Cloud Computing Assignment: Development of Personally Identifiable Information (PII)
Question
Task
You are to write a report on cloud computing assignment that proposes appropriate policies for DAS in the following areas:
- Develop a PII strategy proposal for the DAS MyLicence portal. The strategy should consider the threats and risks to both Privacy and data protection for the PII data collected in the MyLicence portal as well as possible controls to mitigate the identified risks.
- Develop a strategy to protect the informal Digital Identity that a user may create in the MyLicence portal. You should consider both the privacy and data protection aspects for a digital identity as well as possible controls to mitigate the identified risks.
- Develop a strategy to ensure data sovereignty for the MyLicence portal
Answer
Executive Summary
In the current situation, organizations are looking forward to implementing advanced technologies to sustain their operational processes. The Australian government is also inclined towards adopting new technologies, such as 'cloud computing' on a public host and maintain a 'centralized database' to the government department. The 'department of administrative services' (DAS) enables the Australian government in providing various services, such as personnel management, HRM, 'contract' tendering management, 'contractor' management, and procurement. DAS mainly manages the services of these departments through their database in their 'data centers.' Currently, the Australian government is planning to create a new portal for conducting works related to licensing applications, processes, and renewal systems.
The motive is to make DAS a centralized department that will consolidate the services from various agencies and departments that regulate the license system called ‘MyLicence Portal.’ The new portal will help in processing the license application, renewal process, documentation, and management of the personal information of the users, and make the whole process in a single workflow. The current report has assessed the potential risks and threats in adopting the ‘cloud computing’ technology based on a public host in securing the ‘Personally Identifiable Information’ (PII) and ‘Digital Identity’ of the citizen of Australia. The current report presents a strategic report based on the risks and mitigation factors of PII and ‘digital identity’ on the ‘MyLicence Portal’ alongside with developing strategies in maintaining ‘data sovereignty’ according to the Australian ‘soil’ law.
1. Introduction
Cloud computing is a medium to deliver various services through cyberspace. Cloud computing can store data in the "cloud-based" spaced in the software; it will help to secure the data and store it in a very secure space. Cloud computing has a very popular demand in any business organization. Cloud computing can help the user to store the data in any space in the virtual world and not need any specific place to access it. Cloud computing can also help to secure any data. As security is a major part of any institution. Lack of security can lose highly sensitive data causing damage to the company. Cloud computing can help to save and secure the data and it provides security services to the consumers(Subramanian & Jeyaraj, 2018). It helps users to work on data remotely. If one uploads the data in the cloud, it can be easily accessible from any device; it doesn't require any specific device. There are public and private cloud services.
Public cloud service provides services through the virtual world but the private cloud only gives services to certain peoples. Private clouds can secure highly sensitive data in the cyberspace. There are numerous types of cloud computing systems like "Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)", "Infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS)", "Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)". These services can help to restrain the data in the virtual space. Advance cloud computing can also help users to access emails and other pieces of stuff from other devices. The Australian government has decided to implement cloud computing to secure the data of the citizens who have applied for the license. The government wants to centralize the cloud computing service through "The Department of Administrative Services” (DAS). It will save the data to get misplaced because taking multiple services can lose the data easily. In this report, the risks have been discussed if any misplaced of data has happened and how to resolve it can also converse.
2. Overview of the Scenario
The Australian government has decided to centralized license renewal and application through cloud computing. As cloud computing can help to save the data of the applicant as well as it will secure it from leakage. Through centralizing the service, the data will become secure and easily accessible to the government. Sharing services can easily misplace any applicant data. Thus, "The Department of Administrative Services (DAS)" has decided to centralize the data service methods. Through cloud computing, the data will be secure in the portal. As the government will adopting the way of centralizing the data it will make the service more efficient for the applicant(Mohammed et al., 2017). The centralized data will manage data existence as well as it will easily searchable in any large data(Cisneros-Montemayor et al., 2017). The government has introduced the "MyLicence" portal which can help DAS to centralize the data in cyberspace. It will help to maintain the data workflow and if any changes can be done in the specific license through this portal. the portal will show the data and applicant identity on one single page. “MyLicence” portal has been under the host called “Cloud First” which will help to centralize the service. This portal will help to remain the data in the Australian country and maintained the “data sovereignty”.
Appropriate Policy Development for the ‘Development of Administrative Services’ (DAS)
‘Personally Identifiable Information’ (PII) Strategy Proposal for DAS ‘MyLicence Portal’
“DAS MyLicence” portal will have to hold a lot of incoming individual data. Hence, MyLicence needs a huge data-list of all the PIIs in their database of Australian civilians. To tackle the risks and threats to the data and privacy security policies, an organized checklist of “strategies to follow” may prove beneficial.
3.1.1 Strategy
A ten Step Strategy that can be considered is given below,
a. PII identification
Identify types of data stored in the company database about personnel and customers connected to the company. Personal data like Tax File Number (TFN), mobile number, mail ids, and passwords for the portal etcetera has to be identified (Onik et al., 2018). The data needs to be then categorized according to the level of security needed.
b. PII storage
Digital Data can be stored in multiple forms. It can be stored on the cloud, on devices, or dedicated storage drives like SSD and HDD. The 3 Major forms of storage in use presently are,
- Live data: The data that the MyLicence employees will be using daily to access information is called live data. The components that store these data are volatile storage devices like RAM or self-destructing data packets, such as self-destructing Emails.
- Resting data: The data, that will be stored permanently to be archived and the use of it are only for occasional purposes, is resting data. These data will have to be stored in Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), Solid State Drives (SDDs), non-volatile writeable storage devices (CD and DVDs), Local database Servers, laptops, Cloud Servers, and SharePoint.
- Dynamic data: Data that is in the transition from one device to another is called dynamic data. These are the data that will be transacted between the citizen and the MyLicence server or cloud, and also from the MyLicence server to the employees that use them. A track of where the data is can enable DAS to pinpoint security breach and the connected offenders (Marciano et al., 2018). Activity tracking is a positive side effect of this.
c. PII sensitivity classification
Data classification based on sensitivity is a necessary step to sort and group-administered PII. The following attributes need to be kept in mind while sorting,
- Recognizable: The data file should have a unique identification number.
- Data grouping: The data should be grouped according to their relevancy.
- Storage tracking: Which PII is stored on which storage device needs tracking.
- Conformity: Data collected should agree with the norms of data collection policies of the DAS ‘MyLicence Portal’ (Huang et al., 2019).
d. PII redundant data deletion
Any irrelevant, invalid, redundant and obsolete PII data needs to be actively removed from MyLicence servers to save space and increase security quality.
e. PII usage policy
An acceptable Usage Policy (AUP) needs to be formed for accessing PII from the portal.
f. PII encryption
PII data needs to be encrypted with multi-level security with no compromise. This is the most important step for the whole system as this deals with the core security clause of the data (Alnemari et al., 2019).
g. PII Permission error rectification
DAS needs to curate and check data access protocols and permission grants to employees. Employing the Principal of Least Privilege ensures that the data can be accessed only by the active employees of the ‘MyLicence Portal’ (Majeed et al., 2017). The permission grants should be given according to their level on the floor.
h. PII knowledge center
Proper education to the employees of the ‘MyLicence Portal’ about the rules of engagement policies is necessary to assure the smooth working of the portal.
i. Employee departure process standardization
No employees should have company data when they leave. A standardized procedure needs to be formed containing access removal from the ‘MyLicence Portal’ server, signatures on legal notices for non-breaching of company information, and a signed Confidentiality Agreement.
j. Suspicious behavior reporting mechanism
A secure line of contact should be set up that can enable employees to contact the security managers in case of suspicious activities on the server or office.
3.1.2 Consideration of Risks and Threats in Privacy and Data Protection
|
Potential Risks and Threats |
Likelihood |
Control Process |
|
Credential theft |
Medium |
|
|
Phishing |
High |
|
|
Malware infection |
High |
|
|
Stolen or lost physical device |
Medium |
|
|
Unauthorized access to device |
High |
|
3.1.3 PII Data Collection in ‘MyLicence Portal’ to Mitigate Identified Risks as a Part of the ‘Control Management’
The main motive behind creating the PII data secured is to identify, locate, and contract an individual by their details, such as name, birth date, information, and credit details. The potential risks related to this data are related to stealing 'credential,' affecting by any 'malware' infection, misplacement of the 'physical evidence', and 'unauthorized' external network interference into the 'MyLicence Portal.' The government in various countries have implemented a 'personal information protection' law to make an appropriate risk assessment on the threats related to PII and change the policies according to the requirement (Lin et al., 2016). The developers of the current new portal imposing by the Australian government can take the following steps to mitigate the risks and threats related to PII,
- The assessment of credentials from the users is mainly influenced by the exposure of the username and password that is being stolen from their email activities (Thomas et al., 2017). The new ‘MyLicence Portal’ can use the mechanism of ‘one-time password’ (OTP) during the verification process of the users to make them avoid getting personal information via email.
- In the management sector of DAS, the documentation of the ‘physical evidence’ situated at the ‘centralize database’ needed to be checked regularly to avoid any misplacement situation at the required time. It will also help in identifying any problematic area to resolve them in advance.
- The network process at the DAS needed to be secured from interfering from an external source to access the database in an ‘unauthorized’ way to steal data from the ‘cloud’ device.
- Currently, various advanced malware is responsible for stealing sensitive data from the users, such as contact details, bank information, and the password of other devices, and it tends to destroy large portion data over online (Eze & Chukwunonso, 2018). The installation of strong anti-malware software at the ‘centralize database’ can prevent the malware attack effectively.
3.2 Strategy Development for Protecting Information ‘Digital Identity’ in the ‘MyLicence Portal’
3.2.1 Strategy Development
|
Strategy |
Discussions |
|
Maintenance of multiple identities will only become more awkward because the digital era explains the ‘digital identity’ (Bakre et al., 2017). Multiple virtual identities need maintenance to make sure about the interchangeable uses among the users. One should make a personal identity initially to protect the ‘MyLicence Portal’. Creating an email id of an individual are usable only for banks or government records. One should never link a bank or any government records with social media applications. The user must have to create another email id for the uses of the 'MyLicence portal’. Different email ids should be made for several uses. Try not to link any personal email ids in social media applications. |
|
One must have different passwords for different types of accounts. Many users often failed to create a strong password (Seitz & Hussmann, 2017). These users must know the uses of “Password Manager”. “Password Managers” should be used to create passwords. These “Password Managers” are “Daslane”, “LastPass' and '1Password'. Users should avoid passwords and create Passphrases. In the Passphrase, users have to put three random words. Including spaces, one Passphrase should have eight characters. Sixteen characters should have to be implemented to create a secure password. In the Passphrases, no personal information should be given. Random strong Passphrases should be generated. Repetitions of the Passphrase should be avoided. In cloud security devices these techniques will help to create the 'MyLicense portal’ personally. |
|
It is not always safe to have strong usernames and passwords. To increase the resistance from cyber-attacks of the user's account, the system administrators have adopted the two-factor authentication (Tiller, 2020). A hacker can easily hack someone's password if the passwords re compromised. The reason for creating two-step verification is because of thi9s hacking. Always try to keep another identity to access one account. |
|
There are many practices that help to create a "digital identity" in the "MyLicense portal”. Internet users are suffering from online security threats in the recent few years (Jiang et al., 2016). The first thing is to develop antivirus software or firewall software on devices that includes smartphones and tablets. These devices have to check on a regular basis that the software is being updated or not. Always have to check that any existing email ids have already been compromised or not. For future Scam Alert, one should register their applications. Avoid using public wi-fi which includes hotels and airports. Always delete any personal information from profiles in social media applications. Always have a watch on any kind of 'phishing' emails. Always have to be alert on any suspicious emails like financial offers and about any credit cards that are pre-approved or like this. |
|
Always have to be informed by the bank statements and follow the mails daily. Strictly have a watch on emails to avoid unfamiliar transactions. Stay always alert about major data news that is covered by the news. Sometimes users faced that online games ask for personal information and passwords. These online games should strictly be avoided to have a secured online account. Always keep an eye on other crimes so that one could protect and be alert about their own data. Always avoid messages which ask for personal information like passwords, PINs, credit card numbers, and so on like this. |
3.2.2 Consideration of Privacy and Data Protection in ‘Digital Identity’
Digital identity is an entity that represents the computer system. This host can be a person or an organization. Here the Australian government is the host of the portal is securing the following factors,
- Every digital host has a unique id number. To protect the digital identity, one should hide the id number.
- One should update the security of the software system.
- To protect the data in cyberspace one should take the backup of the data on an external device.
- To protect the digital identity the user should keep in mind before downloading any application and should choose a strong password for any digital platform.
- Users should always use the encrypted version of any application.
3.2.3 Possible Controls in ‘Digital Identity’ in Mitigating Potential Risks
|
Potential Risks |
Likelihood |
Control Process |
|
High |
At first, the priority is to keep the data in a protected condition. Many strategies of the downfall of security control are too general and too thinly spread. Some steps of prioritization increase the effectiveness by seeking the most important assets of safeguards. Always have to maintain a documented process and follow it. Users have to make a part of the process. It is a forgotten aspect that often response to the end-users. |
|
Medium |
To secure the sensitive data or information the users should use strong passwords which will prevent the unethical person to hack the system. One should use encrypted documents for sensitive data like "digital identity". The users should update the security system of the devices to protect the software. To protect sensitive data, one should not use illegal devices on the secure. Secure the internal network to prevent interference from cyber-attack. Implementation of organizational law to prevent employees from stealing sensitive information. |
3.3 Strategy Development for ‘Data Sovereignty’ in ‘MyLicence Portal’
Through cloud computing service the Australian government has presented a new approach to centralized data through the "MyLicence" portal. The Australian government has also followed data sovereignty to keep the data into the country. Data Sovereignty will help to keep the data secure and the data will not be leaked in the abroad portals.
- To save the data from stealing from cyberspace the government should apply the 'Data Sovereignty’ through cloud computing.
- As the Australian government maintains the Data Sovereignty to keep the data secure, the hybrid cloud strategy will help to advance the technology as well as it will protect the data from third-party breaching. It also helps to maintain the privacy of the country's data from other foreign countries.
- Hybrid clouding would help the authorities to keep the data on track and the government would have the access to which data would keep in the cloud and which is not.
- With the help of the "Microsoft Azure" public cloud, the scalability and flexibility of the data can be secure in the cloud. Other than “Microsoft Azure” there are other tools that will help to develop the hybrid clouding rapidly like “Microsoft Azure Stack”. This tool will help to maintain the data sovereignty law of the country.
- The hybrid cloud can also help to increase the speed and efficiency of the portal. It will solve any problems on the premise.
- Hybrid clouding will help to mitigate any problem regarding data sovereignty. It will resolve the matter easily and with an active solution (Trakadas et al., 2019).
- Data security is very crucial nowadays, that's why through hybrid cloud computing the data can get secure (Gupta & Kumar, 2019).
- "Optimal Triple Data Encryption Standards (OTDES)" can help to encrypt the data from the third party. This will also help to maintain the data sovereignty of the country. This encrypted information can only access by the authorities or the users.
- Cloud computing is a cybernetic way to put all data on the cyberspace. It will help to elevate the administrative processing of the country (Irion, 2011). It will also save the data of the citizens.
- Develop countries like Australia also faced the sovereignty crisis. Like the cost of the system can affect cloud computing (Kushwaha & Watson, 2020). Sometimes it will affect the economy of the country.
4. Recommendations
In the ‘MyLicence Portal,’ the developers have been identified the main problematic areas – PII, ‘digital identity’ protection, and maintaining the ‘data sovereignty.’ The current report has already assessed the potential risks related to these areas and their potential mitigation process. The provider of the public hosting in establishing the ‘cloud computing’ technology is required ‘Identity-as-a-Service’ (IDaaS) that secured the management accessibility on the cloud service after assessing the demand (Vo et al., 2019). The Australian government is also determined in presenting its 'Cloud First' policy to ensure the database and information are managed within the Australian soil to protect the 'data sovereignty.'
In the PII protection process, it is required to provide the utmost security to the users in securing their personal information. the Australian government's main motive behind centralizing the license data center is to assess the citizen's information stored at a particular place to make a constructive decision related to them. The automation and continuous 'replication' process make the 'database management system' (DBMS) migration process to perform multiple services simultaneously in the system (RAO et al., 2018). The DAS should also adopt a strong anti-malware software in the database to secure the system from exposing in front of ‘malware infection.’ Other recommendations can be,
- Maintaining the ‘digital identity’ of the users is important via ‘cloud’ technology without sending any information directly to the user’s email to provide any password.
- Maintaining the Australian law for ‘data sovereignty’ to secure sensitive data from the users to prevent them to not cross the Australian soil.
- The PII protection needed to be established by the developers of the 'cloud computing' system at DAS to secure the user's personal information effectively. The Australian government is determined to use the user's data during any emergency.
- The ‘MyLicence Portal' needs to introduce additional functions where the users can ask their required queries and make the management to solve their questions within a small amount of time. The digitalization of the license application process will eventually make the interaction process between the authority and the citizen time-efficient.
5. Conclusion
In the current report, the Australian government “The Department of Administrative Services (DAS)" has wanted to implement the “MyLicence” portal through cloud computing. It will help to provide the service to the applicants of the country. The portal will help to track the data and to see all the applications virtually. It will also maintain the workflow of the data. The portal will help the citizen to make the license over the website. It will help to make the process simple and it can track the data analytically. Cloud computing can also help to secure the data on the cyberspace.
The Australian government is using the public cloud to provide the service. Data Sovereignty will also be followed by the country. It means that all the data are saved in the cloud within the country. “MyLicence” portal maintains the data sovereignty policy to maintain the data in the states of Australia. It will also secure virtual data. The portal will also encrypt the data of the users from third-party breaching. All of these will elevate the administrative process of the country. The license will be easily accessible in the portal so the data can be available in the system. It will help to find any kind of data effortlessly.
6. References
Alnemari, A., Raj, R. K., Romanowski, C. J., & Mishra, S. (2019). Protecting Personally Identifiable Information (PII) in Critical Infrastructure Data Using Differential Privacy. 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Technologies for Homeland Security (HST), 1–6.
Bakre, A., Patil, N., & Gupta, S. (2017). Implementing decentralized digital identity using blockchain. International Journal of Engineering Technology Science and Research, 4(10), 379–385.
Cisneros-Montemayor, A. M., Cheung, W. W. L., Bodtker, K., Teh, L., Steiner, N., Bailey, M., Hoover, C., & Sumaila, U. R. (2017). Towards an integrated database on Canadian ocean resources: benefits, current states, and research gaps. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 74(1), 65–74.
Eze, A. O., & Chukwunonso, C. (2018). Malware analysis and mitigation in information preservation. IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering, 20(4), 53–62.
Gupta, S. C., & Kumar, V. (2019). Minimizing the Security Risks in Hybrid Cloud Networks with the Aid of Optimal Triple Data Encryption Standard Algorithm.
Huang, J., Klee, B., Schuckers, D., Hou, D., & Schuckers, S. (2019). Removing Personally Identifiable Information from Shared Dataset for Keystroke Authentication Research. 2019 IEEE 5th International Conference on Identity, Security, and Behavior Analysis (ISBA), 1–7.
Irion, K. (2011). Government cloud computing and the policies of data sovereignty.
Jiang, M., Tsai, H. S., Cotten, S. R., Rifon, N. J., LaRose, R., & Alhabash, S. (2016). Generational differences in online safety perceptions, knowledge, and practices. Educational Gerontology, 42(9), 621–634.
Kushwaha, N., & Watson, B. W. (2020). Crown in the Clouds: A Canadian Data Sovereignty Crisis. ICCWS 2020 15th International Conference on Cyber Warfare and Security, 286.
Lin, I.-C., Lin, Y.-W., & Wu, Y.-S. (2016). Corresponding Security Level with the Risk Factors of Personally Identifiable Information through the Analytic Hierarchy Process. JCP, 11(2), 124–131.
Majeed, A., Ullah, F., & Lee, S. (2017). Vulnerability-and diversity-aware anonymization of personally identifiable information for improving user privacy and utility of publishing data. Sensors, 17(5), 1059.
Marciano, R., Underwood, W., Hanaee, M., Mullane, C., Singh, A., & Tethong, Z. (2018). Automating the detection of personally identifiable information (PII) in japanese-american WWII incarceration camp records. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), 2725–2732.
Mohammed, F., Ibrahim, O., Nilashi, M., & Alzurqa, E. (2017). Cloud computing adoption model for e-government implementation. Information Development, 33(3), 303–323.
Onik, M. M. H., Al-Zaben, N., Yang, J., Lee, N.-Y., & Kim, C.-S. (2018). Risk Identification of Personally Identifiable Information from Collective Mobile App Data. 2018 International Conference on Computing, Electronics & Communications Engineering (ICCECE), 71–76.
RAO, G. R. G., Kumarasamy, P., Vallabhaneni, B., POLIMERA, R., & Chintala, N. D. (2018). Migration of a database management system to cloud storage. Google Patents.
Seitz, T., & Hussmann, H. (2017). PASDJO: quantifying password strength perceptions with an online game. Proceedings of the 29th Australian Conference on Computer-Human Interaction, 117–125.
Subramanian, N., & Jeyaraj, A. (2018). Recent security challenges in cloud computing. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 71, 28–42.
Thomas, K., Li, F., Zand, A., Barrett, J., Ranieri, J., Invernizzi, L., Markov, Y., Comanescu, O., Eranti, V., & Moscicki, A. (2017). Data breaches, phishing, or malware? Understanding the risks of stolen credentials. Proceedings of the 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, 1421–1434.Tiller, L. N. (2020). Account Recovery Methods for Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): An Exploratory Study.
Trakadas, P., Nomikos, N., Michailidis, E. T., Zahariadis, T., Facca, F. M., Breitgand, D., Rizou, S., Masip, X., & Gkonis, P. (2019). Hybrid clouds for data-Intensive, 5G-Enabled IoT applications: an overview, key issues and relevant architecture. Sensors, 19(16), 3591.
Vo, T. H., Fuhrmann, W., Fischer-Hellmann, K.-P., & Furnell, S. (2019). Identity-as-a-Service: An adaptive security infrastructure and privacy-preserving user identity for the cloud environment. Future Internet, 11(5), 116.
7. Appendices
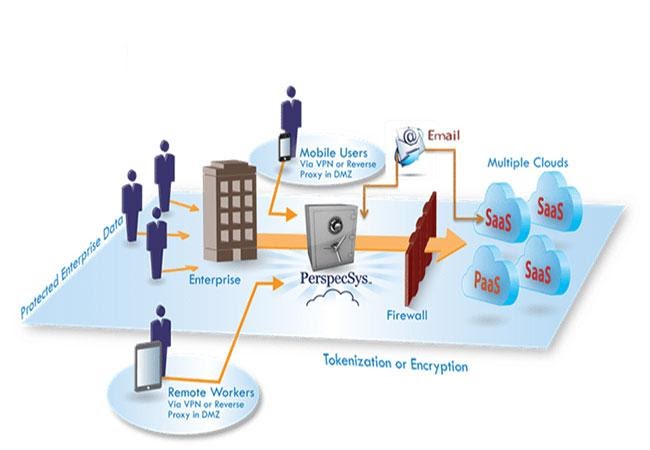
7.1 Appendix A: PII Strategy for ‘MyLicence Portal’
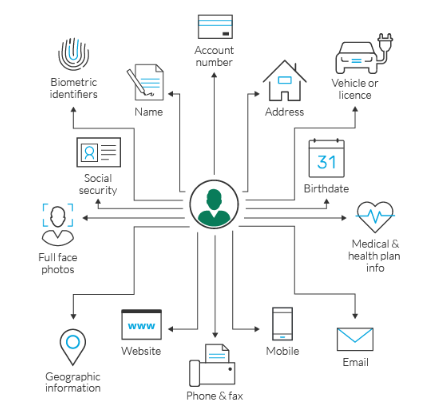
7.2 Appendix B: ‘Digital Identity’ Strategy for ‘MyLicence Portal’

7.3 Appendix C: ‘Data Sovereignty’ Strategy for ‘MyLicence Portal’