Nursing Assignment: Surgical Case Study Analysis of Mrs Geraldine Berry
Question
Task: Nursing Assignment Case Scenario: Incident: 72 yr old female Mrs Geraldine Berry sustained left fractured neck of femur (#NOF) and laceration to her head 5cm while walking her dog. Tripped on an uneven pathway.
PMH: Hypertension and depression
Current Medications: Coversyl 5mg
Doxepin 25mg daily
Atorvastatin 40mg daily
SHx: Lives with elderly husband. Is the primary carer for elderly husband who has had a stroke previously and is mildly impaired. Attends church every Sunday and is responsible for arranging flowers for every Sunday service. She has started volunteering at the St Vincent De Paul’s Meals on Wheels distribution centre two days a week. She lost two children 5 years ago in a car accident. Geraldine is concerned who will look after her husband and their dog Nala. Geraldine and her husband have no children or relatives nearby.
Current presentation
Day 3 post op left total hip replacement, increasing pain in hip unable to weight bear, pain score currently 7/10. Geraldine has been prescribed oral tramadol tds, Ibroprofen prn, paracetamol prn, IV Amoxicillin 1000mg tds and Clexane 40mg SC BD. Suture line on hip appears red and swollen.
Consider the above case and answer the following questions:
1. Using the CRC and the information presented about Geraldine, identify the abnormal cues, and discuss why these are considered abnormal (200 words).
2. Using relevant literature, discuss the pathophysiology related to the two postoperative issues of concern from the abnormal cues you have identified in question one (500 words).
3. Using the template provided below, complete all the sections which include (200 words):
a. Identify the nursing goal for each identified issue/problem (2).
b. List at least two nursing interventions for each issue/problem.
4. Using relevant literature, provide a rationale for the listed interventions and discuss how the interventions will be evaluated (500 words).
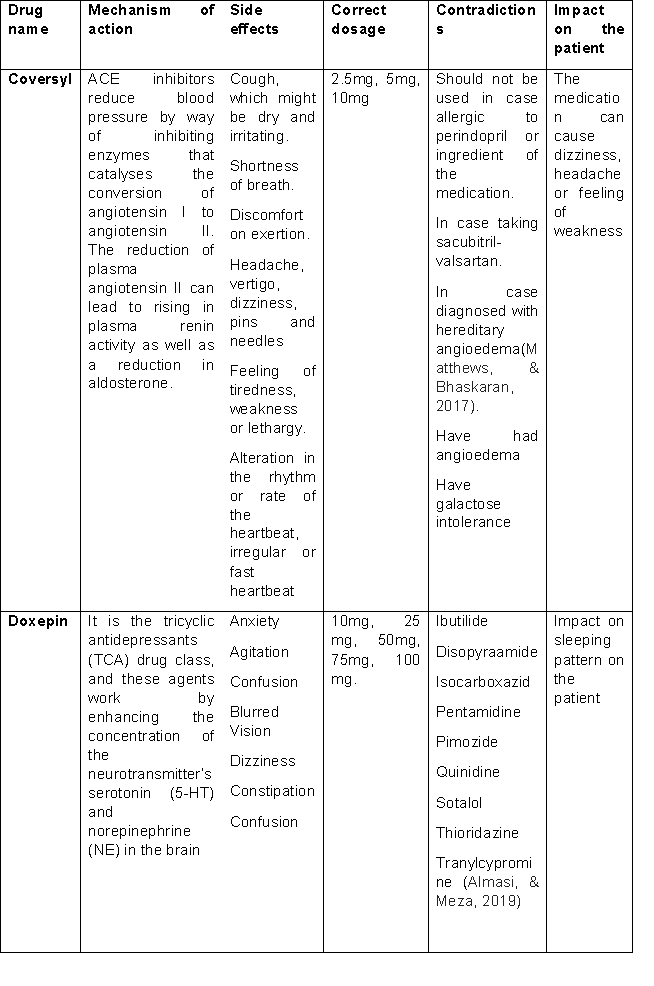
5. Identify 2 medications that were prescribed for the patient’s pre-operative condition. (Coversyl 5mg, Doxepin 25mg daily, Atorvastatin 40mg daily) used in this case study. Provide the mechanism of action, side effects correct dosage and contraindications for each medication. Explain how this might affect Geraldine in the post-operative period (400 words). 6. Using the Roper-Logan Tierney Model, identify one (1) potential cultural/biopsychosocial issue/problem and discuss how this will affect the patient post-operatively or on discharge (200 words)
Answer
1. Applying the CRC with the information presented about Geraldine, identification of the abnormal cues, and their discussion
The current case scenario analysed herein nursing assignment concerns Mrs Geraldine Berry, who lives with her elderly husband had a fracture has been observed. By undertaking the clinical reasoning cycle (CRC), the abnormal cues have been collected for the patient along with relevant justification.
Considering the patient situation:The patient is a 72-year-old female with a left fractured neck of the femur with a laceration to her head 5 cm. This took place while she tripped on an uneven pathway while walking her dog. Her past medical history includes depression and hypertension, her medication includes Coversyl, Doxepin and Atorvastatin. She appears to be having considerable pain 7/10 score, 3-day post operations of her left total hip replacement and has been unable to bear her weight. Though she has been prescribed oral tramadol tds, paracetamol prn, Ibroprofen prn, Amoxicillin and Clexane yet her hip appears red and swollen. This is abnormal as the medications should have reduced the inflammation along with the pain.
Collecting cues/ information: Collecting relevant cues regarding her situation reveals that she has abnormal pulse rate at 120, high RR, normal BP, with high pain score, high temperature, BGL 6.8 mmol/l, with heat pain and redness at the suture site with no indication of mobilising of the pain. Even after medications, the patient’s symptoms have not subsided.
Process information:Processing relevant information reveals that post-surgical pain might arise from recurring tendonitis, low back pain and bursitis or a pinched nerve.
Identify problems/ issues: The main problem or issue faced by the patient is the continuing pain even after 3-day of surgery.
Establish goals: The goal of nursing care will to analyse the reason behind the pain and to undertake action to attend to it.
Take action: Assume necessary action for pain reduction also reduce swelling.
Evaluate outcomes: Outcomes of such action will be relieving in pain of the patient also bearing weight.
Reflect on the process and new learning: New learning includes administering pain relief medication and providing appropriate nursing care.
2. Pathophysiology related to the two postoperative issues of concern from the abnormal cues One of the major post-operative issues of concern from the abnormal cues identified is pain and another one is swelling. Erlenwein, Müller, Falla, Przemeck, Pfingsten, Budde, Quintel, and Petzke, (2017) points out that the development of chronic postoperative pain is being observed in several postoperative surgical procedures. Due to the significant number of surgical procedures performed every year, the focus is mainly on acute pain management. The incidence of such pain is primarily dependent on surgical, genetic, psychological and social risk factors. The author points out that orthopaedic procedures can complicate postoperative pain in case there is pre-existing condition present. Postoperative pain post hip replacement is seen to range between 27% and 38% which impact daily life and the quality of the patient's life, which further adds to the pain. The pathophysiology associated with pain is highlighted by Lavand'homme, (2017) is characterised by a neuropathic component that is seen in around 35% of cases. The likelihood of prevalence of neuropathic pain is dependent upon surgical iatrogenic nerve injury. Also, as in the current patient case, signs of neuropathic pain are essential to detect as they impair quality of life affecting higher intensity. Pogatzki-Zahn, Segelcke, and Schug, (2017) points out that inflammation and neural tissue damage is prevalent post-surgery, the pathophysiology is unique. This study indicates that after incision there are different facto that is relevant for the prolongation of incisional pain leading to translation of chronic pain after surgery.
Another post-operative cue collected was swelling, pain and redness at the suture site with refusal to mobile pain. As pointed out by Wainwright, Burgess, and Middleton, (2018) points out that though there are positive results demonstrated in patients in total hip replacement, there need to be adopted pain management strategies for enhancing recovery post-surgery and thereafter improvised outcomes. In this article, it was also pointed out that one of the primary clinical reason behind delayed discharge was pain, redness, dizziness and general weakness. The pathophysiology behind redness and swelling can be connected to a decrease in muscle functioning or weakness post-operation due to atrophy. Oedema can be regarded as a build-up of abnormal interstitial fluid in the body leading to the production of palpable swelling. This not only leads to trauma post-surgery but also a decrease in mobility which in turn leads to venous return that prevents the fluids from the tissues back into the blood vessels. This leads to an imbalance between the capillary filtration also lymph damage that causes swelling(Richards et al., 2018). There remains limited evidence that can be used for describing the impacts of oedema on recovery but there need to be adopted nursing strategies for resolving issues related to the same.
3. a. Identification of the nursing goal for each identified issue/problem
b. Nursing interventions for each issue/problem
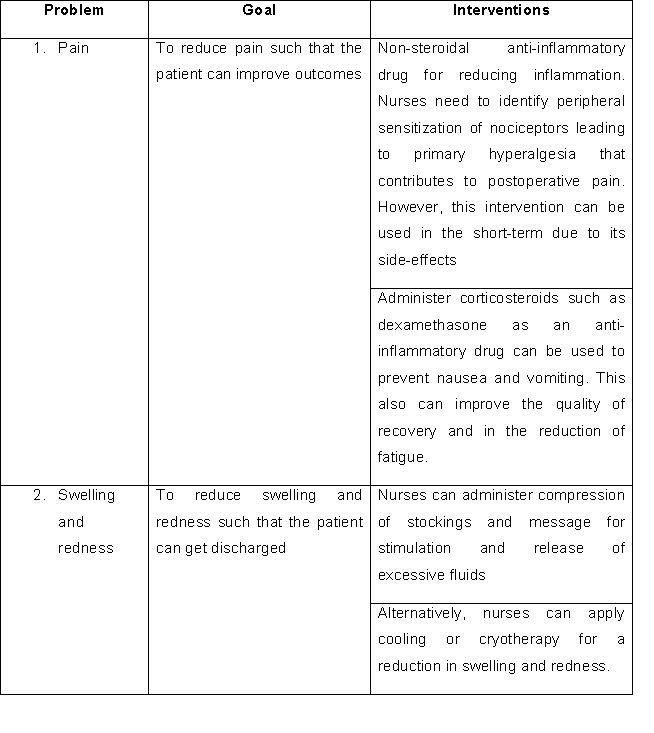
4. Rationale for the interventions and evaluation of interventions
For clinical management of pain Pogatzki-Zahn, Segelcke, and Schug, (2017) rightly points out that postoperative pain manifests from acute pain and is considered more complex than it was thought originally. Hence due to the complexity of postoperative pain, there is necessary specialised nursing care rather than applying mere opioids as is done generally. There remains a very vast amount of scientific evidence for managing postoperative pain. The Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists has summarised some of the evidence in the 4th edition of the document "Acute Pain Management: Scientific Evidence". From such evidence, it can be drawn that the concept of multimodal analgesia can be administered for the management of postoperative pain. It can deliver superior results in different site of actions and can reduce the usage of opioids, hence thus reducing the side effects of opioids as well. As peripheral sensitization of nociceptors which leads to primary hyperalgesia has been seen to be contributing to postoperative pain, hence NSAIDs can be effective (Crotty et al., 2019). The impacts of NSAIDs can be increased by administering paracetamol and can be used for short-term use.
Also, the administering of dexamethasone has been seen to improve the quality of patient life in recovery and reducing fatigue (Mori,Hageman, &Zimmerly, 2017). Nurses can administer its dosage using therapeutic care for the reduction of postoperative pain scores and opioid consumptions as well. Though there remains significantly low clinical relevance as the debate regarding their potential risks remains. The evaluation of such intervention can directly be understood by checking the patient pain score. In case the pain score is lowered then the mechanism can prove successful.
For the management of swelling and redness as pointed out by Wainwright, Burgess, and Middleton, (2018) colling or cryotherapy, compression stockings and the massage was suggested. Findings from this study indicate that though there exists several methods for the reduction of oedema, however colling or cryotherapy, compression stockings and massage can help relieve swelling, though there remain certain limitations in the methodology.
5. Medications for the patient’s pre-operative condition
6. Applying the Roper-Logan Tierney Modelpotential cultural/biopsychosocial issue/problem that will affect the patient post-operatively or on discharge
The Roper-Logan Tierney Model of the nursing process can provide a guide for holistic assessment of the patient for devising a care plan for the patient. Within this clinical setting, the R-L-T model of nursing can answer questions regarding the functional deficits identified in patients that are needed to address nursing care (Ciftci, 2019). One biopsychosocial problem that will affect the patient post-operatively or on discharge includes family circumstances. Her husband is elderly and had a stroke and is mildly impaired. She had lost two children in a car accident, 5 years ago. This implies that she will not be able to depend on anyone once she is discharged which might eventually impact her quality of life. Hence upon discharge, an appropriate nursing care plan needs to be devised such that she does not have to depend on others for taking her care.
References
Almasi, A., & Meza, C. E. (2019). Doxepin. Retrieved from [https://europepmc.org/article/NBK/nbk542306]
Ciftci, B. (2019). NURSING CARE ACCORDING TO ROPER-LOGAN-TIERNEY MODEL OF LIVING IN CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE: A CASE REPORT-Chapter 2. New Horizons in Health Sciences, 25.
Crotty, M., Killington, M., Liu, E., Cameron, I. D., Kurrle, S., Kaambwa, B., ... & Ratcliffe, J. (2019). Should we provide outreach rehabilitation to very old people living in Nursing Care Facilities after a hip fracture? A randomised controlled trial. Age and ageing, 48(3), 373-380.
Erlenwein, J., Müller, M., Falla, D., Przemeck, M., Pfingsten, M., Budde, S., ... & Petzke, F. (2017). Clinical relevance of persistent postoperative pain after total hip replacement–a prospective observational cohort study. Journal of pain research, 10, 2183.
Lavand'homme, P. (2017). Transition from acute to chronic pain after surgery. Pain, 158, S50-S54.
Matthews, A., & Bhaskaran, K. (2017). Therapy code list-ACE inhibitors. Retrieved from [https://datacompass.lshtm.ac.uk/id/eprint/417/1/cr_codelist_acei.txt]
Mori, C., Hageman, D., &Zimmerly, K. (2017). Nursing care of the patient undergoing an anterior approach to total hip arthroplasty. Orthopaedic Nursing, 36(2), 124-130.
Pogatzki-Zahn, E. M., Segelcke, D., & Schug, S. A. (2017). Postoperative pain—from mechanisms to treatment. Pain reports, 2(2).
Richards, D. A., Hilli, A., Pentecost, C., Goodwin, V. A., & Frost, J. (2018). Fundamental nursing care:
A systematic review of the evidence on the effect of nursing care interventions for nutrition, elimination, mobility and hygiene. Journal of clinical nursing, 27(11-12), 2179-2188.
Wainwright, T. W., Burgess, L. C., & Middleton, R. G. (2018). A feasibility randomised controlled trial to evaluate the effectiveness of a novel neuromuscular electro-stimulation device in preventing the formation of oedema following total hip replacement surgery. Heliyon, 4(7), e00697.












