Fast Lane Case Study: Critical Analysis On The Supplier Management
Question
Task: Fast Lane Ltd manufactures motorbikes and is located in Brisbane. More than 70% of the cost of the company’s motoibikes consist of material and components, which are purchased from Australian suppliers.
About three years ago, Fast Lane introduced a comprehensive supplier evaluation system to monitor the performance of its suppliers. Each supplier was given a 3 year contract that guaranteed large orders as long as it performed according to Fast Lan’s strict requirements. Each supplier’s performance was measured by considering its adherence to delivery schedules (Fast Lane works on a JIT system), accuracy of orders delivered, number of components rejected on delivery, and it’s achievements in reducing its production costs (and, therefore, its material and component prices) over the contract period.
Performance in all these areas will determine whether Fast Lane renews the supplier’s contract or offers the contract to another supplier. The suppliers are aware that there are many alternative component suppliers who would be eager to enter into a long-term with Fast Lane.
After holding discussions with their purchasing manager, as part of the review process, the financial controller has conducted a study to determine the full cost of dealing with suppliers. While the company uses a series of non-financial performance measures to measure most aspects of supplier performance, the financial controller believes that the calculation of the total cost of ownership will provide an additional perspective to viewing supplier performance. For the most recent year, the following supplier related activities and costs have been identified:
|
|
Total Cost $ |
Number of Activities |
|
Order components from supplier |
1 800 000 |
6000 orders |
|
Receive order |
9 000 000 |
10 000 deliveries |
|
Return reject components to supplier |
38 500 |
55 returns |
|
Receive late deliveries |
260 000 |
130 late deliveries |
|
Production downtime due to late delivery |
2 400 000 |
800 hours |
|
Production downtime due to defective material |
3 600 000 |
3 000 hours |
|
Process invoice and pay supplier |
1 050 000 |
3 000 invoices |
|
Dispute invoiced amount |
40 000 |
50 disputes |
|
Quality audit of suppliers |
500 000 |
10 audits |
Fast Lane obtains its exhaust systems from two suppliers: Hot Exhaust and Chrome Manufacturers. Last year, Fast Lane purchased 3000 units from Hot Exhaust at $100 per unit, and 4000 units from Chrome Manufacturers at $90 per unit. Both supplies provide and identical component.
The analysis revealed that last year the following activities related to the two suppliers column:
|
|
Hot Exhausts |
Chrome Mftg |
|
Order components from supplier |
90 orders |
130 orders |
|
Receive order |
90 deliveries |
150 deliveries |
|
Return reject components to supplier |
15 returns |
16 returns |
|
Receive late deliveries |
6 late deliveries |
28 late deliveries |
|
Production downtime due to late delivery |
45 hours |
59 hours |
|
Production downtime due to defective material |
20 hours |
29 hours |
|
Process invoice and pay supplier |
12 invoices |
130 invoices |
|
Dispute invoiced amount |
3 disputes |
3 disputes |
|
Quality audit of suppliers |
1 audit |
2 audits |
Required:
- Construct an Excel spreadsheet. to determine the cost per unit of activity driver for each supplier related and the total cost of ownership and the total cost per unit for the two suppliers.
- Calculate the supplier performance index for the two suppliers.
- Compare the performance of the two supplies.
- What is the total cost per unit for Chrome manufacturers if the number of late deliveries is reduced to 12 and the production downtime due to late delivery is reduced to 30 hours.
- Describe the changes that the purchasing manager and financial controller could implement to minimise supplier related cost.
- Critena used by Fast Lane to determine whether oi not supplier contracts would be renewed. For each criterion, suggest two performance measures that Fast Lane might use to evaluate suppliers’ performance.
- Fast Lane is considering implementing electronic systems for transacting with suppliers. Outline some advantages that might accrue to both Fast Lane and supplies from such systems.
Answer
1. Introduction
This report is being prepared on the basis of Fast Lane case study to evaluate the different aspects of the supplier management of Fast Lane and also to evaluate the performance of their two suppliers, named Hot Exhausts and Chrome Manufactures. For evaluation of the two supplier’s performance, the total cost of ownership, the total cost per unit of the inventory that the business has got from these two suppliers will be calculated. Then to evaluate and compare the performance of the two suppliers, supplier performance index will be calculated and other aspects will also analyses. Then the different ways by which the purchase manager and financial controller can minimize the supplier-related cost will be identified. Then different criteria and performance measures by which it will be decided whether the supplier contract will be renewed or not will be discussed. After which, the advantages of using the electronic system to transact with the supplier will be discussed from both the perspectives of the suppliers and Fast Lane. In the end, a summary of all the main points of the Fast Lane case study covered within this report will be given in the conclusion part.
2. Calculation of the cost per unit of activity, the total cost of ownership and total cost per unit and Supplier performance index of the two suppliers
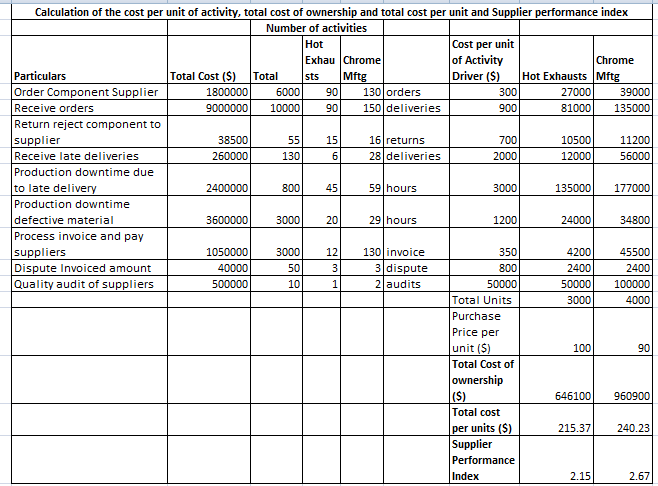
Table 1: Calculation of the cost per unit of activity and, the total cost of ownership, total cost per unit and supplier performance index of the two suppliers
(Source: Calculated by the learner)
3. Comparison of the performance of the two suppliers
There are two suppliers of Fast Lane as mentioned in the Fast Lane case study whose performances will be evaluated in this section from the different aspects with the use of the different measures. The two suppliers whose performance will be evaluated are Hot Exhausts and Chrome Manufacturers. The first measures which will be used assess the two suppliers’ performance is the supplier performance index is the measure which measures the ratio between the total cost incurred of the inventory procured from a certain supplier and purchase cost of the goods which has been procured from the supplier. The total cost incurred due to the procurement of goods from a certain supplier contains the purchase cost and nonperformance cost of the inventory (Krishnadevarajan, et al., 2015). Therefore, the performance of the supplier is considered to be goods when the index value is nearer to 1 and the more further value is from 1, the worse the performance of the supplier is considered. If the supplier performance index is considered then the performance of Hot Exhausts is found to better than Chrome Manufacturers as the Supplier Performance Index of Hot Exhausts, and Chrome Manufacturers is 2.15 and 2.67 respectively. Therefore, as the value of the Supplier Performance Index of Hot Exhausts is near to 1 compared to Chrome Manufacturers which indicate the lower proportion of non-performance cost in the total cost of Hot Exhausts among the two, the performance of Hot Exhausts is found to be better under this measure.
The second measure based on the Fast Lane case study analysis is the total cost per unit which assessed the total cost taking into account all type of cost incurred by the business from procurement until that until of inventory is used by the business for each unit of inventory procured from the supplier (Saccani, Perona and Bacchetti, 2017.). The total cost per unit of goods procured from Hot Exhausts and Chrome Manufacturers is $215.37 and $240.23 respectively. Therefore, as it can be seen in the context of Fast Lane case study that Fast Lane is incurring less amount of cost to procure and maintain the goods from Hot Exhausts among the two suppliers. Therefore, the performance of Hot Exhausts is found to better among the two from this performance measure assessment.
Also, the readings utilized from the Fast Lane case study signifies that after the individually the total cost under each cost driver activities is assessed of the two suppliers, it has been found out that the cost incurred by Hot Exhausts is significantly lower than Chrome Manufacturers and this is another indication that the performance of the Hot Exhausts is better than Chrome Manufacturers as supplier of Fast Lane.
Therefore, it has been concluded from the Fast Lane case study analysis though it can be seen that the Chrome Manufacturers is selling their goods to Fast Lane is much cheaper rate of $90 per unit compared to Hot Exhausts who is selling the goods at $100 per unit but in overall to maintain and to conduct different processes related to the inventory, the cost of goods which is procured from Chrome Manufacturers seem higher than Hot Exhausts. Therefore, the performance of Hot Exhausts as mentioned in the Fast Lane case study is analyzed is to be better as the supplier of Fast Lane compared to Chrome Manufacturers.
4. The total cost per unit for Chrome Manufacturer if the number of deliveries is reduced to 12 and the production downtime due to late deliveries is reduced to 30 hours
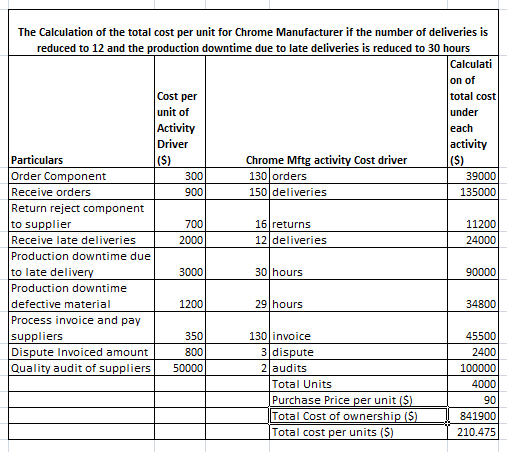
Table 2: Calculation of the total cost per unit for Chrome Manufacturer if the number of deliveries is reduced to 12 and the production downtime due to late deliveries is reduced to 30 hours
(Source: Calculated by the learner)
5. Describe the changes that the purchase manager and financial controller could implement to reduce the supplier-related cost as mentioned in the Fast Lane case study
There are many changes that the purchase manager and financial controller could implement to reduce the supplier-related cost, and these changes will be discussed here in the below sections.
- High penalty to the supplier for giving defective material– The first step that can be taken by the purchase manager is to charge high penalty from the supplier for giving defective materials which have led to Fast lane production process being affected and increasing legal rights to do so by making such contract that will give better legal right to the company to do so (Murumkar, Teli and Loni, 2018).
- Cancellation of the order if the order is too late or charges a late delivery fine – As per the Fast Lane case study analysis, the second step that can be taken by the purchase manager is to cancel the order if it is found that order has arrived late due to supplier incompetency. This step may lead to the production process of Fast lane being affected in the short run due to the company not having inventory for production but the instances of the late deliveries could be reduced in the long run if the supplier found their material is not accepted due to being late. Also, the financial controller can charge late delivery fee to the supplier for the late delivery as an alternative option which can compensate for the late delivery negative financial consequences of the company (Kamalahmadi and Mellat-Parast, 2016).
- Arrangement of the return of the rejected materials by the supplier – The third step explored in the Fast Lane case study that can be taken by the business is that arrangement to the take back the rejected material should be done by the supplier instead of Fast lane as this is increasing the supplier cost of the business.
- Blacklisting of the supplier if the supplier cost of a particular supplier is significantly higher than the rest – The fourth step that can be taken by Fast Lane is to formulate a policy in which if the supplier-related cost of a particular supplier is found to be significantly higher than the rest of the supplier of the business, then it would lead to the blacklisting of that supplier and this would lead to the supplier making a conscious effort not to send low quality of inventory to the business.
- Increasing efficiency in relationship to the supplier-related cost – Purchase manager of Fast Lane can also try to increase the efficiency of their different processes related to the supplier management and reduce the cost which is happening due to fulfillment of the different processes like cost of processing invoice can be reduced with the help of technologies which can automate these processes of the business.
- Setting a fixed price or uniform pricing for taking the inventory from different suppliers – Another step that can be taken by the purchase manager is setting a standard price at which company will purchase the same type of inventory from the different suppliers, and this will lead to prevention of the increase of the cost of the inventory due to the company taking inventory from different price from different supplier.
All these are the steps discussed in the above section based on the basis of Fast Lane case study that have been identified that purchase manager of Fast Lane can take to minimize the supplier-related cost of the company.
6. The two performance measures under each criterion that Fast Lane might use to evaluate the supplier performance
The readings used from the Fast Lane case study illustrates that there are different criteria that the Fast Lane should use to evaluate the performance of their suppliers and these criteria and the two performance measures under each criterion will be formulated and discussed in the below section which should be used by the Fast Lane to decide whether or not to renew the contract of the supplier.
- Quality Control – One of the most significant criteria for the supplier management should be quality control as keeping certain level of quality of its product is important to the business and the two performance measures which will be discussed here. The first performance measure by which the performance under this criterion should be measured is the cost of rejected units return to the supplier, and the second performance measure will be to cost of production downtime caused by the defective material given by the suppliers (Arndt et al., 2019).
- Delivery – The second criteria that should be used to decide whether the supplier contract should be renewed or not are the delivery and the two performance measures under this criterion will be discussed herein Fast Lane case study analysis. The first performance measures under the delivery criterion should be cost of lost sales or customers of the business due to the company getting the inventory late and the second performance measure should be the cost of disruption in the production or the production downtime that has happened due to the late delivery of inventory (Abebe, 2017).
- Processing – This third criterion will be the different cost which the business has to incur during the processing of the order from the supplier and the payment to the suppliers. The first measures will be the cost of placing the order for Fast Lane, and the second measure is the cost of payment of the invoiced amount to the suppliers.
- Legal Risk– The fourth criteria should be legal risk which the business is taking by doing business with certain suppliers. The critical analysis on the Fast Lane case study done in this report clarifies that the first performance under this criterion is the number of the dispute with the supplier over the invoiced amount and this is taken as a performance measure as the dispute over the invoice amount can create high legal contingency liabilities for the business. The second performance measure is the number of item return to the supplier as supplier can create a problem for the business stating that it is creating a breach of contract by unfairly rejecting their goods.
7. The advantages of implementing the electronic system for transacting with the suppliers from both Fast Lane and Suppliers Perspectives
There are many advantages of implementing the electronic system for transacting with the supplier for both Fast Lane and Supplier Perspectives. First of all, the advantages that Fast Lane will get from implementing the electronic system for transacting with the suppliers will be discussed. According to the scenario explored within the Fast Lane case study, the first benefit for Fast Lane is that it helps the business reduce the cost which the business was incurring due to the placing the order and other supplier-related processes like the payment of invoice to the supplier by using the automated processes as these processes will be automatically fulfilled by the system with the use of the much lesser amount of use of the different resources of the company like human resource or stationary (Soomro et al., 2018). The second benefit is that the chances of the miscommunication between the supplier and business, and inefficiencies regarding supplier management will be reduced as the communication between supplier and business will be much quicker and transparent.
The third benefit is that the time taken to fulfil one process under supplier management will reduce significantly under the electronic system compared to the manual system. The fourth benefit is that reduction in the different errors or mistake which may lead to the supplier mismanagement can be reduced by the use of this electronic system of the business. The fifth benefit is that as the lesser resources of the business is used and completion of the different process become faster, this will lead to an increase in the productivity of Fast Lane (Schoenherr, 2019). These are the advantages which Fast Lane will get from the implementation of the electronic system for transacting with the suppliers.
There are also some benefits of implementing the electronic system for transacting with the suppliers. The first benefit is that the reduction of cost for transacting with the supplier a when Fast Lane is using manual way for transacting with the supplier, it has also to use manual system of communicating which can lead to the increase in the cost of transacting for the supplier also as time and effort is taken more under this method. The second benefit is that less chances of miscommunication as the transaction processes are fulfilled in a reliable and transparent way and this will help the supplier create a better relationship with Fast Lane (Yu, Yevu, and Nani, 2019). The third benefit acquired from the Fast Lane case study analysis is that the time taken to finish different formalities and processes will also be reduced due to the use of the electronic system. These are the advantages which Suppliers of Fast Lane will get from the implementation of the electronic system in the business for transacting with the suppliers.
All these are the criteria and their performance measures which has been identified in this section.
8. Conclusion
There are different factors about the supplier management of Fast Lane which had been identified from the completion of the different requirement of this report. The first finding obtained from the Fast Lane case study is that the performance of Hot Exhausts is better than Chrome Manufacturers. The second finding is that there are many ways by which the supplier-related cost of the business can be reduced. The third finding achieved from the Fast Lane case study analysis is that there are different performance measures by which the performance of the supplier should be measured. The fourth finding is that there are many benefits of using an electronic system for transacting with the suppliers for both Fast Lane and its suppliers.
References
Abebe, A., 2017. Effects of Supplier Relationship Management on the Timely Delivery and Quality of Products in Commercial Banks in Ethiopia Fast Lane case study (Doctoral dissertation, Addis Ababa University).
Arndt, T., Kumar, M., Lanza, G. and Tiwari, M.K., 2019. Integrated approach for optimizing quality control in international manufacturing networks. Production Planning & Control, 30(2-3), pp.225-238.
Kamalahmadi, M. and Mellat-Parast, M., 2016. Developing a resilient supply chain through supplier flexibility and reliability assessment. International Journal of Production Research, 54(1), pp.302-321.
Krishnadevarajan, P.K., Ravichandran, V., Balasubramanian, S. and Kannan, N., 2015. Supplier Management: A Framework for Selection, Evaluation and Performance. Fast Lane case study International Journal of Management, 6(9).
Murumkar, A.B., Teli, S.N. and Loni, R.R., 2018. Framework for Reduction of Quality Cost. International Journal for Research in Engineering Application & Management, Special Issue-ICSGUPSTM, pp.156-162.
Saccani, N., Perona, M. and Bacchetti, A., 2017. The total cost of ownership of durable consumer goods: A conceptual model and an empirical application. International Journal of Production Economics, 183, pp.1-13.
Schoenherr, T., 2019. Why You Cannot Neglect Electronic Procurement. Fast Lane case study In The Evolution of Electronic Procurement (pp. 9-32). Palgrave Pivot, Cham.
Soomro, Z.A., Ahmed, J., Muhammad, R., Hayes, D. and Shah, M.H., 2018. Critical success factors in implementing an e-rostering system in a healthcare organisation. Health services management research, 31(3), pp.130-137.
Yu, A.T.W., Yevu, S.K. and Nani, G., 2019. Towards an integration framework for promoting electronic procurement and sustainable procurement in the construction industry: A systematic literature review. Fast Lane case study Journal of Cleaner Production, p.119493.












