Strategic Management Assignment: Case Analysis of Unilever
Question
Task: Strategic Management Assignment Instructions: You are required to study the case study “Unilever’s New Global Strategy: Competing through Sustainability” and attempt the tasks below:
(Task - A)
Drawing on the functional areas of management (HRM, Marketing and Finance) and using the quantitative and qualitative data provided in the case study, conduct an internal analysis on the company. Justify your response. (Approximately 500 words)
(Task - B)
Using relevant models, critically discuss the impact of external forces on the company. Critically evaluate the structure of its industry and discuss the implications for the company. (Approximately 500 words)
(Task - C)
As a change consultant, what interventions would you have implemented within Unilever to mitigate the impact of economic factors? (Approximately 750 words)
(Task - D)
Consider a scenario in which you were called upon to participate as a change agent in a strategic change management program. Critically reflect upon your experience in overcoming blockers and capitalizing on facilitators of change. To what extent do you agree that reflective learning is a means of enhancing one’s leadership ability in the context of change management? Justify your analysis by using theory.
Answer
Task A: Company background statement and internal analysis
Overview of the company
Unilever is a globally renowned company that manufactures and sells consumer-related goods such products related to personal care, beverages and cleaning. The company was initiated in 1929 as a result of a merger between a soap maker and a margarine producer. Unilever is dual-listed in the stock market that consists of Unilever PLC in London and Unilever NV in Rotterdam(Unilever, 2015).The purpose of the company is to make a commonplace for sustainable living, and thus it emphasizes on features that makes theproduct of the company gain a competitive edge. The business of Unilever makes massive upfront investments that are possible to be recouped only in the longer term, and this is the company's unique business strategy. However, this strategy of the company has brought a complex set of challenges despite the company delivering its financial expectations along with social and environmental commitments. The main challenge is regarding the ability of the company to continue with its delicate balancing measures even in the future. The CEO of Unilever, Polman, considered the progress of USLP (Unilever Sustainable Living Plan) as to be satisfactory, but there was a level of limitation in such approach, and thus the management of the company understood the requirement of bigger initiatives to meet its target of water usage and GHG.
Analysis of Unilever’s microenvironment (Internal Analysis)
Marketing: The marketing strategy of Unilever gained tremendous prominence as everyone became familiar with the company's marketing of Lifebuoy that achieved tremendous success. In addition to that, Unilever assigned leaders for each of the seven pillars of its USLP as a part of its marketing strategy. The company recently recruited Marc Mathieu as the company’s Senior Vice President of marketing and he started a program called CB4L (Crafting Brands for Life); and the main objective of this marketing campaign was to successfully link the company's brand strategy to the principles of USLP (Thomas and Hirani, 2018). The CB4L consisted of three principles, with the first principle being putting people first, the second principle was to build "brand love," and the third or the last principle was to unlock magic along with logic in execution.
HRM: Human resource refers to the art of managing the employees or workforce of a company in such a way that it helps the company to achieve its goals (Inc, 2018). In the context of Unilever, the company’s HRM plays a crucial role in terms of recruiting and managing the best talents available in the market. The HRM of the company continuously strives to improve the resources of the company so that the company can deliver the best possible results in terms of the market competition. Overall, the HRM of Unilever creates a sustainable value in its business operation, which is also an important aspect of its resource management.
Finance: The financial analysis of the company demonstrates that the financial performance of the company has shown a 2.9% sales growth in 2015, which is the lowest for the company in the decade. The decline in sales results was due to depressed growth in the shrinking demand in emerging markets, and the company is not expecting any significant improvements in the market conditions.
Task B: Macro environment analysis of the company
PESTLE analysis
Political: Unilever has to follow the regulations set by government to follow the product standards. As the company works with different product division, it needs to follow the regulation for each product division to ensure that the product quality and the business process are abided by law. In such case, support of government is a great thing.The extensive support from the UN is a major growth opportunity for Unilever as the CEO of Unilever was invited to join the UN global compact and to be a part of post-2015 development. The support from the government is a major strength for the company to carry out its operations successfully. The sustainability policy of the company and partnership with NGOs and government is a political strength for the company to align with its strategy. Most of the countries where Unilever works are politically stable. The strict trade reforms of US are a threat factor for Unilever that may bring potential challenges.
Economic: The increasing disposable income of consumers is one of the biggest opportunities for consumer goods industry because the disposable income increases the demand of the consumer goods. It is beneficial for Unilever to extend its product line and to enhance the sales of existing products. Economic stability in the developed countries is good, which ensures good opportunities for the company. The increasing wages may add additional costs for the manufacturing of products, which may reduce the amount of profit for the industry as well as for Unilever.
Social: The actions undertaken by organizations form consumer goods industry reflect their image in front of stakeholders, specially the CSR activities.Unilever has undertaken numerous social campaigns and activities to raise social awareness and to reflect on specific issues. Some of the products such as Lifebuoy is promoted such a way that it presents a specific concern towards the society (handwashing practice by Lifebuoy).
Technological: The consumer goods industry tends to adopt newer technologies to enhance the manufacturing activities and other business areas. The use of technology in most of the business areas is common for the consumer goods industry.The increasing automation in the manufacturing and other activities of the business is a technological strength for the company, and it is also encouraging potential investments for R&D. The cost of transportation is also decreased, which reduced the overall cost of business, and it is possible because of technological efficiencies.
Legal: The legal policies adopted by consumer goods industry and legislation followed differs from one country to others, so following the legislation in a country is important for an entity to carry out the business activities successfully.The policies of Unilever showed special concern toward the environment, which is an opportunity for the company to meet the need of environmental regulations of the countries where it has operated. The CSR of the company, namely brand imprint, guides to make each brand of Unilever socially responsible and abide by adequate legislation.
Environmental: The concern related to environment is more for consumer goods industry, as it involves in manufacturing activities that may lead to harmful consequences. The organizations from the industry implementing several environmental based strategies to male their business activities more sustainable.Unilever aims to reduce its environmental footprint in its business operations, so it has undertaken several environmental-related policies to minimize the harm to the environment.
Porter's five forces model
Competitive rivalry: The competition within the industry is strong for Unilever because there are more firms providing similar products and the low switching cost is another threat for the company, which is because of strong competition in the market. Competitors such as Nestle and P&G are major rivals in the market.
Bargaining power of customers: The power of bargaining for customers is also high for Unilever because the customers have the choice to select similar products provided by other competitors in the market, and the switching cost is very low. The information available for the customers about other products is also a threat factor for the company.
Bargaining power of suppliers: The suppliers' power is somehow moderate because the availability of suppliers cannot provide a chance to implement intense force by the suppliers. The partner-to-win strategy of Unilever is an example of its strength over the supply network.
Substitution threat: The cost factor is a threat for Unilever in terms of substitution, but the low availability of substitute products acts as a strong force for the company. The low performance and low customer satisfaction of substitute products increase the chance of the company to develop a strong brand presence.
New entry threat: The threat of new entry is low for Unilever because the brand development cost is high. The economies of scale and competitive advantage for Unilever are high in the market, which will be a disadvantage for new firms.
Task C: Identification of Unilever’s best strategic intervention
ANSOFF Matrix
Market development: This strategy helps the company to enter new geographical segments based on its desire to expand the business operation. Unilever predominantly aims at staying in the local market, but at the same time, the company keeps on developing new strategies for the market (Khankasi, 2020). Over the years, the company has enjoyed continuous success in the European market, and based n its success, Unilever has implemented market development plans for the American and Asian markets so that the business of the company continues to grow, and this has primarily been developed by the company by considering the diverse customer base.
Diversification: Unilever has adopted a diversification strategy based on various unrelated and related means of diversification. The company indulges in ownership and acquisition of various subsidiaries based on unrelated diversification. Some prominent examples of unrelated diversification of Unilever are Dermalogica, Tatcha LLC, and Seventh Generation that are mainly based on the cosmetics and beauty industry (Khankasi, 2020). On the other hand, in terms of related diversification, the company has been consistently increasing its product line. Over the years, various units of businesses have been developed for achieving related diversification, such as refreshment brands, dairy brands, and food brands.
Product development: The concept of product development is linked to creativity and innovation, and thus it focuses on the company regularly improving the products or coming up with new products for the customers. Unilever has efficiently understood the necessity of improving the line of products along with regularly developing new products so that various segments of the customers can be attracted (Khankasi, 2020). Over the years, the company has achieved major benefits from its diverse customer base, and this has been made possible by a wide range of product offerings. Overall, the strategy of product development has kept the company on the path to success as this strategy has been regularly providing the customers with new and improved products.
Market penetration: The strategy of market penetration has been implemented by Unilever for achieving tremendous success in the company. After introducing a new product in the market, Unilever sells it with the intention of market penetration (Khankasi, 2020). The company does not emphasize selling its products to few customers and accordingly moves it to the next market. Unilever emphasizes economies of scale, and this has been a major reason for the company’s success. However, this strategy has sometimes resulted in product failure as well.
Porter’s generic approach
Unilever uses the generic strategy of broad differentiation to gain a competitive advantage. The main emphasis of Unilever's broad diversification strategy is to make its products stand out against the competitors by improving and developing products. For example, the company produces Dove cream bars for attracting and satisfying the customers' needs as a form of soap that is harsh on the skin or dry (Young, 2016). Thus, despite the fact that the company's products have higher selling prices, Unilever is still able to achieve competitive advantage because the ability of its products to stand out against competitors. In addition to that, the broad diversification strategy attracts the consumers with products that have specifically designed to their unique needs. However, this strategy also fails sometimes as there some people who looks for product at a cheaper price and thus compares the products of various companies and accordingly choose the best products for them. The broad diversification strategy of Unilever aligns with the company's mission and vision statement that thrives to support the global sustainability along with increasing the vitality of consumers' lives. Unilever's strategic objective based on the differentiation strategy is to ensure that the company grows through intensive efforts based on the development of products. This objective of the company emphasizes developing products that can stand out in the tremendous market competition and successfully attract customers.
The main concern for Unilever in its generic strategy of broad differentiation is based on the fact that there is a potential of some consumers being not happy with their pricing, and thus this may result in the company missing out on those sections of the consumers. Overall, the broad differentiation strategy has enabled the company to achieve a competitive advantage by a massive extent, and the results are reflected in its strong financial performance in the market of consumer goods. In the future, the company wants to keep improving its line of products and further diversify its product portfolio so that the factor of sustainability remains intact.
Task D: Change management
Use of change management model
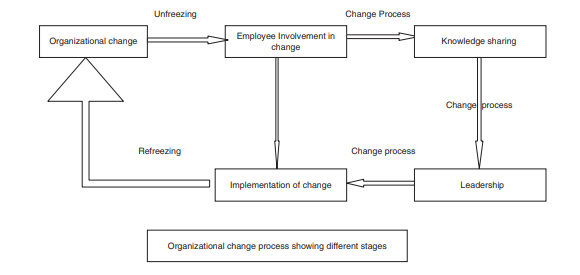
The change related to environmental and social goals is one of the key factors for Unilever; the change management process needs to be followed based on specific steps to implement successful change. For Unilever and its change related to environmental policies with external partnerships, Lewin's change management process is discussed below to show the steps that Unilever needs to undertaken while implementing change.
1. Unfreezing: It is the first stage in the process of change management that makes the internal stakeholders aware of the specific change and its benefits. At this stage, the key employees who need to be related to the specific change are motivated about the positive outcomes of the change (Cummings, Bridgman, and Brown, 2015). For example, the involvement of external partners for the environmental initiatives at Unilever, the internal stakeholders need to be well communicated about the change initiatives and their benefits. At this stage, the role of effective communication is important to ensure that the message is well communicated to each target group and its members. Before implementing the change, it is important to unfreeze the existing situation of the organization where the change is going to take place. The unfreezing stage helps to reflect on the existing flaws and key areas of consideration that should be counted as major areas of concern while implementing the change. The unfreezing stage is important; the change in the organization may bring expected change in group behavior, so it needs to be tackled earlier.
2. Change: At this stage, the actual change is implemented, and it is undertaken in several steps. The key thing that needs to be considered for this stage is effective communication, strategic planning, encouraging the individuals involved in the change, and risk planning to address the expected risk during change implementation (Hussain et al., 2016). While implementing change related to the environmental policy of Unilever, the key things need to be considered for better implementation of change and to manage the risks. At this stage, there are many unexpected risks that may occur, but the implementation of an on-time and effective strategy is crucial to mitigate those risks.
3. Refreezing: It is the last stage in the process, and at this stage, the employees and individuals who are related to the change work as per the implemented change (Burnes, 2019). The ultimate success of implemented change is calculated at the refreezing stage because it depicts whether the employees are able to accept the change or not. To encourage the employees towards the change, they need to be rewarded as it is a strategy to reinforce and strengthen the behavior.
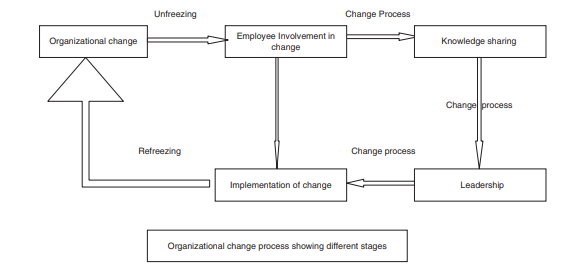
Figure 1: Breakdown of Lewin’s change model
Source: (Hussain et al., 2016)
Gibbs’ reflective cycle
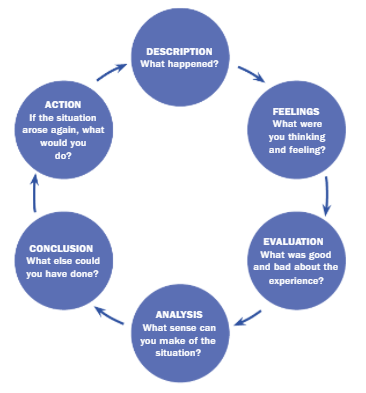
There are six stages in Gibbs' reflective cycle, and in the present context, using the cycle, the relationship between leadership ability and reflective learning is shown based on change management.
1. Description: A leader needs to describe the situation in detail to make others realize the importance of specific change. What, why, how, when, the answers to all these questions should find out by the leader to implement the change effectively (Adeani, Febriani, and Syafryadin, 2020).
2. Feelings: The thoughts and feelings of the leaders need to be clearly communicated with the subordinates to ensure they get a clear representation of the leader's perspectives. The ideas that are represented by the leaders show the effective communication skill of the leader, which is a key part of change management.
3. Evaluation: The leader needs to focus on both positive and negative aspects of the change initiative and should plan for ways to minimize the negative impact on the change.
4. Analysis: The detailed analysis of the situation is important for a leader (Wain, 2017). Detail analysis of the leader reflects the analytical skill of the individual, which is a crucial thing for the change management process.
5. Conclusion: The summarization of the key learning is important. The key learnings are the importance of selecting an adequate change management process, the importance of selecting growth strategies, analysis of the macro environment of business, and alignment of strategies with company objectives.
6. Action plan: In a similar situation, as a leader, one needs to focus on the current situation of the company, whether the company is ready to accept the change or not.
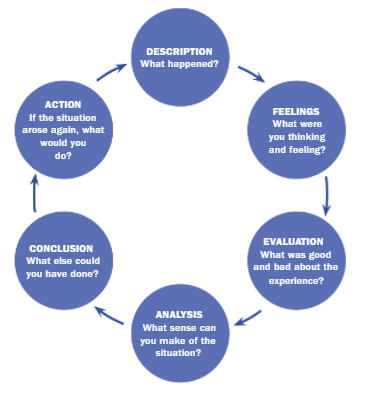
Figure 2: Gibbs’ Reflective cycle
Source: (Wain, 2017)
References
Adeani, I.S., Febriani, R.B. and Syafryadin, S. (2020). USING GIBBS’ REFLECTIVE CYCLE IN MAKING REFLECTIONS OF LITERARY ANALYSIS.Indonesian EFL Journal, [online] 6(2), p.139. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Syafryadin-Syafryadin/publication/343599316_Using_GIBBS%27_reflective_cycle_in_making_reflections_of_literary_analysis
/links/5f335a50a6fdcccc43c20399/Using-GIBBS-reflective-cycle-in-making-
reflections-of-literary-analysis.pdf [Accessed 19 Jul. 2021].
Burnes, B. (2019). The Origins of Lewin’s Three-Step Model of Change. The Journal of Applied Behavioral Science, [online] 56(1), pp.32–59. Available at: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/0021886319892685 [Accessed 19 Jul. 2021].
Cummings, S., Bridgman, T. and Brown, K.G. (2015). Unfreezing Change as Three steps: Rethinking Kurt Lewin’s Legacy for Change Management. Human Relations, [online] 69(1), pp.33–60. Available at: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/0018726715577707 [Accessed 17 Jul. 2021].
Hussain, S.T., Lei, S., Akram, T., Haider, M.J., Hussain, S.H. and Ali, M. (2016). Kurt Lewin’s Change model: a Critical Review of the Role of Leadership and Employee Involvement in Organizational Change. Journal of Innovation & Knowledge, [online] 3(3), pp.123–127. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2444569X16300087 [Accessed 19 Jul. 2021].
Inc (2018).Human Resource Management. [online] Inc.com. Available at: https://www.inc.com/encyclopedia/human-resource-management.html [Accessed 20 Jul. 2021].
Khankasi, A. (2020). Ansoff Matrix for Unilever. [online] Ansoff Matrix. Available at: https://ansoffs.com/ansoff-matrix-for-unilever/ [Accessed 20 Jul. 2021].
Thomas, T.K. and Hirani, A. (2018).It’s all about finding the truth, sharing it. [online] @businessline. Available at: https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/catalyst/its-all-about-finding-the-truth-sharing-it/article7202095.ece [Accessed 20 Jul. 2021].
Unilever (2015).The Formation of Unilever. [online] unilever.co.uk. Available at: https://www.unilever.co.uk/Images/the-formation-of-unilever_tcm1252-520314_en.pdf [Accessed 20 Jul. 2021].
Wain, A. (2017). learning through reflection. [online] ResearchGate. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320342913_Learning_through_reflection [Accessed 19 Jul. 2021].
Young, J. (2016). Unilever’s Generic Strategy & Intensive Growth Strategies. [online] Panmore Institute. Available at: http://panmore.com/unilever-generic-strategy-intensive-growth-strategies#:~:text=thereby%20supporting%20growth.- [Accessed 20 Jul. 2021].
Appendices
Appendix 1
Appendix 2












