International Economics Assignment: EU Trade Agreements From Japan To South America
Question
Task:
In this international economics assignment, you have to mention about impact on economy of European Union and the countries comes under route of Japan to South America by (EU agreement with Japan to South America for international trade). Please mention how GDP, International trade, International trade factor, competitive advantages, Tarrifs and non Tarrifs.
Answer
Introduction:
According to the investigation on international economics assignment, it is clear that the development of the international trade has been shaping the world economy since last five decades. When it comes to the European Union (EU), then all the neighbouring countries holds an important role in cherishing the international trade. Over the last three decades, since 1990s, there has been good amount of development in the EU trade with different states, whereas, bilateral trade agreements were existing between nations within EU since 1950s (Saint et al. 2019). These EU trade relations has flourishing with the various economies around the world when EU started to brought in Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) (Domenech and Bahn 2019). With special economies zone provision and reduce import and export tariff EU started to bring in trade growth that impacted the local as well as international economies. Through the present studies, here analysis has been made to understand how recent trade agreement between EU and other nations like Japan, Singapore, Vietnam, Central Asia, Asian countries, Brazil, Uruguay, Paraguay, US has been impacted.
EU trade agreements:
EU has trade relation with as many as 70 no-EU nations and out of them EU has FTA with 27 countries. As the leading trading partner of the EU, China, US, UK, Switzerland, Japan, Russia, India can be mentioned. Apart from these, there are countries from the central and south east Asia, Argentina, Brazil, Uruguay, Paraguay and many more. EU is the largest trading partner of Asian countries and for the western countries also EU region holds much amount of importance in trading terms. Through the development the trading partnership with countries like Japan through Economic Partnership Agreement (EPA), FTA with Singapore, Vietnam and central Asian countries, EU has smoothened its trade relationship (Sampson 2017). These trade connections have long lasting impact on the local as well as the international market too.
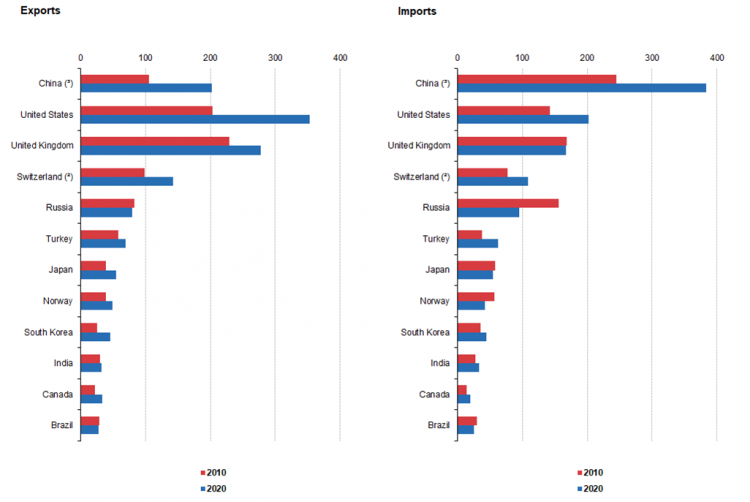
Figure 1: EU main trading partners from 2010 to 2020
Source: (ec.europa.eu 2020)
As per the figure 1, it can be seen that major exporting country from EU was UK during 2010, whereas, it become US during 2020 followed by China. On the other hand, major imports in EU market was done from China during 2010 and it is same during 2020 too followed by US, UK. Though the EU has no direct trade agreement either with US or China, however, over the last one-decade trading has increased, whereas countries which have dedicated trade agreement like Japan, India, has faced fall in export and import during 2020 compared to 2010 (ec.europa.eu 2020).
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) has essentially completed its ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA) and has now committed itself to a single market and production base in the form of the ASEAN Economic Community (AEC) by 2015. It has also set in place FTAs with several countries, including Australia, India, Japan, New Zealand, China, and Korea. Singapore has many bilateral FTAs, including its model P4 FTA with Brunei, New Zealand, and Chile, which has attracted considerable interest from the United States (ec.europa.eu 2021).
Possible impact trade agreements could have on local and world economy:
Impact of the trade agreement between EU and the nations like Japan, Singapore, Vietnam, Central Asia, Asian countries, Brazil, Uruguay, Paraguay, US can be demonstrated from dual perspective. Above mentioned trade relations have impacted the economy of the trading partners as well as impacted the social life style of the people in trading nations. One of the major impacts in terms of trade relation effect through trade agreements can be observed in terms of tariff and non-tariff impact. For instance, when the trade relation between Japan and EU is considered, then it can be seen that both the countries has liberalised the tariff on import and export. EU has liberalised 99% export tariff and 100% import tariff, whereas, Japan has liberalised 97% export tariff and 99% import tariff (ec.europa.eu 2021). When case of the US is considered, then it can be seen that through the FTA between EU and US, 99% trade liberalisation has taken place. Trading between EU and US comprises more than 40% of the global trade of goods and services, making both the EU and US a strong and stable trading partner. High amount of the trade relation between the EU, and US has shaped the standard of living of the people to a great extent (Li et al. 2018). On the other hand, case of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and GDP growth can also be mentioned here through the expansion of the trade and trade agreement between EU nations and other trading partners. Though, Japan, US is developed nations, however, free high amount of trade between the EU and these states has enabled them to have high growth in the business. On the other hand, domestic GDP of the trading nations from EU has also expanded over the decade through trade. For instance, Hungary, Ireland, Poland and Malta has faced 6% annual growth rate during last decade and one of the major reasons for the same is increased trading (Alola et al. 2019).
Coming to the impact of the EU trade agreement on the Asian economies and south American economies, it can be seen that it has been developing at a rapid rate in recent years. The EU is a significant objective market for emerging countries, all the more so previous settlements of nations inside the EU (trade.ec.europa.eu 2021). The extra advantages are conceded to countries that comply with the set guidelines of the EU, for example, worldwide work privileges, exercise of good administration and food of the climate. In order to enhance the world-wide program of trade agreement, Economic Partnership Program (EPA) was introduced. The details of the program might be viewed as the best trade agreement program around the world. Presently the program has 49 recipients. The EPAs primary reason for existing is the advancement of practical improvement inside the African, Caribbean and Pacific countries, destitution decrease and provincial reconciliation (trade.ec.europa.eu 2021). Among the participatory countries incorporate those inside the East African Community (EAC) like Kenya and in Sothern African Development Community (SADC) (Campos et al. 2019). Moreover, there are central and south west Asian countries too which was focused to enhance its economic operation through the business with EU. With the increased trade agreement between the nations in Asian market and EU over the last two decades has enabled the free factor movement within nations allowing cost of production in EU market to go down. Moreover, there has been scope for both the Asian and EU market to enhance their respective profits through the trade with dedicated trade agreement. As the trade agreements allowed movement of the factors of production from Asian economies to EU, on the other hand, EU market has gained special economic zones to enhance their business in the Asian markets through reduced tax.
EU trade routes with japan, US and translantic nations comprise 40% of the world trade as of now which has increase from 23% back in 2000 (ec.europa.eu 2021). With the increased trade, export of the goods and services has also increased subsequently during the last two decades and it aided both the EU economies and trading partners to have increased GDP. Another major impact of the trade agreement lies within the movement of the factor. With the opening of the trade relation between US, Japan, Vietnam, Brazil and central and south Asian nations, there has been mobility of the labours. Skilled labours have moved from their domestic economies to the EU economies for the better standard of living. Besides this, movement of the labour and increased factor mobility has allowed growth of globalisation (Huang et al. 2017). Firms from the EU market has transformed their business line-up in Asian economies due to the low labour cost. As the Asian markets has labour abundance, hence cost of production is low allowing lower cost of production. For instance, exporting of the Automobile, service and telecommunication industry to the Asian economies from EU has taken place through the trade agreement. On the other hand, there has been outsourcing of the services, growth in tourism industry for the trading partners due to the trade agreement.
As the theoretical perspective of the EU trade agreements and the development of the economies can be explained with the help of the factor movement model. As per the model international factor movements, for example movement of labour, capital and other production factor between the countries has been enhanced post globalisation. Now, factors can move from one place to another freely allowing factor freely moveable without transaction cost. As the EU economies has come in trade agreement with various economies, thus, there has been good growth of the factor movement within the economies allowing skilled labours to move from developing Asian economies to EU economy and technology to be transferred from EU economies to the Asian economies. During present time international labour migration has become a common phenomenon, however, there has been significant political and legal interference in this matter. Targeted trade agreement between the nations has been focused on solving the biliterate factor movement issue and thus, EU trade impact has large impact on the factor movement too. Through the dedicated trade agreement EU and its trading partner has been able to move labour and other factor of production from one place to another without international attention. Thus, the trade agreement has long lasting impact on the factor movement too.
This movement of the factor of production can be explained through Ricardian model that use the comparative advantage model. EU has comparative advantage in the capital abundant production and lacks in case of the labour. Hence, countries which has abundance of labour exports goods and services to the EU market which are labour abundant. On the other hand, EU market exports capital intensive product (Saint et al. 2019). Thus, the EU market largely export automobile output and defence output. For instance, France has proved itself as one of the major suppliers of the arms and defence products in the international market. On the other hand, Turkey is also there that exports and imports defence products from the western market and Asian market. Contrary to this, countries like Vietnam, brazil, Singapore sends skilled employees to the European market (Ntanso et al. 2018).
Another major influence of the EU trade agreements can be seen in terms of the technology transfer. EU being technologically developed, export their technologies to the developing countries like brazil, Singapore, Vietnam, India and central Asian countries. Through the transfer of technologies, trading partner of EU faced increased output capacity as they have enhanced technology (Domenech and Bahn 2019). Moreover, recently EU economies has been exporting green technologies that enabled the trading partner to have higher capacity to produce goods and services with green energy.
Conclusion:
Analysis of the trade agreements between the EU and the other nations like Japan, Singapore, Vietnam, Central Asia, Asian countries, Brazil, Uruguay, Paraguay, US demonstrates that there has been moderate to high impact on the trading partners. For instance, US, Japan, countries from central Asia has faced good growth in their GDP, production possibilities, technological development, growth of multinational companies and outsourcing. One of the major impacts for the trade agreements between the nations can be seen in terms of the factor movement, where skilled labours moved from domestic market to EU market for better livelihood. On the other hand, there has been growth in the globalisation due to the changing composition of trade as EU trade accounts for 1/3rd of international trade. Countries which has comparative advantage in production of specific goods and services has faced increase in their GDP growth through trade as EU has emerged as one of the major places for export in recent time through dedicated trade agreements with different nations.
Reference:
Alola, A.A., Bekun, F.V. and Sarkodie, S.A., 2019. Dynamic impact of trade policy, economic growth, fertility rate, renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on ecological footprint in Europe. Science of the Total Environment, 685, pp.702-709. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969719321643
Campos, N.F., Coricelli, F. and Moretti, L., 2019. Institutional integration and economic growth in Europe. Journal of Monetary Economics, 103, pp.88-104. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304393218301648
Domenech, T. and Bahn-Walkowiak, B., 2019. Transition towards a resource efficient circular economy in Europe: policy lessons from the EU and the member states. Ecological Economics, 155, pp.7-19. https://epub.wupperinst.org/files/6903/6903_Domenech.pdf
ec.europa.eu 2021. International trade in goods - Statistics Explained. https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=International_trade_in_goods
ec.europa.eu 2021. United States - Trade - European Commission. https://ec.europa.eu/trade/policy/countries-and-regions/countries/united-states/
Huang, G.O., Pessoa, J.P., Sampson, T., Van Reenen, J. and Gancia, G., 2017. Comments on “The Costs and Benefits of Leaving the EU: Trade Effects” by S. Dhingra, H. https://www.crei.cat/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/BrexitDiscussion.pdf
Li, C., He, C. and Lin, C., 2018. Economic impacts of the possible China–US trade war. International economics assignment Emerging Markets Finance and Trade, 54(7), pp.1557-1577. https://phd-proposal.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/Economic-Impacts-of-the-Possible-China%E2%80%93US-Trade-War-2018.pdf
Ntanos, S., Skordoulis, M., Kyriakopoulos, G., Arabatzis, G., Chalikias, M., Galatsidas, S., Batzios, A. and Katsarou, A., 2018. Renewable energy and economic growth: Evidence from European countries. Sustainability, 10(8), p.2626. https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/10/8/2626/pdf
Saint Akadiri, S., Alola, A.A., Akadiri, A.C. and Alola, U.V., 2019. Renewable energy consumption in EU-28 countries: policy toward pollution mitigation and economic sustainability. Energy Policy, 132, pp.803-810. http://95.183.203.22/xmlui/bitstream/handle/11363/1468/Renewable%20energy%20consu
mption%20in%20EU-28%20countries.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
Sampson, T., 2017. Brexit: the economics of international disintegration. Journal of Economic perspectives, 31(4), pp.163-84. https://pubs.aeaweb.org/doi/pdfplus/10.1257/jep.31.4.163
trade.ec.europa.eu 2021. Access2Markets Everything but Arms (EBA). https://trade.ec.europa.eu/access-to-markets/en/content/everything-arms-eba
Zeitlin, J. and Vanhercke, B., 2018. Socializing the European Semester: EU social and economic policy co-ordination in crisis and beyond. Journal of European Public Policy, 25(2), pp.149-174. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/13501763.2017.1363269












