IT Management Assignment: Mobile Banking Ecosystem In India
Question
Task:
The IT management assignment requires an individual report that explains a chosen case of mobile banking system and answers the two-questions given below.
Your first task is to select a developing economy where mobile banking is still at its early stages and gain understanding of the current mobile ecosystem of the economy.
Then answer the following questions:
- Section A) –Explain the mobile banking ecosystem of your chosen country, stakeholders, early adapters and main developments.
- Section B) –Identify and evaluate the possibilities offered by Mobile banking system to your selected developing economy in achieving financial inclusion and cash less economy. The discussion should focus on its potential benefits and threats to the financial system and society.
- Section C)-Critically evaluates approaches towards innovations in mobile banking. The discussion should evaluate the merits and demerits of incremental and radical innovation. And what disruptor tools you would suggest are best suited for your selected economy.
Answer
Introduction
According to the research on IT management assignment, there are several developments and innovations that are taking place in the field of technology. The banking sector has also witnessed massive changes with the technological development and innovation. Mobile banking refers to the process of carrying out financial transactions using the mobile device. These devices could be the tablets, Smartphones, or others. The customers can remotely carry out the transactions using the services that are provided by their respective banks and financial institutions.
Mobile Banking Ecosystem – India
Reserve Bank of India, RBI is the central bank in India that is responsible for controlling and supplying the Indian Rupee. The regulation of all the banking services in India is conducted by RBI. The first set of mobile banking guidelines were issued by the RBI in 2008 (Rbi, 2014). As per these guidelines, the banks got the ability to carry out the funds transfer and other mobile banking activities through the remote medium. There were numerous aspects that were considered for the banking activities that included the customer registration, regulatory issues, interbank clearing, and likewise(Bryson et al., 2015). There are three categories of mobile banking services that are offered in India. These include the services that are offered by the mobile banking applications that are developed and deployed by the specific financial institutions. For example, State Bank of India, SBI has developed the Yono app. The second form of mobile banking services that are conducted is done via SMS and it is now provided by all the public and private sector banks. There are also mobile banking services that are offered via Unstructured Supplementary Service Data (USSD). The architecture that is followed for SIM Tool Kit (STK) based application is shown in the image below.
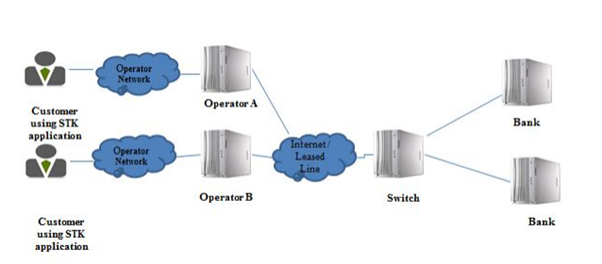
STK-based Application Architecture (Sharma and Joseph, 2017)
The USSD-based architecture that is followed in the mobile banking services is shown in the image below. There are a number of stakeholders that are associated with the mobile banking services in India. The primary is the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) which is the central bank that provides, regulates, and manages all the banking activities(Stephan, Lakshmi and Kalaiarasi, 2017). The Government of India is the central authority that is accountable for the regulation of the banking services. Currently, there are a total of 34 banks in India. 12 of these banks are the public sector banks and the rest 22 are the private sector banks in India. ICICI Bank is the first bank that started the online banking service in India. It is also the first bank in India to provide the mobile ATM.
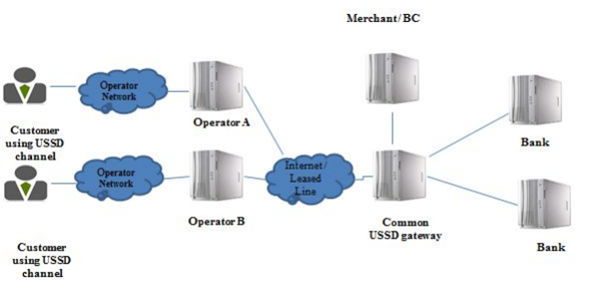
USSD-based Architecture
Possibilities of Mobile Banking System
The Digital India drive that is initiated and carried out by the Government of India has an objective of carrying out the online activities and financial transactions in order to boost the cashless economy. There are a number e-wallet services that are also launched recently and these are being used by the customers all across India. Some of the popular e-wallets that are used include Paytm, Google Pay, PhonePe, and others. There is a lot of promotion that is now being done for the cashless economy; however, a majority of the payments is done using the credit or debit cards. There are also various other mediums for digital payments that is being used. These cover the point of sales (POS) machines, use of the digital wallets, and a lot more. The main objective behind the same is to bring down the circulation of liquid currency. The increased use and developments in the field of Smartphones is also having a significant role to promote the initiative(Al Asheq et al., 2020).
The use of mobile phones is being done for a number of professional and personal activities. There are withdrawals and deposits that are being made in the bank accounts using these phones. The model of financial inclusion that is followed in India has emphasis on the cost-effectiveness along with the increase in the account that can be done with the automated deposit and withdrawal. The purpose is to make sure that the cashless transactions are done and there is increased possibility to create savings. This will also lead to the generation of the records that would reflect the savings behavior and will assist in the regulation of the payments and transactions that are carried out. The assessment of the credit worthiness will be effectively done using the same (Sheerin, 2019).
The major contribution that mobile banking will have towards the financial inclusion will be the assistance that will be offered to the low-income groups so that they may avail credit with further ease. There are different ways and mechanisms that can be used to carry out the mobile banking services in India as explained above. One of these aspects is the conduction of the financial transactions and mobile banking services through USSD. These can be easily carried out from any of the basic phones that do not even require the network connectivity. This can be further useful for the low income groups in India.
Benefits and Threats
The mobile banking services that are offered in India and across the globe come with their own share of benefits and drawbacks. There is enhanced cost-effectiveness and profitability that is associated with the mobile banking services and it is in accordance with the Business Correspondent, BC model followed in India as well. There is marked difference in the transaction cost associated with branch banking and mobile banking. In the former method, the cost of transaction varies between INR 70 to 75. However, in the case of mobile banking, the cost is determined to be less than one rupee. The report published by Global Findex in 2017 stated that approximately 66% of the inactive account holders in India own a mobile phone. Also, 90% of the Indian population is digitally illiterate. However, the increase in the use of the mobile phone can provide the benefits of enhancing the financial inclusion which may be difficult to carry out using any other form of technology (Irma, 2015).
There are various other benefits that are offered by mobile banking services in India. The Indian population is the second highest in the world. The number of bank branches are limited and there is a lot of rush that is common in almost all the branches. The mobile banking services can be easily used to save time and effort of visiting the branch to conduct the financial transactions. The reduced circulation of the hard cash can also result in the ability to control money laundering and other banking frauds. There can be two or more bank accounts that a person may have. The mobile banking services provide the ability to easily keep a track of all of these services. The world is currently dealing with the global pandemic of Covid-19. India is currently at the second place in terms of the total number of cases due to the virus. In such scenarios, it is safer to be able to remotely carry out the financial transactions so that the social distancing norms can be practiced. The mobile banking services have provided the ability to the people to conduct the remote financial transactions.
There are also various threats and issues that are also determined with the mobile banking services in India. The primary issue that is associated with the mobile service is the possible violation of security and privacy. There are various forms of security and privacy risks that may occur. There was a massive data breach that was reported in June, 2020, and it resulted in the exposure of over 7 million users (Securitymagazine, 2020). The data breach occurred on the mobile banking app called Bharat Interface for Money (BHIM) website. There have been similar security issues and concerns that have taken place in the past. There is also cost of INR 0.5 that is associated with every USSD transaction. This may not be managed by the low-income groups. Also, the USSD transactions once initiated cannot be rolled bank. The encryption protocol that is associated with USSD is also weak and is exposed to the higher possibilities of data breaches.
Approaches towards Innovation
Mobile banking is one of the significant aspects that are associated with the banking and financial services in India. It is essential to carry out the innovation in the mobile banking sector and to make sure that the security and privacy issues that are associated with the banks are controlled.
One of the primary approaches that are being used and will be further expanded in the future will be the use of Big Data to analyse and detect the financial threats. There are massive data sets that can be gathered through the Big Data tools that can come from the mobile banking websites and applications. The information can then be analysed to recover the patterns and trends associated with them. The determination of the risks and issues around the mobile banking services can then be detected in advance to implement the necessary security controls(Hassani, Huang and Silva, 2018).
One of the significant aspects is the customer service and assistance that can be offered using the mobile banking services and platforms. The customers wish to have the personalized learning experience through the mobile banking platforms. Also, there are a lot of customers that will make transition from the offline to the online and mobile banking modes of services. The trend will further expand in India and the use of Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence will be done to offer customer service. There are currently issues around customer service experience and there is enhanced discrepancy that is associated with the mobile banking services as shown in the graphs below.
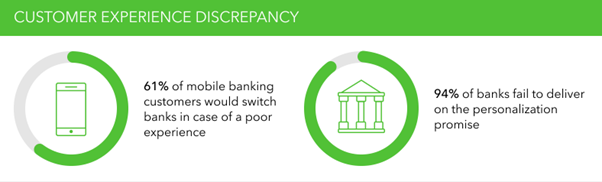
The use of ML and AI tools will assist in the development of chatbots and superior customer service experience so that improved personalization can be offered and the streamlined mobile banking services execution is possible(Chakraborty and Joseph, 2017).
There are security concerns that are also identified with the ATM transactions. There are tampering issues that are becoming common along with the cloning of the cards of the customers. The innovations in the mobile banking technology will assist in the promotion of cardless withdrawals. The assets of the customers will remain safe and protected from all forms of security attacks even in the scenario of ATM tampering.
Disruptor Tools
There are numerous disruptor tools that are expected to gain enhanced popularity and usage in the years to come. One of the primary trends that are being witnessed is the Blockchain technology and tools. The Blockchain technology is a distributed and decentralized public ledger. The use of the Blockchain tools can be done in the mobile banking sector in the years to come in order to avoid the network and data security issues and attacks. The use of the Blockchain networks will be done in the years to come by the banks to safeguard the cashless transactions (Martino, 2019). These tools will include the use of Blockchain technology that will have cryptographic hash functions implemented to avoid the forging and unauthorised access.
As stated earlier, there are other technology tools that will be used and implemented to disrupt the mobile banking services. The use of Big Data tools along with the AI and ML tools will be commonly seen in the years to come. These will assist in further automating the mobile banking services that are executed. The overall integration and execution of the mobile banking services will become easier with the aid of the technology.
Conclusion
Mobile banking has made considerable changes in the banking services and financial transactions that are conducted. There are increased mobile banking applications and services that are now developed and implemented in India. As per the trend, it is observed that the increase in the mobile banking customers will be witnessed in the years to come. There are some of the emerging technologies that will be promoted in the mobile banking services. These will include the Blockchain technology, Big Data, Artificial Intelligence, and Machine Learning. The use of these technologies will assist in controlling the security and privacy issues.
References
Al Asheq, A., Uzzal Hossain, Md., Akhter, A. and Mobarak Karim, Md. (2020). Exploring customer intentions to adopt mobile banking services: evidence from a developing country. Banks and Bank Systems, 15(2), pp.105–116.
Bryson, D., Atwal, G., Chaudhuri, H.R. and Dave, K. (2015). Understanding the Antecedents of Intention to Use Mobile Internet Banking in India: Opportunities for Microfinance Institutions. Strategic Change, 24(3), pp.207–224.
Chakraborty, C. and Joseph, A. (2017). Machine Learning at Central Banks. SSRN Electronic Journal.
Hassani, H., Huang, X. and Silva, E. (2018). Digitalisation and Big Data Mining in Banking. Big Data and Cognitive Computing, [online] 2(3), p.18. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/2504-2289/2/3/18/pdf [Accessed 25 Sep. 2019].
Irma (2015). Banking, finance, and accounting?: concepts, methodologies, tools, and applications. IT management assignment Hershey, Pa: Business Science Reference, An Imprint OfIgi Global.
Martino, P. (2019). Blockchain technology: challenges and opportunities for banks. International Journal of Financial Innovation in Banking, 2(4), p.314.
Rbi (2014). MOBILE BANKING REPORT OF THE TECHNICAL COMMITTEE RESERVE BANK OF INDIA. [online] Available at: https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/PublicationReport/Pdfs/TMB070214BF.pdf [Accessed 12 Oct. 2020].
Securitymagazine (2020). Indian e-Payments App Exposes More Than 7 Million Users in Massive Data Breach. [online] www.securitymagazine.com. Available at: https://www.securitymagazine.com/articles/92495-indian-e-payments-app-exposes-more-than-7-million-users-in-massive-data-breach [Accessed 12 Oct. 2020].
Sharma, M.A. and Joseph, J. (2017). The Impact of Mobile Banking on Financial Performance of Banks in India. SSRN Electronic Journal.
Sheerin, A. (2019). Cashless Economy in India: Challenges and Opportunities. SSRN Electronic Journal.
Stephan, A., Lakshmi, P. and Kalaiarasi, H. (2017). Adoption of self service banking channels - the case of mobile banking in India. International Journal of Business Information Systems, 26(1), p.1.












