the hardware industry
- Reduction in purchase of hardware products by domestic consumers as the prominence of contractors is increasing in the market and the latter takes care of all the maintenance jobs
5. Appendices
Include all supporting information here, including the figures below.
5.1. Competitor Profiles
|
Competitor |
Criteria 1 (Key competitive advantage)
|
Criteria 2 (Target market) |
Criteria 3 (Products and services) |
Criteria 4 (Strengths and weaknesses |
|
True Value Hardware |
Quality products, exceptional service and expert advice
|
Independent retailers and wholesale customers |
Automotive, bath, building materials, electrical, hardware, heating and cooling, kitchen, lawns and garden, lighting and ceiling fans, storage and organization. |
Focuses extensively on independent stores and retailers but fails to analyse the importance of wholesalers |
|
Mitre 10 |
High brand popularity and brand value being awarded as most trusted 11 times |
Increased range of Customers and trade professionals |
Automotive and garage, bathroom, building supplies, camping and beach, flooring and tiles, electric hardware hand tools, petcare, plumbing and others |
Wide range of products and the largest home improvement and garden retailer of NZ. |
|
Australian Outdoor Living |
Personalised service with custom designed solutions |
Customers from seven locations of Australia
|
Outdoor blinds, artificial grass, roller shutters, swimming pools, timber decking and pergolas and verandas |
Differentiated products than other brands |
|
Home Hardware |
Both hardware store and building centre products |
Mainly customers for home renovation, repair and maintenance |
Everyday living, kitchen, lighting, outdoor, paint, plumbing, floors, heating and cooling |
Around 100,000 different items available |
5.2. Strategic Group Map






5.3. PESTEL Analysis
|
Dimension |
Trend |
|
Political |
The instability of the political situation in Australiaaffectsthe business of the hardware industry. The frequent amendments in the government regulations act as political barrier to the hardware business of Bunnings Warehouse. However, in Australia the governmental support fosters better growth of the local hardware companies. The government sometimes imposes tariffs on imports of the home improvement and building products. This could hinder the free business of hardware products. Thus, political factors impact the business of Bunnings Warehouse. |
|
Economic |
In the Australian economy, the unstable prices, the economic instability andcrisis in the market has adverse effect on the business of Bunnings Warehouse. The global recession caused by Covid-19 pandemic affected the economy and hence the business of Bunnings Warehouse. The stores of Bunnings Warehouse have the home improvement and hardware which they retail. However, due to the recession the disposable income of the customers have reduced, which eventually lowers the sales of Bunnings Warehouse. The consumer behaviour has changed due to the pandemic. The customers focus on purchase of essentials over luxury, home décor items. |
|
Sociocultural |
The social environment and lifestyle of the people of Australia and New Zealand create demand for hardware and home improvement products. Thus, per capita consumption of hardware is high in Australia and New Zealand as they have large gardens, number of home ownerships is high and weather conditions are dry. The improvements in the social lifestyle of the people in Australia and New Zealand would increase the demand for Bunnings Warehouse’s products. The new tailored kitchen setup or the new air conditioners’ installation enhances the demand for the company’s products. |
|
Technological |
The installation of hardware products and their designing requires innovation and technological advancement. Thus, technology highly impacts the business of Bunnings Warehouse. The quality of products and new materials’ development is affected by technological development. Technology facilitates better material and product utilisation.
|
|
Ecological |
The government of Australia is showing its concern towards the protection of the environment. This has led to the imposition of restrictions and abandonment of various operations. Thus, to sustain in such regulated environment, Bunnings Warehouse has to improve its recycling operations. They should also consider finding ways of reducing the emission of carbon and lowering energy use while carrying out their production of home improvement and hardware products. The program of Bunnings Warehouse which aimed at achieving carbon neutrality by 2015 was designed to meet the environmental concerns of the government. |
|
Legal |
The legal restrictions which impact the business of Bunnings Warehouse are related to forest operation management. The company has to meet the compliance requirements, have proper license and adhere to the trade laws to operate legally in Australia and New Zealand.
|
5.4. Porters 5 Forces Analysis





5.5. Value Chain
5.6. VRIO Analysis
TIP: Modify or replace the headings in the table if they are not fully applicable to your company.
|
Resource/ Capability |
V |
R |
I |
O |
Result |
|
Infrastructure |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warehouses and land |
? |
|
|
|
Low |
|
Leasehold and freehold properties across Australia and NZ |
? |
|
|
|
Competitive |
|
Sites in metropolitan and regional locations |
? |
? |
|
|
advantage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HRM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Team members |
? |
|
|
|
Low |
|
Recognizing and rewarding efforts |
? |
|
|
|
Competitive |
|
Fun and safe workplace |
? |
|
|
|
advantage |
|
270 water tanks across Australia, and 10 in New Zealand |
? |
? |
? |
? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Strong supply chain systems |
? |
? |
|
? |
Moderate |
|
Modern and flexible technology base |
? |
? |
|
? |
Competitive |
|
|
|
|
|
|
advantage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Procurement |
|
|
|
|
|
|
High quality materials |
? |
? |
|
|
High |
|
Lowest prices |
? |
? |
|
? |
Competitive |
|
Wide range of products (45,000) |
? |
? |
? |
? |
advantage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reputational |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Strong brand name and popularity |
? |
? |
? |
? |
High |
|
Market leader in big box hardware |
? |
? |
? |
? |
Competitive |
|
|
|
|
|
|
advantage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sustainability |
|
|
|
|
|
|
100% renewable electricity by 2025 |
? |
? |
|
|
Z |
|
80 solar PV systems |
? |
? |
? |
? |
Competitive |
|
Reusing rainwater |
? |
? |
|
? |
advantage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outbound Logistics |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Free D.I.Y. workshops for adults and children |
? |
? |
|
? |
High |
|
free trailer hire, same day home delivery, |
? |
? |
? |
? |
Competitive |
|
expert advice and great service |
? |
? |
? |
? |
advantage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Marketing/Sales |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
After Sales Service |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.7. SWOT
6. Reference List
Ad?güzel, S. (2020). Market and brand positioning and sustainability strategies in international marketing. International Journal of Scientific Research and Management, 8(9), 9-24.
Boyd, K. (2018). Improving air quality with indoor plants at the Honey Tree Preschool Bellbird. Every Child, 24(1), 12-13.
Bruijl, G. H. T. (2018). The relevance of Porter's five forces in today's innovative and changing business environment. Available at SSRN 3192207.
Butters, L. R. (2019). Development of a Machine Vision System to Localise a Zinc Die Cast Product (Doctoral dissertation, Auckland University of Technology).
Cavagnino, A. (2019). Deficiencies in Australia's Current Merger Regime: The Call to Combat Creeping Acquisitions. Int'l Trade & Bus. L. Rev., 22, 119.
Feng, T. T., Zhang, X., Tan, L. L., & Liu, H. P. (2021). CROSS-CULTURAL ADAPTATION AND VALIDATION OF THE STRATEGIC LEARNING ASSESSMENT MAP FOR CHINESE NURSING ORGANIZATION: A CROSS-SECTIONAL STUDY. Nurse Education in Practice, 103185.
Grimmer, L. (2017). Bunnings Warehouse online shopping and home delivery is coming: interview with Lucy Bortolazzo.
Keil, S. (2019). How to sack a customer. Plumbing Connection, (Autumn 2019), 54-56.
Manassakis, E. S. (2019). The'table project'. Educating Young Children: Learning and Teaching in the Early Childhood Years, 25(3), 9-11.
Mapley, M., Lu, Y., Gregory, S. D., Pauls, J. P., Tansley, G., & Busch, A. (2020). Development and validation of a low-cost polymer selective laser sintering machine. HardwareX, 8, e00119.
May, P. (2019). Get smarter: Why smarter warehouses demand smarter risk strategies. MHD Supply Chain Solutions, 49(2), 20-21.
Nienaber, L. M., Cresswell, S. L., Carter, J. F., & Peter, T. (2018). A comparison of plastic cable ties based on physical, chemical and stable isotopic measurements. Business strategy assignment Science & Justice, 58(1), 67-75.
Redman, A., Belleville, B., & Dakin, T. (2019). Advancing enhanced wood manufacturing industries in Laos and Australia-PML Easbeam Study Tour.
Straková, J., Rajiani, I., Pártlová, P., Váchal, J., &Dobrovi?, J. (2020). Use of the Value Chain in the Process of Generating a Sustainable Business Strategy on the Example of Manufacturing and Industrial Enterprises in the Czech Republic. Sustainability, 12(4), 1520.
Tan, B., Ji, Y., Hu, Y., Yuan, B., Hu, X., & Huang, Z. (2020). Pretreatment using diluted epoxy adhesive resin solution for improving bond strength between steel and wood surfaces. International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives, 98, 102502.
Tarrant, D. (2019). Customer clout. Company Director, 35(7), 34-41.
Verma, A. (2018). The competitive dynamics of MNE market entry on host country incumbents: word/action responses to Amazon’s retail entry into the Australian retail sector (Doctoral dissertation, Auckland University of Technology).
Weaver, C. (2021). Application of the WHO Integrated Person-Centred Care Framework (IPCC) in the development of a large Health Hub in the Northern Suburbs of Brisbane. International Journal of Integrated Care, 20(3).












