Corporate Accounting Assignment Analyses Financial Statements of Australian Companies
Question
Task
The questions to be answered in the corporate accounting assignment are:
Question 1
At 30 June 2019, Beta Ltd had the following deferred tax balances:
Deferred tax liability $18,000
Deferred tax asset 15,000
Beta Ltd recorded a profit before tax of $80,000 for the year to 30 June 2020, which included the following items:
Depreciation expense – plant $7,000
Doubtful debts expense 3,000
Long-service leave expense 4,000
For taxation purposes the following amounts are allowable deductions for the year to 30 June 2020: Tax depreciation – plant $8,000
Bad debts written off 2,000
Depreciation ratesfor taxation purposes are higher than for accounting purposes. A corporate tax rate of 30% applies.
Required:
a) Determine the taxable income and income tax payable for the year to 30 June 2020.
b) Determine by what amount the balances of the deferred liability and deferred tax asset will increase or decrease for the year to 30 June 2020 because of depreciation, doubtful debts and long-service leave.
c) Prepare the necessary journal entries to account for income tax assuming recognition criteria are satisfied.
d) What are the balances of the deferred tax liability and deferred tax asset at 30 June 2020?
Question 2
On 1 July 2019, Quick Buck Ltd took control of the assets and liabilities of Eldorado Ltd. Quick Buck Ltd issued 80,000 shares having a fair value of $2.40 per share in exchange for the net assets of Eldorado Ltd. The costs of issuing the shares by Quick Buck Ltd cost $1,600.
At this date the statement of financial position of Eldorado Ltd was as follows:
|
Carrying amount |
Fair value |
|
|
Machinery |
$40,000 |
$67,000 |
|
Fixtures & fittings |
60,000 |
68,000 |
|
Vehicles |
35,000 |
35,000 |
|
Current assets |
10,000 |
12,000 |
|
Current liabilities |
(16,000) |
(18,000) |
|
Total net assets |
$129,000 |
|
|
Share capital (80,000 shares at $1.00 per share) |
$80,000 |
|
|
General reserve |
20,000 |
|
|
Retained earnings |
29,000 |
|
|
Total equity |
$129,000 |
Required: Prepare the journal entries in the records of Quick Buck Ltd at 1 July 2019 for the acquisition.
Question 3
a) Liala Ltd acquired all the issued shares of Jordan Ltd on 1 January 2015. The following transactions occurred between the two entities:
- On 1 June 2016, Liala Ltd sold inventory to Jordan Ltd for $12,000, this inventory previously costed Liala Ltd $10,000. By 30 June 2016, Jordan Ltd had sold 20% of this inventory to other entities for $3,000. The other 80% was all sold to external entities by 30 June 2017 for $13,000.
- During the 2016–17 period, Jordan Ltd sold inventory to Liala Ltd for $6,000, this being at cost plus 20% mark-up. Of this inventory, 20 % remained on hand in Liala Ltd at 30 June 2017. The tax rate is 30%.
Required:
(i) Prepare the consolidation worksheet entries for Liala Ltd at 30 June 2017 in relation to the intragroup transfers of inventory.
(ii) Compute the amount of cost of goods sold to be reported in the consolidated income statement for 2017 relating to the relevant intra-group sales.
a) On 1 July 2016, Liala ltd sold an item of plant to Jordan Ltd Ltd for $150,000 when its carrying value in Liala Ltd book was $200,000 (costs $300,000, accumulated depreciation $100,000). This plant has a remaining useful life of five (5) years form the date of sale. The group measures its property plants and equipment using a costs model. Tax rate is 30 percent.
Required: Prepare the necessary journal entries in 30 June 2017 to eliminate the intra-group transfer of equipment.
Question 4
Giant Ltd acquired 80 percent share capital of Expert Ltd. On 1 July 2018 for a cost of $1,600,000. As at the date of acquisition, all assets and liabilities of Expert Ltd were fairly valued except a land that has a carrying value $150,000 less than the fair value. The recorded balance of equity of Expert Ltd as at 1 July 2018 was as:|
Share capital |
$800,000 |
|
Retained earnings |
$200,000 |
|
General Reserve |
$400,000 |
|
Total |
$1,400,000 |
Additional information:
- The management of Giant Ltd values non-controlling interest at the proportionate share of Expert Ltd identifiable net assets.
- Expert Ltd has a profit after tax of $200,000 for the year ended 30 June 2019.
- During the financial year to 30 June 2019, Expert Ltd sold inventory to Giant Ltd for a price of $120,000. The inventory costs Expert Ltd $60,000 to produce. 25 percent of the inventory are still on the hand of Giant Ltd as at 30 June 2019.
- During the year Expert Ltd paid $60,000 in consultancy fees to Giant Ltd.
- On 1 July 2018, Expert Ltd sold an item of plant to Giant Ltd $80000. The equipment had a carrying value of $60,000 (Cost $100,000, accumulated depreciation $40,000). At the date of sale, it was expected that the equipment had a remaining life of 4 years and no residual value. The tax rate is 30 percent.
Required:
a) Based on the above information, calculate the non-controlling interest as at 30 June 2019.
b) Prepare the necessary journal entries to recognise the non-controlling interest as at 30 June 2019.
Question 5
The Daddy Group has the following group structure:
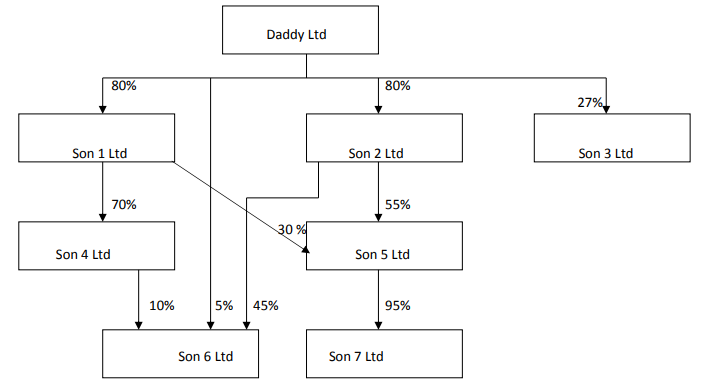
(a) Reproduce and complete the following controlling and non-controlling interest table. Show your calculations.
(b) What percentage of the voting in Son 7 Ltd will be controlled by the Daddy Ltd?
(c) What percentage of the dividend declared by Son 7 Ltd will be received by the Daddy Ltd?
Answer
Corporate Accounting Assignment Question 1:
1.A.
|
Profit before tax |
$80000 |
|
Add: Depreciation expense – plant |
$7000 |
|
Add: Doubtful debts expense |
$3000 |
|
Add: Long-service leave expense |
$4000 |
|
Minus: Bad debts written off |
($8000) |
|
Minus: Tax depreciation – plant |
($2000) |
|
Taxable Income |
$84000 |
|
Income tax payable (30% of $84000) |
$25200 |
Hence taxable income and tax payable on 30 June 2020 are $84000 and $25200 respectively
1.B.
- Doubtful debts expense> bad debts written off by an amount of ($3000 –$2000) i.e. $1000
Doubtful debts expense - bad debts written off = ($3000 –$2000) = $1000
So, increase in deferred tax asset = $1000 x 30% = $300
- Long service leave expense> long service leave paid by an amount of ($4000 – $0) i.e. $4000
Long service leave expense > long service leave paid = ($4000 – $0) = $4000
So, increase in deferred tax asset = $4000 x 30% = $1200
- Tax depreciation > depreciation expense
Tax depreciation - depreciation expense = ($8000 –$7000) = $1000
So, increase in deferred tax liability = $1000 x 30% = $300
Hence, changes in deferred liability and deferred tax asset are increase of $1500 and increase of $300respectively
1.C.
|
Journal Entries to account for income tax |
||
|
Debit |
Credit |
|
|
Account: Current Tax |
||
|
Income tax expense |
$25200 |
|
|
Current tax liability |
$25200 |
|
|
Account: Deferred Tax |
||
|
Deferred tax asset |
$1500 |
|
|
Deferred tax liability |
$300 |
|
|
Income tax expense |
$1200 |
|
1.D.
|
Beginning balance |
$15000 |
|
Add: Increase during this period |
$1500 |
|
Ending Balance |
$16500 |
|
Beginning balance |
$18000 |
|
Add: Increase during this period |
$300 |
|
Ending Balance |
$18300 |
Question 2:
|
Fair value of Net Assets on 1 July 2019 |
|
|
Machinery |
$67000 |
|
Fixtures & fittings |
$68000 |
|
Vehicles |
$35000 |
|
Current assets |
$12000 |
|
Minus: Current liabilities |
($18000) |
|
Total |
$164000 |
Acquisition price or buy value = 80000 * $2.40 = $192000
So, goodwill = $192000 - $164000 = $28000
|
Journal Entries for acquisition of Eldorado Ltd. |
|||
|
Date |
Debit |
Credit |
|
|
July 1, 2019 |
Machinery |
$67000 |
|
|
Fixtures & fittings |
$68000 |
||
|
Vehicles |
$35000 |
||
|
Current assets |
$12000 |
||
|
Goodwill |
$28000 |
||
|
Current Liabilities |
$18000 |
||
|
Total share price |
$192000 |
||
|
(Recording acquisition of Eldorado Ltd.) |
|||
|
July 1, 2019 |
Costs of issuing the shares |
$1600 |
|
|
Cash |
$1600 |
||
|
(Recording cost of shares issue) |
|||
Question.3
3.A.i.
For Liala Ltd.,
Profit Margin = (Sales price-Cost Price)/Sales Price = ($12000-$10000)/$12000 = 16.67%
Remaining inventory after selling = 80% i.e. $12000 * 80% = $9600
Unrealised remaining profit = $9600 * 16.67% = $1600
|
Liala Ltd Consolidation Entries |
|||
|
Date |
Particular |
Debit |
Credit |
|
June 30, 2016 |
Sales |
$12000 |
|
|
Cost of inventory sold |
$12000 |
||
|
(For eliminating intra entity sales) |
|||
|
Cost of inventory sold |
$1600 |
||
|
Inventory |
$1600 |
||
|
(For eliminating intra entity profit from inventory) |
|||
|
30 June 2017 |
No is needed |
||
On June 30, 2017, there is no need of adjustments intercompany profit is realised through reselling of inventory to external companies
For Jordan Ltd.,
Remaining unrealised profit = $6000 * 20% =$1200
Mark-up = 20%
So, Unrealised profit= $1200 *20/120 = $200
|
Jordan LtdConsolidation Entries |
|||
|
Date |
Particular |
Debit |
Credit |
|
June 30, 2017 |
Retained earnings |
$200 |
|
|
Cost of inventory sold |
$200 |
||
|
(For recognising profit of Jordan Ltd from sale of inventory) |
|||
3.A.ii.
|
Particular |
Amount |
|
Cost of goods sold of Liala Ltd. |
$9600 |
|
Cost of goods sold of Jordan Ltd. |
$6000 |
|
Minus: Unrealised Profit |
($200) |
|
Cost of goods sold in consolidated income statement |
$15400 |
3.B.
Liala ltd sold an item of plant to Jordan Ltd Ltd for $150000
Carrying value = $200000
So, loss = $200000-$150000= $50000
Useful life remaining = 5 yrs
At year end, depreciation expense which is recorded by Liala ltd =$ 200000/5 = $40000
But actual depreciation expenses =$150000 /5 = $30000
So, it is required to adjust depreciation expense of ($40000-$30000) = $10000
So, intra-entity loss of $50000 and Understated depreciation expense $10000 have to be considered.
|
Journal Entries to on 30 June 2017 |
|||
|
Date |
Deatil |
Debit |
Credit |
|
June 30, 2017 |
Plant |
$50000 |
|
|
Loss on sale of plant |
$50000 |
||
|
(Eliminating intra-entity transfer of plant) |
|||
|
June 30, 2017 |
Depreciation Expense |
$10000 |
|
|
Accumulated Depreciation |
$10000 |
||
|
(Adjusting depreciation which is understated) |
|||
Question 4:
4.A.
First unrealised profit from inventory and sales of equipment has to be calculated.
|
Calculation of unrealised profit from Inventory |
|
|
Sales price |
$120000 |
|
Minus: Cost |
($60000) |
|
Profit Before tax |
$60000 |
|
Minus: Income Tax (30%) |
($18000) |
|
PAT or Profit After Tax |
$42000 |
|
Unsold Stock |
$0 |
|
Unrealised Profit (25%) |
$10500 |
|
Calculation of unrealised profit from Salesof Equipment |
|
|
Sales price |
$80000 |
|
Minus: Cost |
($60000) |
|
Profit Before tax |
$20000 |
|
Minus :IncomeTax (30%) |
($6000) |
|
PAT or Profit After Tax |
$14000 |
|
Unrealised Profit (3/4 * $14000) |
$10500 |
Expert Ltd.’s profit for the year 2018-19 = $200000 - $10500 - $10500 = $179000
|
Particulars |
Total Value |
Non-controlling Amount (20% share of total value) |
|
Share Capital |
$800000 |
$160000 |
|
Retained earnings |
$200000 |
$40000 |
|
General Reserve |
$400000 |
$80000 |
|
Profit for the year 2018-19 |
$179000 |
$35800 |
|
Non-controlling interest |
NA |
$315800 |
Hence, the non-controlling interest as on June 30, 2019 is $315800
4.B.
Below is shown journal entries to recognise the non-controlling interest as on June 30, 2019.
|
Journal Entries to for acquisition as onJune 30, 2019 |
|||
|
Date |
Debit |
Credit |
|
|
June 30, 2019 |
Profit for the FY2019 |
$21000 |
|
|
Inventory Reserve |
$10500 |
||
|
Equipment Reserve |
$35000 |
$10500 |
|
|
(For recording unrealised profit) |
|||
|
Profit for the FY2019 |
$179000 |
||
|
Consolidated Surplus and Reserve |
$35800 |
||
|
Non-controlling interest |
$143200 |
||
|
(For recordingrealised profit) |
|||
5.A.
- Son 4 has no direct controlling interest. Indirect controlling interest = 0.70 * 80% = 56%
- Son 5 has no direct controlling interest. Indirect controlling interest = 0.55*80%+0.30*80%= 68%
- Son 7 has no direct controlling interest. Indirect controlling interest = 0.95*68%=64.60%
- Son 6 has 5% direct controlling interest and Indirect controlling interest through Son 2 and Son 4=0.45*80%+0.1*56%=41.6%
- Son 1 has direct non-controlling interest of (100%-80%)=20%
- Son 4 has direct non-controlling interest of 100%-56%-14%=30%
- Son 2 has direct non-controlling interest of 100%-80%=20%
- Son 5 has direct non-controlling interest of 100%-68%-17%=15%
- Son 7 has direct non-controlling interest of 100%-64.6%-30.4%=5%
- Son 6 has direct non-controlling interest of 100%-41.6%-5%-13.4%=40%
- Son 3 has direct non-controlling interest of 100%-27%=73%
- Son 4 has indirect non-controlling interest(coming through Son 1) of 0.7*20%=14%
- Son 5 has indirect non-controlling interest(coming through Son 1 7 Son 2) of 0.55*20%+0.3*20%= 17%
- Son 7 has indirect non-controlling interest(coming through Son 5) of (100%-(24+44)%)*0.95=30.40%
- Son 6 has indirect non-controlling interest(coming through Son 2 and Son 4) of 0.1*44%+0.2*45%=13.4
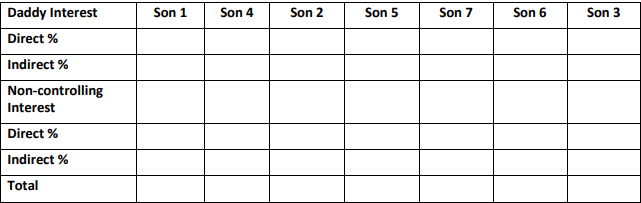
|
Table for Controlling and Non-controlling Interest |
|||||||
|
Daddy Interest |
Son 1 |
Son 4 |
Son 2 |
Son 5 |
Son 7 |
Son 6 |
Son 3 |
|
Direct % |
80% |
0% |
80% |
0% |
0% |
5% |
27% |
|
Indirect % |
0% |
56% |
0% |
68% |
64.60% |
41.6% |
0% |
|
Non-controlling Interest |
|||||||
|
Direct % |
20% |
30% |
20% |
15% |
5% |
40% |
73% |
|
Indirect % |
0% |
14% |
0% |
17% |
30.40% |
13.4% |
0% |
|
Total |
100% |
100% |
100% |
100% |
100% |
100% |
100% |
5.B.
Percentage of the voting in Son 7 Ltd that will be controlled by the Daddy Ltd is same as controlling interest i.e. 64.6%
5.C.
Percentage of the dividend declared by Son 7 that will be received by the Daddy Ltd is same as controlling interest = 64.6%
CHECK THE PRICEFOR YOUR PROJECT
Related Samples
- Understanding Impairment testing assignments and Their Impact on Asset Management
- Career development plan: Advancing in Accounting and Finance
- (U10473) Accounting assignment analysing the practice of financial accounting and management accounting
- (GP39 04)Accounting for Leaders assignment on Tesco leadership accounting strategies
- (ACCT801)Accounting assignment for New Adventures Travel and Tourism
- (MOD003319)An accounting assignment analysing the financial performance of Surya Trading
- Analysis for Tesco using performance measurement assignment stratogies
- Accounting Assignment: Workplace For Costing Products And Services Using Tools
- Managerial Accounting Assignment: Questions and Answers
- (HI5017) Strategic Management Accounting Assignment: Impact of top management team characteristics and financial performance
- (ACC5MCR) Management Accounting Assignment: Issue With Existing Budgeting Process Of AMCOR
- Accounting Assignment: Financial Analysis Of Britvic
- (ACT5112) Accounting Assignment: Financial Analysis Of Ahmad Zaki Resources Berhad (AZRB) & BinaPuri Holdings Bhd
- Business Accounting Assignment Evaluating Organisational Scenarios
- Accounting Assignment: Budgeting In Managerial Accounting
- Accounting Assignment Evaluating Financial Data Of Businesses
- Business Accounting Assignment: Analysing Financial Scenarios Of Business Cases
- Business Accounting Assignment: Financial Analysis Of Uber
- Accounting Assignment: Business Case Analysis
- (ACFI3009) Accounting Assignment: Reflection On Knowledge & Insights Gained From Contemporary Issues
- Accounting Assignment: Discussion On Effectiveness Of Sustainable Investment
- Career Development Essay: Employability Skills for Accountants
- (ACC303) Accounting Assignment: Contemporary Issues at Commonwealth Bank of Australia
- (ACC302) Corporate Accounting Assignment: Analysis of Financial &Market Performance of BHP Group
- Managerial Accounting Assignment Analysing Current Challenges Faced by NHS





Other Assignment Services
- My Assignment Help
- SCM Assignment Help
- HRM Assignment Help
- Business Report Writing
- Finance Assignment Help
- Sociology Assignment Help
- Marketing Assignment Help
- Accounting Assignment Help
- Dissertation Assignment Help
- Management Assignment Help
- IT Management Assignment Help
- Marketing Analysis Assignment Help
- Personal Finance Assignment Help
- Corporate Finance Assignment Help
- Financial Accounting Assignment Help
- Managerial Accounting Assignment Help
- Operations Management Assignment Help
- Cost Accounting Assignment Help
- Marketing Research Assignment Help
- Project Management Assignment Help
- Business Statistics Assignment Help
- Information Technology Assignment Help


AU ADDRESS
US ADDRESS
CONTACT
ESCALATION EMAIL
help.com





