Disease management assignment on plant pests and disease management
Question
Task: how can plant pests and diseases be management using Disease management assignment research techniques
Answer
1. Introduction
This Disease management assignment will assess information relating to plant pests and diseases. A plant disease is typically defined as improper plant development and function. Diseases are the outcome of some disruption in the plant's regular life cycle. There are both living and non-living sources of disease. Biotic disorders are brought on by living things like bacteria, fungus, and viruses. Abiotic diseases are caused by inanimate environmental factors such as soil compaction, wind, frost, salt damage to the soil, and girdling roots. Wide range of plants are afflicted by the widespread fungus known as powdery mildew. It is simple to recognise and looks as light grey or white powdery spots that are typically seen on infected leaves. However, they can also be found on the stems, soil underneath, or on the undersides of wheat plants.
2. Disease management assignment - Pathogen description
2.1. Identification of plant diseases in Wheat Crops
Disease management assignment research shows that everywhere the winter wheat is farmed in the US and Canada, powdery mildew is a prevalent disease of wheat. It affects the eastern soft winter wheat region economically and is brought on by "Blumeriagraminis f. sp. tritici". Fluffy, white to grey fungal growth on the top surface of leaves is the tell-tale indication of the powdery mildew infection. On the underside of leaves, yellowish patches frequently appear beneath the fungal growth and lower leaves are where signs are most common (Raveau, Fontaine &Lounès-Hadj Sahraoui, 2020). Fungicide needs to be used as soon as the disease manifests as they have some systemic activity, fungicides that contain triazoles are the most effective. Follow fertility recommendations and steer clear of over fertilization. Practices that promote dense stands and high yields promote mildew development.

Figure 1: Powdery Mildew in Wheat Crops
(Source: Osu.edu, 2022)
2.2. Disease-cycle
Wheat plants are particularly vulnerable while they are growing quickly, especially between the stages of growth known as stem elongation and heading. Although these early infections are typically difficult to spot, wheat typically contracts powdery mildew in the fall, shortly after planting. Fall infections are caused by spores that grow on stray wheat plants or in cleistothecia on crop leftovers. Disease management assignment research also shows on wheat straw or on diseased wheat, the mildew fungus survives the winter as mycelium. In chilly, humid circumstances, spores grow and infect plants although high relative humidity of about 100% is not necessary for infection to occur on plant surfaces. Temperatures above 77° F hinder the growth of powdery mildew, which thrives between 59 and 71° F. In dense stands of wheat that has been highly fertilised, mildew is more severe. Every 7 to 10 days, a fresh crop of conidia is produced under ideal circumstances. The disease spreads up the plant and between plants as a result of conidia being wind-dispersed to fresh leaves (Álvarez,López&Biosca,2019). New cleistothecia are formed as the season ages, temperatures rise, and the plant and fungus grow.
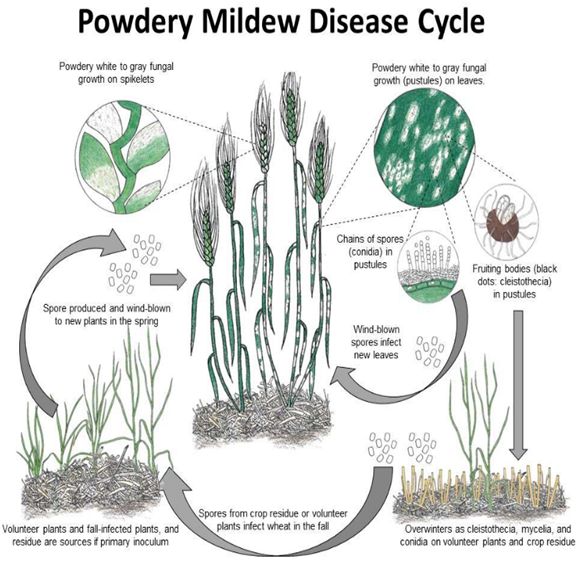
Figure 2: Disease Cycle of Powdery Mildew
(Source: Osu.edu, 2022)
3. Outline of integrated disease management program including a description of a set action threshold
3.1. Steps for Pest Management program
• IPM Prevention Methods
• Monitoring
• Maps for identifying pests
• Thresholds for record-keeping actions
• Examine and Select Alternatives
3.2. Describe commercially relevant plant diseases
The intensity of powdery mildew is greatly determined by the weather as per reports made on most Disease management assignment papers. Winter wheat growing regions are more prone to early and severe mildew development. While extended periods of cool, humid weather in the spring can allow the disease to reach the flag leaf and cause yield losses, cool, humid, dry circumstances encourage infection. The severity of a disease can be exacerbated by excess nitrogen, dense plant populations, or other circumstances that promote excessive farming (Berbegalet al. 2020). Disease is easier to spread in lighter, sandier soils. Powdery mildew is completely or partially resistant to several kinds that are modest resistance on its own is frequently sufficient to control powdery mildew. Selecting resistant cultivars is crucial when using numerous fungicides that are approved for the treatment of powdery mildew in areas vulnerable to major outbreaks. Varietal susceptibility, anticipated weather, and yield potential all have an impact on the choice to apply a fungicide. Fungicides are not necessary for resistant or moderately resistant types. As soon as the disease manifests, fungicides should be used and they have some systemic activity, fungicides containing triazoles work best.
3.3. Analyse and describe the relationships between hosts and pathogens
The pathogen interacts intensely with the host and the environment around it as soon as it touches the host surface during the pre-penetration stage. The environment, which is made up of all external factors such as temperature, moisture in humidity, light, and competing microorganisms. Again, the best environment for a pathogen's growth depends on the type of pathogen and the host surface.
The most significant component that regulates the overall course of illness development is the pathogen's nature and behaviour. The pathogen's inoculum potential is reflected in its nature and behaviour (Alfiky& Weisskopf, 2021). The biological energy that is accessible for colonising a host is measured once more by the inoculum ability.
When a pathogen has an incubation time and infection is only established after the incubation period has passed, there may be a delay. The pathogen's ability to compete with the host for nutrients, produce enzymes and poisonous chemicals, and affect the host's metabolic processes are all important factors in the post-penetration process' effectiveness.
4. Table of integrated disease management program
|
Components |
Description |
|
Acceptable level of pest
|
IDM contends that while complete eradication of a population is unachievable, maintaining it at a manageable, economically feasible, and environmentally safe level should be the main focus. |
|
Monitoring |
AnDisease management assignmentIDM programme can be guided by regular crop monitoring and record keeping, which yields trustworthy information. It's vital to inspect the flowers and foliage, ideally once a week (Aliet al. 2020).. |
|
Host-plant resistance |
Especially for wheat, rice, potatoes, cassava, chickpeas, peanuts, and cowpeas, host plant resistance is a crucial tool in the fight against disease in poor nations' primary food crops. Farmers with limited resources favour the usage is environmentally friendly. |
|
Pesticide impact in Environment |
Pesticides have the potential to pollute lawn, water, and other vegetation. Pesticides can be poisonous to a variety of different organisms in addition to insects and weeds, such as birds, fish, helpful insects, and non-target plants. |
|
Necessity of management |
The objective of integrated pest management is not to eradicate all pests; some pests are acceptable and necessary so that their natural enemies are still present in the crop. Instead, it's to get insect populations down to levels that are not really harmful. |
Table 1: Integrated disease management program
(Source: Researcher)
5. Conclusion
From the Disease management assignmenton plant disease management, it can be concluded that the infections that cause plant diseases must be very virulent organisms. A pathogen that can cause numerous plant diseases is referred to as virulent. The series of actions that take place as a result of a disease developing in a plant is known as the plant disease cycle. There are three requirements that must be met for any plant disease to develop; they do not just happen.
References
Journals
Alfiky, A., & Weisskopf, L. (2021). Deciphering Trichoderma–plant–pathogen interactions for better development of biocontrol applications. Journal of Fungi, 7(1), 61.https://www.mdpi.com/2309-608X/7/1/61/pdfDisease management assignment
Ali, M., Ahmed, T., Wu, W., Hossain, A., Hafeez, R., Islam Masum, M., ... & Li, B. (2020). Advancements in plant and microbe-based synthesis of metallic nanoparticles and their antimicrobial activity against plant pathogens.
Nanomaterials, 10(6), 1146.https://www.mdpi.com/2079-4991/10/6/1146/pdf version=1591871101
Álvarez, B., López, M. M., &Biosca, E. G. (2019). Biocontrol of the major plant pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum in irrigation water and host plants by novel waterborne lytic bacteriophages. Frontiers in Microbiology, 10, 2813. Doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02813
Berbegal, M., Ramón Albalat, A., León, M., &Armengol, J. (2020). Evaluation of long term protection from nursery to vineyard provided by Trichoderma atroviride SC1 against fungal grapevine trunk pathogens. Pest management science,Disease management assignment 76(3), 967-977.https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.5605
Raveau, R., Fontaine, J., &Lounès-HadjSahraoui, A. (2020). Essential oils as potential alternative biocontrol products against plant pathogens and weeds: A review. Foods, 9(3), 365.https://www.mdpi.com/2304-8158/9/3/365/pdf
Websites
Osu.edu (2022), Powdery Mildew of Wheat, Retrieved from: https://ohioline.osu.edu/factsheet/plpath-cer-11#:~:text=As%20the%20plant%20matures%2C%20the,as%20plants%20mature%20in%20Jun[Accessed on: 1st September, 2022] Disease management assignment












