Operations Management Assignment: A Case Study Of Lidl Barking
Question
Task:
Prepare a well-researched operations management assignment on the topic “Change of business strategy due to COVID-19: A Case study of Lidl Barking, London”.
Answer
Abstract
Topic, Research Questions and Significance:The topic of this research on operations management is “Change of business strategy due to COVID-19: A Case study of Lidl Barking, London”. It aims to answer the questions regarding the impact of COVID-19 on Lidl Barking’s business operations. It also tries to find out the challenges faced by Lidl Barking due to COVID-19 and strategies used to adapt to the changes brought by it.
Methods:The descriptive design is chosen for the data collection along with interpretivism philosophy. Moreover, the inductive approach and the qualitative strategy was used to conduct an interview among five employees of Lidl Barking at London, who were asked five open-ended questions. It was analysed by adequately evaluating the overall interview data and making the data credible and valid.
Results: It is obtained from the answers of the Lidl Barking employees to the interview questions that communication reduced between the higher authorities and the employees and customers, which reduced overall profit. Customers not following the COVID-19 safety guidelines and weak transport system weakened the supply chain creating challenges. The demand of customers fluctuated largely, while few got a large number of items and others returned empty-handed. Lack of essential goods at Lidl Barking dissatisfied the customers and strictness of the COVID-19 safety rules. Lidl Barking implemented sneeze proof checkout screens, disinfectants at the stores and offered free mask to adapt to the pandemic situation.
Conclusion: From the collected data, it can be concluded that through data collection, the researcher was able to meet the aim and objectives and answer the research questions to make the whole paper successful.
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1 Background and Research Rationale
From the onset of COVID-19 at the end of 2019 and its rapid spread in all the corners of the world in the first quarter of 2020, changes have come in every aspect of life. Businesses around the world came to a standstill, and the economy fell (Cummins et al., 2020). Even in the UK, the retail sector faces its negative effect. In contrast, due to dealing with essentials, this sector was able to continue its operations. However, it has to bring many changes compared to the normal operations of retail firms to adapt to the situation brought by COVID-19 for the safety of the consumers as well as the employees working there (Sayyidaet al., 2021). Due to the relevance of the factors to the current situation, this topic was chosen for research.
1.2 Aim
The aim of the research is to evaluate the changes happening in the strategy of business operations due to the impact of COVID-19. The company chosen for this dissertation is Lidl Barking which operates in London, UK.
1.3 Research Objectives
- To determine the impact of COVID-19 on the business operations of Lidl Barking
- To identify the challenges faced by Lidl Barking due to COVID-19
- To assess the strategies used byLidl Barking to adapt to the changes brought by COVID-19
1.4 Research Questions
- What is the impact of COVID-19 on the business operations of Lidl Barking?
- What challenges are faced by Lidl Barking due to COVID-19?
- What are the strategies used by Lidl Barking to adapt to the changes brought by COVID-19?
1.5Literature Gap
In the previous literature sources about the topic of the impact of COVID-19 on the business operation of a retail company in the UK, there is not much information about the influence it has created in the business processes. Moreover, it lacked information about the challenges the companies have to face while conducting their business operations. It did not contain data about the strategies those companies are using to adapt to the changes, which are considered the gaps of the researches (Kim, 2020). Through the conduction of the research, the researcher has tried to fulfil those gaps and find answers to the research questions.
1.6 Methodology
In order to collect data for this research, an interview session was conducted among five employees who are working in Lidl Barking in London. For the data collection, the descriptive design was chosen, followed by an inductive approach (Azungah, 2018). Moreover, the interpretivism philosophy and qualitative strategy were chosen to collect primary data from the survey (Ryan, 2018). It was analysed using the analysis tool of evaluating the overall responses while following the research ethics (Bansal, Smithand Vaara, 2018). The chosen methods and the reason behind their selection are given in the “methodology and methods” chapter, which aided in meeting the aim and objectives.
1.7 Research Structure
Figure 1: Structure of the Dissertation
(Source: Created by Author)
Chapter 1- Introduction: This chapter consists of the background and rationale of the dissertation, along with the aim, objectives and research questions. The literature gap, methodology, limitations, ethical concerns and structure of the research is also part of it.
Chapter 2- Literature Review:This chapter consists of the theoretical and conceptual framework.
Chapter 3- Methodology and Methods: The research rationale, philosophy, approach and strategy are part of this chapter, along with sampling, data collection and analysis method. It also consists of information related to validity and credibility, apart from the limitations.
Chapter 4- Findings: The data obtained from the collection is mention and analysed in this chapter to reach a result.
Chapter 5- Conclusions: It consists of the concluding findings of the research, which is linked with the objectives. Few recommendations are given along with future research scope.
1.8 Limitations and Ethical Concerns
There are certain limitations that are faced by the researcher during the conduction of this research. Due to the limited amount of fund and time, it was not possible to conduct a survey among the employees, which would have provided the perspective of them towards changes in the retail sector of the UK brought by COVID-19 (Paradice et al., 2018). While conducting this research, the Data Protection Act, 2018 was followed along with the guidelines provided by the university to maintain authenticity and keep it valid. Apart from that, while conducting primary research, none of the participants was forced to take part or answer the questions (Weinhardt, 2021). Moreover, the collected data is stored in the personal device of the researchers to keep it safe from the third party.
Chapter 2: Literature Review
2.1 Effect of COVID-19 on the Operations of Businesses Functioning in the Industry of Retail in the UK
As per the perception of Kim (2020), the outbreak of COVID-19 has vastly impacted the business operations of the industry of retail in the UK. The pandemic has transformed the operations carried out by retail companies of the country. Several changes can be determined in the operations carried out by retail organisations operating within the market of the UK. As per Seetharaman (2020), the operations related to the business of the UK retail firms were affected by the pandemic. Retail companies were unable to operate during the pandemic. The government of the UK has ordered lockdown throughout the country after the outbreak of COVID-19. The organisations operating within the retail industry were forced to close their operations due to the lockdown in the country. Different retail organisations have changed their business operation strategies after the pandemic. Pantanoet al. (2020) also added that the government of the country had closed all the operations, which has created problems for the employees working in the retail industry of the UK. Customers were unable to visit the stores, as they were informed to stay at home by the government.
Moreover, the options regarding transportation were not available during the pandemic, which has affected the employees. The staffs of retail companies in the UK were unable to operate during the pandemic. Sayyidaet al. (2021) mentioned that firms that are functioning within the retail industry had changed their operations due to the pandemic. Different organisations are providing online services to their consumers. The consumers of the retail companies are gaining an opportunity to order from their home. The demand for unnecessary goods has also changed in the country due to the outbreak of COVID-19.
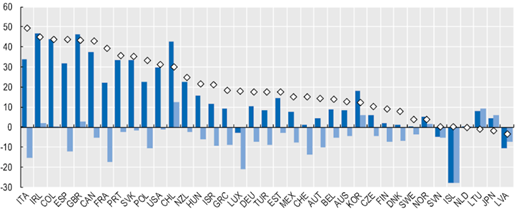
Figure 2: Change in Demand of Non-essential and Essential Retail Goods during Pandemic
(Source: OECD, 2020)
The above graph evaluates the changes in demand of consumers towards the products of retail companies. The changes have been identified among the consumers due to the pandemic. It has also been determined from this graph that the change has been identified in most of the countries. The changes in demand of consumers towards the products have changed as per their necessity during the lockdown in those countries. As mentioned by Cummins et al. (2020), several firms have started to provide home delivery for their consumers. The lack of employees for delivery of products was another challenge faced by the UK retail firms. It has impacted the operations of these firms at that time.
According to the study of Goswami and Chouhan (2021), a vast number of individuals working as employees of the retail industry have lost their jobs due to the pandemic. It has increased the economic problems of these employees. The business operations of the retail companies functioning in the UK have changed due to the pandemic. The number of employees has reduced in these companies. As mentioned by Loske (2020), the reduced number of employees have impacted the operations of these companies during the pandemic. The number of the customer base has reduced during that time, which has minimised the profits of retail organisation functioning in the UK. The sales of non-food products in the country’s retail market has reduced by twenty-three per cent due to COVID-19. Non-essential activities of retail companies have been reduced due to the pandemic. The shortage of labour is another problem that is being faced by the retail companies operating within the UK. Chowdhury et al. (2020) also added that the operations of retail companies regarding marketing have changed due to the pandemic. Most of the firms are focusing on “digital marketing” strategies to attract customers and retain them. These companies have also changed their operations of marketing to improve loyalty among consumers. The changes in operations due to the pandemic have impacted the retail industry of the UK.
2.2 Challenges Faced by Retail Companies of the UK due to COVID-19
In the study conducted by Hobbs (2020), it has been mentioned that there have been unpredictable or unforeseen changes that ushered in due to the spread of COVID-19, which has negatively impacted the functioning of the UK supermarkets. As per the research of Bretas and Alon (2020), it has been stated that in the blink of an eye, there came about noticeable changes in the buying behaviour of the customers, increased or unprecedented demands for basic commodities or their hoardings have led to innumerable challenges faced by supermarkets operating within the UK. As per the research carried out by Atmaret al. (2021), it has been found out that one of the initial challenges that were encountered by the UK supermarkets was the concern over the supply of essential products adequately to the customers. When there was news about the national lockdown due to the outbreak of the virus, there was panic among the customers, which led them to rush to the supermarkets and get hold of the essential items in bulks, which led to a shortage of essential commodities across the place in no time. In the study of Sharma, Adhikary and Borah, (2020), it has been claimed that the supermarkets in the UK were unable to make arrangements for the availability of such goods for the rest of the customers that led to increasing dissatisfaction and frustration among them. Managing the increasing needs or demands of the customers were becoming increasingly difficult for these supermarkets who were in no position to tackle these overnight problems. Procuring goods to make them available to the customers was also a major challenge as there were not enough staffs available at the stores. Supporting the above-mentioned claim, Sulaiman, Ahmed and Shabbir, (2020) further added that besides this scarcity of essential items, there were other associated challenges like constantly disinfecting the commodities and maintaining safe distance amongst all the employees working in the supermarkets, which led to an added effort of bringing about change in the physical layout of the stores. Transportation of goods was also problematic during the times of COVID-19 as there was a shortage of available vehicles to transport items. Employee motivation was also a concerning issue for the supermarkets as the employees were faced with job insecurity. There has also been the shutting down of many physical stores in the UK, which led to massive job loss and also negatively impacting the revenue of the businesses. In the study undertaken by Untaru and Han (2021), it has been found out that those employees who were retained by the companies during the times of the pandemic faced a major issue of transportation as there were restrictions on travels and there were not enough vehicles available to reach home. This was also a major challenge the companies faced while arranging proper transportation for these employees to safely drop them to their destination. Large gatherings in the physical stores by the customers to buy essential goods were becoming challenging for the retail companies to maintain safety standards. Delivering goods to the consumers were increasingly difficult as there were not adequate employees available who could deliver the commodities. Challenge was also encountered while doing sensible short-term planning due to the evolving new guidelines as well as the changing intensity of the situation. As has been critically observed by Didieret al. (2021), it has been found out that there was also an issue related to constraints in the cash flow due to the crisis caused by COVID-19. Some of the retail companies also went bankrupt during the pandemic, and many employees lost their job in the process, which took a toll on the psychological health. Through the study of Roggeveen and Sethuraman (2020), it has been found out that there were also major operational challenges that were encountered by the retail companies in the UK like not having adequate preparedness to carry out work from home, inefficient or insufficient IT tools, inadequate IT infrastructures or saturated internet connectivity. Many employees were also not keeping well during the time, which led to another challenge like slow delivery of services at the stores or inefficient overall management of the performance of the store.
2.3 Strategies implemented by Retail Companies of the UK to improve their Operations related to Business
According to the study put forward by Liet al. (2020), it is stated that in order to respond to the new challenges posed by the global pandemic, there are some effective strategies implemented by the retail companies in the UK in order to improve their operations associated with their business. In the study of Untaru and Han (2021), it has been found out that to cope with the unique situations, strategies like regular use of disinfectants to keep the stores safe from contamination and keeping it clean for the customers as well as the working employees is one of the significant strategies adopted by the supermarkets to improve their business operations and attract customers. As per the perception of Fabeil, Pazim and Langgat, (2020), it has been claimed that there is also the adaptation of selling products through the digital platforms to fulfil the online orders as the trend suggests that the customers are still opting to stay home and have their commodities delivered at their doorstep. This strategy of e-commerce effectively helped in increasing the online sales of the products.
In the study of Chowdhuryet al. (2020), it has been put forward that marketing through the digital platform has helped in keeping the businesses active and engaging with the consumers by reaching out to them to inform them about the latest products as well as stock availability of essential goods. Another effective strategy that has been adopted is the shift in the product lines in order to meet the growing demands like launching new products that hint at safety or valuable at the time of pandemic grabbed the attention of the customers and influenced their buying behaviour. Slightly turning down the cost of essential commodities and providing discounts has also proved to be a successful tactic to attract customers and enhance the operations of the business. This has led to improvement in the level of loyalty among the customers as well as satisfaction. To keep the employees motivated throughout the tenure, there was an emphasis on effective and continuous communication, adequate breaks in-between works to relax, as well as keeping a record of both their physical and psychological health so that they can serve the customers well is another strategy that has been adopted by the retail companies in the UK to enhance their operations associated with the business. Adopting the strategy of triggered alerts have resulted in bringing about benefits and positive outcomes, which helped in notifying the customers about the products in need in real-time.
As observed by Goddard (2020), it has been claimed that another effective strategy has been personalising the experiences of the customers through emails with intense discounts, which made previous purchases or are very likely to make new purchases with the company. This helped in keeping blasts highly relevant in accordance with the consumers’ recent activities. As per the research of Pantanoet al. (2020), it has been put forward that providing masks and sanitisers to the visiting customers to the stores have also helped in improving the operations of the business as the consumers felt satisfied with the safety guidelines being strictly followed in the physical stores to maintain health measures. It has been brought forth in the study by Kristinaeet al. (2020) that developing effective partnership with the influencer marketing has resulted in a positive outcome as it helped in spreading positive word-of-mouth among the customers through the feedbacks and positive recommendations by the influencers who acted as a proof for their followers. Trust building is one of the essential element for any company operating in the digital space, which equally holds true in the case of the retail companies in the UK who took recourse to digitalisation. The influencers can help these companies to operate efficiently on the online platforms through influencing the purchasing behaviour of their followers positively by providing them with adequate knowledge about the products.
2.4 Conceptual Framework
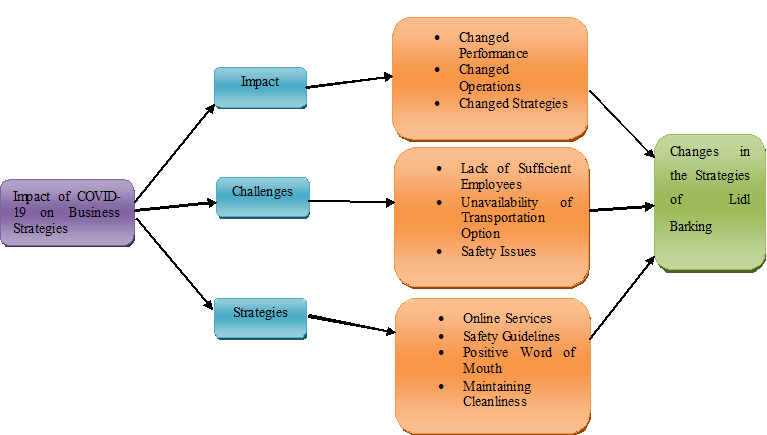
Figure 3: Conceptual Framework
(Source: Created by Author)
It has been identified from the above figure that COVID-19 has drastically affected the growth of Lidl Barking operating in London. It has impacted the organisation and its operations. The profitability has also changed due to the pandemic. Moreover, the operations of the organisation have also changed due to the outbreak of COVID-19. The strategies of the organisations regarding operations have also changed after the pandemic. It has increased different challenges for the company, as it has to change the operations. The lack of employees is one of the challenges that the organisation has faced due to the pandemic. The unavailability of employees is one of the problems for this organisation. Furthermore, the pandemic has also affected the operations of this organisation, and it has increased problems. Various strategies have been implemented by the organisation to improve growth during the pandemic. The company is providing online strategies to improve growth in the market after the pandemic. Furthermore, safety guidelines have also been implemented by the company to improve growth and make employees safe. Another strategy is the maintenance of cleanliness and sanitisation of the firm. These strategies have changed the operations of the organisation during the pandemic.
Chapter 3: Methodology and Methods
3.1 Research Design
In this research study, the descriptive design is chosen from the different types of designs. The descriptive design helped in analysing the perspective of the employees regarding the changes brought by COVID-19 in the business operations of the chosen company Lidl Barking Branch in London (Siedlecki, 2020).Moreover, using the descriptive design, it was possible to give a structure to the research, which helped in finding the challenges faced by retail companies like Lidl in London (Kim, H Sefcikand Bradway, 2017). Along with that, through the use of this descriptive design, the strategies implemented by Lidl in London to cope with the situation and adapt to it can be understood.
3.2 Research Philosophy
In order to collect proper information for this research, the interpretivism philosophy has been chosen. The naturalistic type of the data obtained from the interview makes the selection of interpretivism the right selection for the research paper (Alharahshehand Pius, 2020). Interpretivism philosophy, when used in the collectionof primary data from the interview, helps in reachingthe meaning at the end of the research. This philosophy has helped in meeting the objectives of the paper, which includesfinding out the impact of COVID-19 faced by the companies in the retailsector of the UK, focusing on Lidl. Moreover, the challenges this company has faced due to COVID-19 restrictions are determined with the help of interpretivism (Zahle, 2021). Along with that, it hasalso helped in determining the strategies of adapting to the changes brought by COVID-19 in the operations of the retail companies.
3.3 Research Approach
The research approach which is chosen for this research is the inductive one, as there are three objectives present in the first chapter of the paper, which is to be met through the research. The inductive approach enabled the researcher in developing a theory by reaching a result at the end of the research (Azungah, 2018). In this paper, the inductive approach has guided the researcher in getting an idea of the impact created by COVID-19 on the UK retail sector, and for understanding it well, the focus was given to Lidl, which operates in the country. Moreover, using the inductive approach, it was made possible to identify each of the small and big challenges which are faced by the retail companies, including Lidl in the UK (Woo, O’Boyle and Spector, 2017). Finally, the inductive approach has helped in forming and knowing about the strategies of overcoming the challenges of COVID-19 and cope up through adapting with it.
3.4 Research Strategy
The qualitative strategy is used by the researcher for this research for gathering primary data from an interview among the customers of the chosen retail company in the UK, Lidl. With the use of this strategy, it was possible to gather data that is not quantifiable (Williams and Moser, 2019). The interview answers are descriptive in nature, and due to that, the selection of qualitative strategy is considered the most appropriate. This strategy has aided in understanding the issues faced by Lidl while operating in the retail sector of the UK after the COVID-19 pandemic situation in the country (Anderson, 2017).Along with that, the changes due to COVID-19 had impacted the way of operation of the company, which is finding the strategy. The strategies of overcoming the issues and adapting to the situation are also found using the qualitative approach.
3.5 Sample Size and Sampling Technique
In the research, the employees of the selected retail company in the UK took part in an interview, which is Lidl. The number of employees who were selected was five in number (Etikan and Bala, 2017). In order to reduce the bias of the answers of the employees, the purposive sampling method is used.
3.6Data Collection Method
In order to collect data for this paper, the interview process was selected. Five employees of the selected company Lidl Barking of London took part in the interview, which was conducted online through video conferencing, due to the COVID-19 measures taken by the country government (Archibald et al., 2019). Before conducting the interview, the participants were approached for their consent, and only after each of them willingly agreed to take part they were sent the five open-ended questions so that they can prepare for the final interview. The interview time was set according to the convenience of the selected participants (Hawkins, 2018). The collected primary data was stored in a personal laptop of the researcher, which was password-protected so that no third party have access to it. After using the data in the research and its submission at the university, it is destroyed after few months to protect its authenticity.
3.7 Data Analysis
After the collection of primary data through interview among the employees of Lidl Barking of London, it was analysed to get a result (Castleberry and Nolen, 2018). The interview responseby critical evaluation was considered the most suitable analysis method for analysing the interview data by creating a transcript and evaluating their responses in a significant manner. It helped in meeting the aim and objectives of the paper while answering the research questions as well, regarding issues faced by the UK based retailcompany Lidl Barking situated in London and the strategies they are implementing to cope with the situation and adapt accordingly (Nowell et al., 2017).
3.8Validity and Credibility
In this paper, the reason behind undertaking the study is described clearly in the part of the research rationale and the literature review, and the researcher had done so for academic purpose only. The research was solely funded by the researcher, due to which there is a shortage of it, which created a limitation (Cypress, 2017). Moreover, there is also a discussion about the way data is collected in the previous sections of this chapter, which is through an interview among the employees of the chosen organisation, Lidl Barking, London. The sample size mentioned above is enough for an interview, and also due to the monetary constraints, and the response rate was high, making the whole data collection process valid (Schmidt, 2017). The use of secondary data is only in the literature review section, and it is able to measure the challenges created by COVID-19 on the retail sector of the UK, increasing its credibility, though the findings cannot be generalised in this case due to different measures taken by the government related to the pandemic.
3.9 Research Ethics
While conducting the research, the researcher took the permission of the five employees regarding whether they have given consent to participate in the interview session. After they agreed willingly to participate in the interview session, they were approached with the interview questions through email. They were ensured that the personal data would not be used in the research paper (Dooly, Moore and Vallejo, 2017). Moreover, after collecting the data, it is stored in the personal device of the researcher, which is password protected and cannot be accessed by any other person. Finally, all the collected data will be deleted after six months of the submission of the paper. These measures will ensure that the Data Protection Act, 2018 is strictly followed along with the university guidelines.
3.10 Limitations
The limitations faced by the researcher while conducting the research are related to money and time, as both of those were extremely limited. It hampered the data collection to some extent, which acted as a barrier in the process (Ross and Zaidi, 2019). The availability of more time and money would have helped in conducting a survey among them and gettinga better perspectiveof the overall impact of COVID-19 and the way oftackling it.
Chapter 4: Findings
4.1 Interview Data Analysis
1. In your opinion, what are the effects of COVID-19 on the operations or business functions of your company?
Employee 1 stated that “We work in the retail sector, which mostly consists of things which are needed by people in their daily lives. However, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, people are afraid to come out of their home even for shopping for their essentials. Due to that, the amount of sales per month has steeply fallen after the pandemic hit the countries and the lives here came under threat.”
Employee 2 answered that “Due to COVID-19, it has become challenging for the employees to come to the office during the pandemic due to the fear of contamination of the COVID-19 virus. It is hampering the performance of the company to a large extent, and it has faced much loss during the year 2020, which is continuing in the first as well as the second quarter of 2021.”
Employee 3 has the opinion that “Unlike IT sector and other few sectors, it is not possible for retail companies like Lidl Barking to make us, the employees work from home. Moreover, it requires human interaction, even if it is comparatively less. COVID-19 has made it hard to constantly communicate with the customers and higher authorities, which has slowed down the processes, resulting in loss throughout the year of 2020.”
Employee 4 mentioned that “In my opinion mostly affected part of our retail company is its supply chain. Due to the cancellation of international flights and many other means of transport, it has become impossible to get the delivery of the goods at the right time, and due to that, the stores of Lidl are running out of stock. As a result, the customers are becoming dissatisfied with the service of the company, which is reducing their loyalty towards it.”
Employee 5 said that “Due to the ban in going outside the home without emergency, people are choosing to shop from those companies, which offers online services and home delivery. It is increasing the expenditure of our company compared to the profit it is gaining.”
From the replies of the employees to the question, it can be understood that the number of customers of Lidl has reduced in the UK due to the inefficient services of the company and its employees. The home delivery and online orders have increased the expenditure and brought down the total profit.
2. What are the challenges which your company faced due to the pandemic situation brought by COVID-19?
Employee 1 opined that “Not just the managers of our company, but the consumers too are facing numerous challenges. The greatest challenge was faced during the lockdown period of the UK when every shops and office were closed by the government to stop or slow down the spread of the deadly virus COVID-19. These shutting down affected the UK economy and our company negatively, bringing down the profit.”
Employee 2 replied that, “I consider the retail sector one of the worst-hit industries during the lockdown and other preventive measures taken by the government, which we are part of. The retail sector was likely to make better profits in the absence of the pandemic. However, due to the impact of COVID-19, our company has seennegative growth, rising from which is one of the toughest tasks for our company.”
Employee 3 mentioned that, “I think while trying to stop the loss of our company, our managers and other higher authorities were unable to make plans for growth. Therefore, it is becoming increasingly difficult for us to make plans for advertisements or promotions, which is one of the most effective paths for attracting new customers towards the company and grow.”
Employee 4 is support said that “During the onset of a pandemic when just like other countries, UK government announceda ban in going out of homes, apart from emergency services, people were extremely afraid by the uncertainty of the future. This has made them get panicked and started ‘panic buying’, which cleared out stock of goods faster than normal time. While the rest of the customers were unable to get their hand on the essential goods due to unavailability, which created chaos in our stores.”
Employee 5 was of the opinion that “We were not accustomed to stockpiling of certain essential goods by the customers. Moreover, due to panic buying, the stock was finished fast, which forced us to drop our prices to keep the competition with our rivals strong.”
From the interview answers, it can be found that the shutting down of shops at the onset of the pandemic, COVID-19, one of the worst-hit was the retail sector. The promotional strategies formation came to a halt, and people started panic buying and stockpiling. Due to that many of the customers have to return empty-handed from the shops, making them dissatisfied.
3. Have you noticed changes in the demand of customersfor essential and non-essential goods?
Employee 1 mentioned that “We have seen great changes in the demand of the customers since the pandemic hit our country and the world. One of the positive response from the side of the customers has brought us a title. Due to the rising amount of online shopping by the customers in the last one year after the pandemic, we have performed well and crowned as ‘Supermarket of the Year’ in 2021, keeping behind retail giants Tesco, Sainsbury’s and Aldi.”
Employee 2 had replied that “In contrast to my colleague, I would like to say that we have to go through a rough time regarding demand of customers at the start of the pandemic COVID-19 when the demand for many of the non-essential items faced downfall. We have stocked in those items predicting the future demand, but we had to face loss due to the pandemic.”
Employee 3 answered the question that, “We were planning to grow our business, and due to that, the head officials have added as many as 51 stores during 2019-2020. Moreover, we have also established a new warehouse in the same year in the hope of expansion and reaching out to more customers, which was not possible due to COVID-19 and the measures taken due to it.”
Employee 4 is of the opinion that “I agree with my colleague, and would like to add that apart from opening new stores, we had increased our workforce in the UK by almost eight per cent, by adding 1800 employees before the pandemic hit the country.”
Employee 5 has said that “I would like to mention the positive side of the lockdown measures taken by the UK government. During the second lockdown across the nation, the demand for the products and goods of our supermarkethad seen a steep surge, wherethey spent almost 1 billion Euro more than usual just for foods and drinks when it is compared to the same time in the last year.”
From the answers to the question above,it is clear that there have been a downfall and high-rise both in Lidl after it is hit by the pandemic COVID-19. People feared going out, and it brought down the total sales and profit of the company. On the other hand, when the lockdown measures became loose, then there was a steep rise in the demand for everyday food items and drinks, helping the company to recover from its loss faster.
4. What is your opinion regarding the satisfaction of customers in your services during the COVID-19 pandemic?
Employee 1 said in reply, “In my opinion, at the beginning of the pandemic, people with less awareness of the virus and the fatality it can cause were acting either very carelessly or completely stopped going out of their house. In such a situation, it was not possible for us to keep all the customers satisfied at the same time.”
Employee 2 opined that “I agree with my colleague, and as a responsible citizen of the UK and the employee of Lidl, we were not allowing them to enter the stores without a mask and sanitising them. Many of our customers coming for the shopping of essential items disagreed with this rule and did not wear masks, and we forced them to leave, making them dissatisfied.”
Employee 3 stated that “We have requested our customers to come in our stores alone for shopping unless it is essential. While this was seen as a responsible decision from our side by many of our customers, some of them were dissatisfied with it.”
Employee 4 replied that “For making the shopping process more convenient for the customers and hassle-free, we increased the use of contactless payment and the payment limit too. This was one of the changes in our services, which were liked by the major section of our existing and new customers.”
Employee 5 mentioned that “In order to keep our customers satisfied, we replenish all the items every day, without delay to support the vulnerable and the ones who want to buy the goods for being ready.”
From the answers, it can be understood that the employees were not able to keep each of the customers satisfied with their service, mostly during the start of the pandemic situation.However, gradually with more understanding among the customers, they started following the rules and were highly satisfied with the services Lidl employees provided to them.
5.What strategies have you implemented in Lidl to improve your operations and adapt to the pandemic situation?
Employee 1 said that “Lidl is one of the few companies which was ready with the necessary measures after the pandemic hit the country. For reducing the spread of the coronavirus, we tried to ensure that there are a few customers as possibleat our stores through maintaining social distancing. They are requested to handle only the items they intend to buy, to reduce the spread of the virus.”
Employee 2 replied to the question that, “For keeping our customers and all the residents of the UK safe from the coronavirus, we made it mandatory for everyone entering our stores to wear a mask. However, when any of them are not doing that, we are offering them free masks at the entrance to continue shopping without any hesitance.”
Employee 3 was of the opinion that “Even in our bakery, for making sure the foods are untouched by hands, tongs are kept along with disposable gloves. Moreover, the section of the bakery is currently closely monitored by us to keep everyone safe. Our colleagues who are unable to use face masks have been provided with visors to protect others.”
Employee 4 said, “The screens at the checkout, which were installed after the pandemic, was cough and sneeze proof, which helped in protecting both of our colleague and customers. In order to order to ensure that the item at the store is clean from virus, antiviral disinfectant is used to clean them after each use, while the customers and colleagues alike are provided with hand sanitiser to keep their hands’ virus-free.”
Employee 5 stated that “We make sure to check the temperature of the customers coming at our stores. Additionally, if they have a new or continuous cough, we request them not to come to our stores, and the same goes for high temperature. In case the customers coming to our stores do not have the sense of taste or smell, then they are not permitted to enter our shops.”
From the answers of the employees of Lidl Barking in the UK, it can be understood that Lidl is taking all the necessary preventive measures to make sure that its customers are able to shop fearlessly at the stores and online as well. From providing free masks to sanitising while entering, requesting the existing customers to handle just what they need, checking the temperature at the entrance to not permitting entry to those having cough or sneeze- all the measures are helping the company to sustain during the pandemic. It will help the company to continue its business well even after the COVID-19 subsides and everything becomes normal.
4.2 Findings and Discussion
COVID-19 Impacting Lidl Barking’s Business Operations
In the literature review, it is found that there has been a great change in the retail sector of the UK due to the pandemic situation. Lockdown measures were taken by the UK governmentto stop the deadly virus from spreading (Goswami and Chouhan, 2021). Companies in the retail industry arethe ones whose operationswere mostly affected by it. The transportation in the country was restricted, which made it impossible to replenish the stocks regularly. On the other hand, in the findings section from the answers of the employees in the interview, it is found that the communication among the workers of each level of the company Lidl was hampered due to lack of physical presence. The expansion strategy taken by Lidl faced drawback due to the pandemic, and even after employing a large number of employees in 2019-2020, they have to lay off many, which is considered one of the greatest negative impact created by COVID-19.
Challenges Faced Due To COVID-19 by Lidl Barking
The literature review section contains information about the challenges which retail companies in the UK face due to COVID-19. On the one hand, the customers are afraid to visit the stores and opting for those companies which offer home delivery of essential goods (Sharma, Adhikary and Borah, 2020). Moreover, the necessary measures taken by the retail companies to stop the virus is not satisfactory for many of the customers, which is hampering the business of the company. It is found from the interview session that while keeping an eye on sustaining in the market during the pandemic without facing loss, Lidl is unable to plan for advertising and promotion of the company, which could bring in more new customers. On the other hand, due to the fear of unavailability of the essential goods, people started ‘panic buying’ at the start of the pandemic, due to which the customers unable to get a hand on those goods returned unsatisfied with the company.
Adapting Strategies to COVID-19 Implemented by Lidl Barking
In the literature review, Untaru and Han (2021) mentioned thatin order to keep the retail stores safe from the virus, disinfectants are used multiple times per day. Moreover, many retail companies started using digital marketing platforms to reach out to customers in the tough time, which helped them to sustain the pandemic. The companies have focused more on communicating with the customers to retain them even during the pandemic to become future sustainable. From the interview session with the employees of Lidl, it is found that Lidl installed sneeze and cough proof checkout screens and allowed touchless payment options to reduce the chances of contamination among the employees and customers. Moreover, they were requested to wear a mask and sanitise while shopping at the Lidl stores for ensuring the safety of all.
Chapter 5: Conclusions
5.1 Conclusion
The research aims to evaluate changes in the business operations strategy of Lidl Barking in London, UK, due to the pandemic COVID-19. It has the objective to find out the impact on Lidl Barking’s operations due to COVID-19, the challenges faced by them and the strategies implemented to adapt to the COVID-19 situation. In order to meet the objectives and answer the research questions, apart from gathering the perception of different authors in the literature review section, primary data was collected through an interview among five employees of Lidl Barking. The descriptive design, interpretivism philosophy, inductive approach and qualitative strategy were used for collecting that information through five interview questions, which are then analysed using the tool of evaluating the transcript while keeping the whole process valid and credible.
5.2 Discussion of Findings
From the data collected, it can be understood that both the employees and the customers of Lidl Barking were affected by COVID-19, which hampered the overall performance of the company. The company faced losses and were unable to expand and promote itself, which can be considered few challenges Lidl Barking has to face. The demand of the customers went through changes; while some bought in bulk for storage, many others did not get the chance to get a hand on the essentials goods at all. This led to dissatisfaction of the customers, while a section of them was irritated due to the strict safety measures implemented by Lidl Barking. In order to improve operations, cough and sneeze proof checkout screens, monitoring the bakery section, and social distance maintaining are some strategies used by Lidl Barking to adapt to the pandemic situation.
5.3 Linking with Objectives
5.3.1 COVID-19’s Impact on Lidl Barking’s Business Operations
Due to COVID-19, the UK government ordered for complete lockdown, and the retail companies had to stop their operations as the employees were unable to visit their workplace due to scarcity of transport (Pantanoet al.,2020). From the findings, it is known that it is not possible for Lidl Barking employees to work from home, unlike the IT sector, and the communication became weak while the supply chain was broken.
5.3.2 Challenges Faced ByLidl Barking Due To COVID-19
The national lockdown announcement led the customers to buy essential commodities in bulk, which made it impossible to serve all, leading to their dissatisfaction (Roggeveen and Sethuraman, 2020). People creating crowd at those stores created a challenge for the employees to maintain safety standards. The findings show that there has been a decline in the profits of Lidl Barking due to the increased expenditure for maintaining safety measures from COVID-19 and the lack of promotional strategies.
5.3.3 Strategies of Lidl Barking For Adapting To Changes Brought By COVID-19
Disinfectants were used by the retail stores of the UK to keep the stores, theiremployees and customers safe from COVID-19 contamination. Bringing down the cost of essential communities was a successful effort of these companies (Chowdhury et al., 2020). Lidl Barking made its checkout screen sneeze and cough proof, made face mask mandatory for employees and customers and provided hand sanitiser at the entrance.
5.4 Recommendations
5.4.1 Making Special Transport Available Just for Employees
The employees of the retail companies who are unable to come to the stores on time or are absent due to the same reason should be provided with a transport system which will pick them up and drop them near their homes until the pandemic situation subsides (Eisenmann et al., 2021). It will help in reducing turnover of employees and satisfaction of customers.
5.4.2 Improving Communication with Customers to Stock Items According to their Needs
Either stock of the retail stores got wasted or depleted due to panic buying and stocking by the customers. In order to smoothen the supply chain while maintaining a good relationship with the customers and the suppliers, the retail stores should communicate with them well and stock up as per the needs. It would reduce wastage and increase satisfaction (Britchenko and Bezpartochnyi, 2020).
5.5 Reflection
Through the conduction of the research, as a student, I was able to gather information regarding the issues faced by the retail companies in the UK due to the pandemic situation brought by COVID-19. Moreover, the strategies which the companies are using to cope with the situation and adapt to it are understood during this process of the research. It helped me to get a better overview of the overall situation of the retail industry in the UK, which will help me in the future to better manage the business processes in a retail store.
5.6 Contributions
The research will contribute to the better understanding of future students regardingthe condition of the retail industry during the pandemic of COVID-19. These retail stores in the UK are going through changes, which are large enough and have not been seen for a long time. The changes include facing new kinds of issues due to fear of contamination of the coronavirus. Moreover, the techniques they are applying to mitigate the issues and continue their operations normally are learned from the research, all of which can be considered the contributions of the paper.
5.7 Future Research Scope
In this research, few employees were taken for the interview, while with a greater amount of time and funds, it would have been possible to conduct an online survey among a greater number of employees. The future students have the scope to find out the challenges and mitigation techniques used by other retail companies in the UK and those operating in different other countries, making comparison possible.
Reference List
Alharahsheh, H. and Pius, A., (2020). A review of key paradigms: Positivism VS interpretivism. Global Academic Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences, 2(3), pp.39-43.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Husam-Alharahsheh/publication/338244145_A_Review_of_key_paradigms_positivism_VS_interpretivism/links/5effbc0245851550508a8ab9/A-Review-of-key-paradigms-positivism-VS-interpretivism.pdf
Anderson, V., (2017). Criteria for evaluating qualitative research. Human Resource Development Quarterly, pp.1-9.https://researchportal.port.ac.uk/portal/en/publications/editorial-criteria-for-evaluating-qualitative-research(86d7a124-a74d-402a-8cb2-d09dc342445c).html
Archibald, M.M., Ambagtsheer, R.C., Casey, M.G. and Lawless, M., (2019). Using zoom videoconferencing for qualitative data collection: perceptions and experiences of researchers and participants. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 18, p.1609406919874596.https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/1609406919874596
Atmar, H., Begley, S., Fuerst, J., Rickert, S., Slelatt, R. and Gi, M.T.P., (2020). The next normal: Retail M&A and partnerships after COVID-19.https://www.mckinsey.com/~/media/McKinsey/Business%20Functions/M%20and%20A/ Our%20insights/The%20next%20normal%20Retail%20M%20and%20A%20and%20 partnerships%20after%20COVID%2019/The-next-normal-Retail-M-and-A- and-partnerships-after-COVID-19-vf.pdf
Azungah, T., (2018). Qualitative research: deductive and inductive approaches to data analysis. Qualitative Research Journal.https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/QRJ-D-18-00035/full/html
Bansal, P., Smith, W.K. and Vaara, E., (2018). New ways of seeing through qualitative research.https://journals.aom.org/doi/full/10.5465/amj.2018.4004
Bretas, V.P.G. and Alon, I., (2020). The impact of COVID?19 on franchising in emerging markets: An example from Brazil. Global Business and Organizational Excellence, 39(6), pp.6-16.https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/joe.22053
Britchenko, I. and Bezpartochnyi, M., (2020). Optimisation of commodity stocks the enterprise by means of HML-FMR clustering. Financial and credit activity: problems of theory and practice, 3(34), pp.259-269.http://fkd.org.ua/article/view/215521
Castleberry, A. and Nolen, A., (2018). Analysis of qualitative research data: Is it as easy as it sounds?.Currents in Pharmacy Teaching and Learning, 10(6), pp.807-815.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877129717300606
Chowdhury, M.T., Sarkar, A., Paul, S.K. and Moktadir, M.A., (2020). A case study on strategies to deal with the impacts of COVID-19 pandemic in the food and beverage industry. Operations Management Research, pp.1-13.https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12063-020-00166-9
Chowdhury, M.T., Sarkar, A., Paul, S.K. and Moktadir, M.A., (2020). A case study on strategies to deal with the impacts of COVID-19 pandemic in the food and beverage industry. Operations Management Research, pp.1-13.https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12063-020-00166-9
Cummins, S., Berger, N., Cornelsen, L., Eling, J., Er, V., Greener, R., Kalbus, A., Karapici, A., Law, C., Ndlovu, D. and Yau, A., (2020). COVID-19: impact on the urban food retail system and dietary inequalities in the UK. Cities & Health, pp.1-4.https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/23748834.2020.1785167
Cypress, B.S., (2017). Rigor or reliability and validity in qualitative research: Perspectives, strategies, reconceptualisation, and recommendations. Dimensions of Critical Care Nursing, 36(4), pp.253-263.https://journals.lww.com/dccnjournal/Fulltext/2017/07000/Rigor_or_Reliability_and_Validity_in_Qualitative.6.aspx
Didier, T., Huneeus, F., Larrain, M. and Schmukler, S.L., (2021). Financing firms in hibernation during the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Financial Stability, 53, p.100837.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1572308920301406
Eisenmann, C., Nobis, C., Kolarova, V., Lenz, B. and Winkler, C., (2021). Transport mode use during the COVID-19 lockdown period in Germany: The car became more important, public transport lost ground. Transport Policy, 103, pp.60-67.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0967070X21000184
Etikan, I. and Bala, K., (2017). Sampling and sampling methods. Biometrics & Biostatistics International Journal, 5(6), p.00149.http://www.hmvelms.org/placement/admin/HUMANITIES/PSYCHOLOGY_1919.pdf
Fabeil, N.F., Pazim, K.H. and Langgat, J., (2020). The impact of Covid-19 pandemic crisis on micro-enterprises: Entrepreneurs’ perspective on business continuity and recovery strategy. Journal of Economics and Business, 3(2).https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3612830
Goddard, E., (2020). The impact of COVID?19 on food retail and food service in Canada: Preliminary assessment. Canadian Journal of Agricultural Economics/Revue canadienned'agroeconomie.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7264603/
Goswami, S. and Chouhan, V., (2021). Impact of change in consumer behaviour and need prioritisation on retail industry in Rajasthan during COVID-19 pandemic. Materials Today: Proceedings.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2214785320397583
Hawkins, J.E., (2018). The practical utility and suitability of email interviews in qualitative research. The Qualitative Report, 23(2).https://digitalcommons.odu.edu/nursing_fac_pubs/24/
Hobbs, J.E., (2020). Food supply chains during the COVID?19 pandemic. Canadian Journal of Agricultural Economics/Revue canadienned'agroeconomie, 68(2), pp.171-176.https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/cjag.12237
Kim, H., Sefcik, J.S. and Bradway, C., (2017). Characteristics of qualitative descriptive studies: A systematic review. Research in nursing & health, 40(1), pp.23-42.https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/nur.21768
Kim, R.Y., (2020). The impact of COVID-19 on consumers: Preparing for digital sales. IEEE Engineering Management Review, 48(3), pp.212-218.https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9076858/
Kristinae, V., Wardana, I., Giantari, I.G.A.K. and Rahyuda, A., (2020). The role of powerful business strategy on value innovation capabilities to improve marketing performance during the COVID-19 pandemic. Uncertain Supply Chain Management, 8(4), pp.675-684.http://growingscience.com/beta/uscm/4257-the-role-of-powerful-business-strategy-on-value-innovation-capabilities-to-improve-marketing-performance-during-the-covid-19-pandemic.html
Li, R., Zhang, R., Zhang, M. and Zhang, T., (2020). Investment analysis and strategy for COVID-19. Available at SSRN 3563300.https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3563300
Loske, D., (2020). The impact of COVID-19 on transport volume and freight capacity dynamics: An empirical analysis in German food retail logistics. Transportation Research Interdisciplinary Perspectives, 6, p.100165.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2590198220300762
Nowell, L.S., Norris, J.M., White, D.E. and Moules, N.J., (2017). Thematic analysis: Striving to meet the trustworthiness criteria. International journal of qualitative methods, 16(1), p.1609406917733847.https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/1609406917733847
OECD, (2020). Changes in demand of essential and non-essential retail products during pandemic. Latest News. [Online] available at: https://www.oecd.org/coronavirus/policy-responses/covid-19-and-the-retail-sector-impact-and-policy-responses-371d7599/ Accessed On: 10thApril, 2021]
Pantano, E., Pizzi, G., Scarpi, D. and Dennis, C., (2020). Competing during a pandemic? Retailers’ ups and downs during the COVID-19 outbreak. Journal of Business Research, 116, pp.209-213.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0148296320303209
Paradice, D., Freeman, D., Hao, J., Lee, J. and Hall, D., (2018). A review of ethical issue considerations in the information systems research literature. Foundations and Trends® in Information Systems, 2(2), pp.117-236.http://www.nowpublishers.com/article/Details/ISY-012
Roggeveen, A.L. and Sethuraman, R., (2020). How the COVID-19 pandemic may change the world of Retailing. Journal of Retailing, 96(2), p.169.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc7183942/
Ross, P.T. and Zaidi, N.L.B., (2019). Limited by our limitations. Perspectives on medical education, 8(4), pp.261-264. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40037-019-00530-x
Ryan, G., (2018). Introduction to positivism, interpretivism and critical theory. Nurse researcher, 25(4), pp.41-49.http://oro.open.ac.uk/49591/
Sayyida, S., Hartini, S., Gunawan, S. and Husin, S.N., (2021). The Impact of the Covid-19 Pandemic on Retail Consumer Behavior. Aptisi Transactions on Management (ATM), 5(1), pp.79-88.https://ijc.ilearning.co/index.php/ATM/article/view/1497
Schmidt, F.L., (2017). Beyond questionable research methods: The role of omitted relevant research in the credibility of research. Archives of Scientific Psychology, 5(1), p.32.https://psycnet.apa.org/doiLanding?doi=10.1037/arc0000033
Seetharaman, P., (2020). Business models shifts: Impact of Covid-19. International Journal of Information Management, 54, p.102173.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0268401220309890
Sharma, A., Adhikary, A. and Borah, S.B., (2020). Covid-19? s impact on supply chain decisions: Strategic insights from NASDAQ 100 firms using Twitter data. Journal of Business Research, 117, pp.443-449.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0148296320303210
Siedlecki, S.L., (2020). Understanding descriptive research designs and methods. Clinical Nurse Specialist, 34(1), pp.8-12.https://journals.lww.com/cns-journal/Fulltext/2020/01000/Understanding_Descriptive_Research_Designs_and.4.aspx
Sulaiman, M.A.B.A., Ahmed, M.N. and Shabbir, M.S., (2020). COVID-19 Challenges and Human Resource Management in Organized Retail Operations/Desafios del Covid-19 y la administracion de recursoshumanosenoperacionesminoristasorganizadas. Utopia y Praxis Latinoamericana, 25(SI 12), pp.81-93.https://go.gale.com/ps/i.do?id=GALE%7CA649682925&sid=googleScholar&v=2.1&it=r&linkaccess=abs&issn=13165216&p=IFME&sw=w
Untaru, E.N. and Han, H., (2021). Protective measures against COVID-19 and the business strategies of the retail enterprises: Differences in gender, age, education, and income among shoppers. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 60, p.102446.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0969698921000126
Weinhardt, M., (2021). Big Data: Some Ethical Concerns for the Social Sciences. Social Sciences, 10(2), p.36.https://www.mdpi.com/972248
Williams, M. and Moser, T., (2019). The art of coding and thematic exploration in qualitative research. International Management Review, 15(1), pp.45-55.http://www.imrjournal.org/uploads/1/4/2/8/14286482/imr-v15n1art4.pdf
Woo, S.E., O’Boyle, E.H. and Spector, P.E., (2017). Best practices in developing, conducting, and evaluating inductive research.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1053482216300365
Zahle, J., (2021). Interpretivism and Qualitative Research. In Stephen Turner and the Philosophy of the Social (pp. 202-220). Brill Rodopi.https://brill.com/view/book/edcoll/9789004449602/BP000015.xml
Appendix
Interview Questions
- In your opinion, what are the effects of COVID-19 on the operations or business functions of your company?
- What are the challenges which your company faced due to the pandemic situation brought by COVID-19?
- Have you noticed changes in the demand of customers for essential and non-essential goods?
- What is your opinion regarding the satisfaction of customers in your services during the COVID-19 pandemic?
- What strategies have you implemented in Lidl to improve your operations and adapt to the pandemic situation?












