Finance Assignment Evaluating Financial Performance of GlaxoSmithKline
Question
Task:
Finance Assignment Brief: Case Scenario
After several rounds of interview, you are successfully appointed as the CFO of the Company. The Company has enjoyed considerable success in recent years and the board of directors have decided to adopt a growth strategy by making further investment in their current production line and acquiring an existing company in their industry. As the newly appointed CFO of the Company, you are tasked to evaluate the performance of the Company and prepare a report to the board of directors with evaluation of the potential investment opportunities.
The first investment under consideration is to make further investment in their current product, which needs initial investment between £40,000,000 and £50,000,000 and has a life of 10 years. The finance department appraised some other similar investments before using different investment appraisal techniques.
At the same time, the Company plans to acquire another company in the same industry in the near future. However, the board of directors require more information for the potential target. You are tasked with the responsibility of identifying a potential target company and preparing a report to the board of directors justifying the choice of a target company and potential implications from mergers and acquisitions.
Required:
Suppose you are successfully appointed as the CFO for GlaxoSmithKline.
As the newly appointed CFO of your chosen company, you are required to write a report to the senior management team - fully referenced, and address the following:
Evaluate financial performance: Choose FOUR categories from the list of five categories of financial ratios below and use ONE financial ratio from each category to assess the financial health of your chosen company using past 5-year financial information:
a. Profitability
b. Efficiency
c. Liquidity
d. Financial gearing
e. Investment
Answer
1. Introduction
GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) selected in the present context of finance assignment is one of the biggest pharmaceutical organizations headquartered in the United Kingdom. The firm is known to discover, develop and distribute a wide range of branded human health products. The firm also has other operational headquarters present in the United States of America. It operates in more than 160 countries but most of the business of the organization originates in the USA, France, Germany, UK, and Japan. The company employees over 103,000 people divided between two divisions. The two divisions comprise pharmaceutical and consumer health care products of various brands. The pharmaceuticals sector of the firm is stated to generate over 85% of the firm’s total revenue (GlaxoSmithKline 2019). The top products sold by the organization include Seretide, Advair, and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). Various other drugs like Zentel, Pentosam, Tuberculosis drugs, Anti-Malaria drugs, and Anti-retrovirals are being produced by the organization in a considerable amount.
The firm states to have goodwill in the pharmaceutical market for its respiratory, HIV, immune-inflammation, and oncology medicines which have also helped it to diversify the portfolio. The firm has also tried to improvise its Research and Development programs by focusing on immunology, human genetics, and modernized technology which will help them to attend to the needs of the patients more effectively. The business was observed to gain overall revenue of £17 billion in the year 2019 that is much above the industry average. The company has prioritized to market its products in the USA and the Asia Pacific regions because of the considerable market growth observed in the past inferences (GlaxoSmithKline 2019). The report initiates with the introduction followed by the financial performance of the company where ratios are computed. The ratio projects a better profitability and efficiency however the liquidity and gearing is a hurdle that needs to be sorted by the management. The company is focusing on the acquisition of Sitara that will lead to major landmark in the field of medicine.
2. Evaluation of Financial Performance
Financial ratios are one of the best tools that can be used by the organization's management system, investors, and other stakeholders to analyse the business and make certain decisions for investment or management carefully (Zainudin & Hashim 2016). A detailed monetary analysis for the year 2016 has been presented by GSK in the financial reports. The analysis of the financial report will help the organization to define various trends and policies that are being utilized by businesses and at the same time compare it to its competitors. Further, the organization can also find the difference between the budgeted and actual values that have been spent by it to run the operations. The economic health of the business in accordance with the industry averages have been portrayed in various subsections which can be used by the firm to analyse the different values of the efficiency, profitability, liquidity, and equity ratios (Vernimmen 2017).
Ratio analysis
Ratio analysis is the mechanism through which the financial statement is analyzed and financial data are compared in terms of percentages. It gives an insight into the various parameter of the company such as profitability, liquidity, efficiency, and solvency. Comparing line items helps in providing a valid decision regarding the functioning of the company (Myskov & Hajek 2017). Though the method is prevalent and used for comparing line items it suffers from certain limitations.
- Ratio analysis depends on historic data and has no link with the future or present data. Therefore, predictions are made based on old data.
- It cannot be used to project a study between companies from different firms (Asiri 2015)
- It does not undertake external scenarios such as recession, inflation, etc.
Profitability
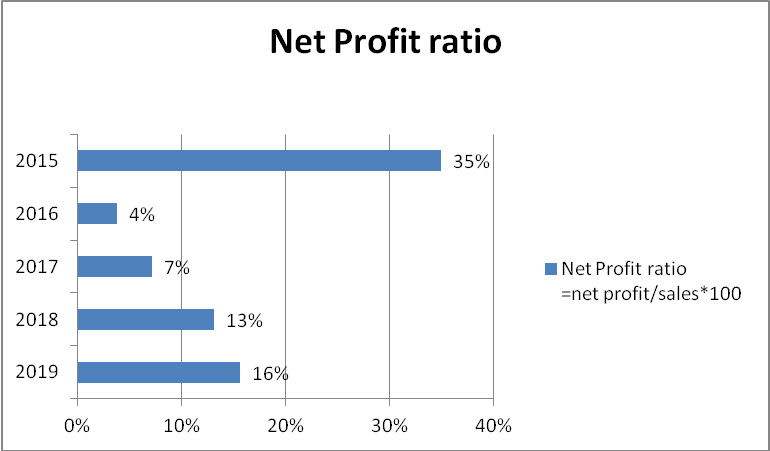
The net profit margin has been considered to analyze the profitability of GlaxoSmithKline. This denotes how much net profit has been generated concerning the revenue percentage (Asiri 2015). As seen from the study, the net profit of the company has shown a sharp reduction in 2015. From a level of 35% it fell to 4% in 2016 however after 2017 the net profit of the company has shown a better increment and in 2019 it stands at 16%. The reason for the increment in the profit is by dint of lower measurement charges on the contingent liabilities, enhanced profit on disposals, and increment in the value of shares in HUL (GSK 2019). In comparison to the net profit margin of Amgen, its major rival, the NPM stands at 33.2% which is significantly high. This means GSK is performing lower in comparison to the peer. Hence, these factors were the sole reason for the increment in the net profit indicating that the company has been able to post good numbers in terms of profits.
Efficiency
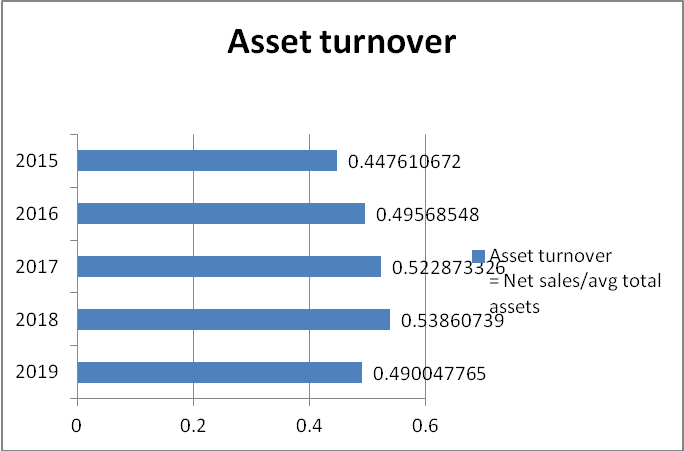
The efficiency ratio denotes the company’s performance to generate income by dint of the fixed resources. For GlaxoSmithKline, we are considering the asset turnover ratio to get an indication of the company’s efficiency. The ATO has remained on average of 0.40 to 0.50 indicating better utilization of assets for generating sales. The ATO of GlaxoSmithKline is 0.49 while its competitor has 0.41 indicating a better utilization of the assets. However, the industry average is 0.62 which means more efficient utilization is needed. The ratio indicates an optimal use of the assets whereby the increment in the level of the assets from 2018 to 2019 has brought favorable sales in 2019.
Liquidity
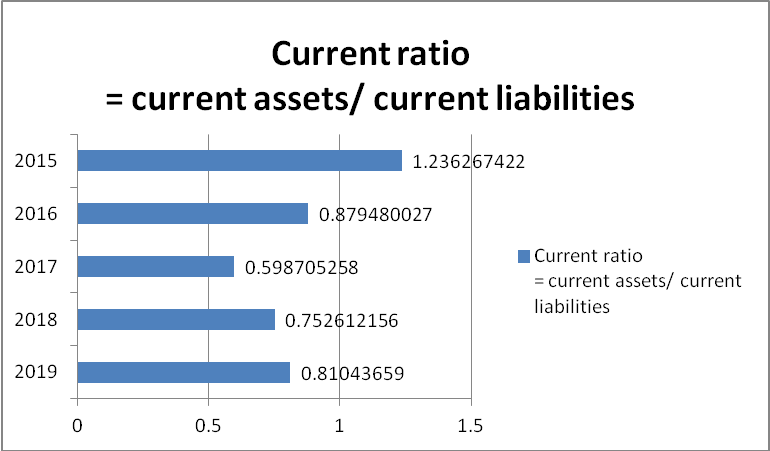
Liquid funds are an important aspect of the business that enables the discharge of obligations. Honoring the short-term debt is an essential consideration that is evaluated by many external parties (Atril 2014). The liquidity ratio of the company is ascertained with the help of the current ratio that denotes the excess of current assets over current liabilities. As seen from the computation the current of GlaxoSmithKline remained below 1 in all the years from 2016-2019 indicating the shortage of current assets in respect to current liabilities. It poses a threat in discharging the obligation because for every $1 of current liabilities the current assets are less than $1. Even it ranks less than the industry average which signifies this to be a critical element. The current ratio of Amgen is 1.66 and hence in this case too GSK ranks lower than its competitor. The industry average is 2.73 which means the ratio of GSK falls way below the industry benchmark.
Gearing ratio
Debt is an essential component for any company which signifies the presence of external debt gives a boost to the company if used in the correct perspective (Sherman 2015). As seen from the computation, the gearing ratio of the company is high. It is owing to the presence of heavy debt in the company. More debt was procured in the year 2019 however with subsequent addition to equity the company has reduced the debt-equity to 3.34 times which is still relatively high. With a crunch of liquidity denotes by the current ratio it will be difficult for the company to honor the debts. Comparatively the debt to equity of Amgen stands at 350.17% which is near to the GSK ratio of 334.12%. In comparison to the industry average of 100.45% both these companies has shown a higher component of debt.

3. Investment Appraisal
In the provided task we have evaluated the NPV, sensitivity, and IRR of the GlaxoSmithKline. The following assumptions are taken into consideration for the NPV evaluation. The discount rate is assumed to be 12% and the cash flow is considered for 5 years.
A discount rate of 12%
Cash flow is taken for 5 years, the cash flow is £10.5, £12, £13, £14.5, £15.5 respectively for 1 to 5 years. In this case, two scenarios are considered for the computation of NPV.
Coming to scenario 1, the initial investment is assumed at £42,000, and in the second scenario the initial investment is projected at £52000. Hence, the company must invest only
when the NPV is positive however if it appears negative NPV investment will be rejected.
Refer: Table 1: Net Present Value
Critical discussion of Sensitivity analysis
The sensitivity analysis for the investment proposal is entirely dependent on the discount rate and if a change is brought into the discount rate from 12% to 11% with an initial investment of £42,000 the sensitivity is supported with 8.33% and a change in the discount rate, the NPV changes to 47% and with the initial investment of £ 50,000 the sensitivity is supported at 8.33% change in the rate of discount the NPV moves to 50%. Hence, the investment proposal with the investment of £ 50,000 is more sensitive concerning the discount rate linked to NPV. The factors that are essential for the support of NPV come from the investment appraisal and the time value of capital is considered. Here, the investment appraisal is undertaken for computation of the investment in terms of the current perspective. However, another factor that needs to be considered is the risk computation which is essentially the rate of risk while undermining the investment appraisal and thereby leads to the accuracy of the investment value (Beaver, W.H., Correia & McNichols 2012).
But the fact is that the risk rate computation is not an easy consideration and complex because of the unavailability of the particular method of computing it. Thereby, it can be commented as one of the critical factors and at the same time, it is challenging in nature. Furthermore, the same involves risk making it complex.
Critical discussion of IRR
(Refer to table 3)
Coming to scenario 1, the IRR of the investment proposal is considered with an investment figure of £ 42,000 and the other factors are silent on it. The discount rate is 21%. This means that if the discount rate remains below 21% the NPV will be positive and the investment proposal will be undertaken if the cost of capital ranks below 21%. It will help in generating shareholder wealth however if the discount rate goes above 18% the investment needs to be rejected.
The IRR of the investment that is projected in scenario 2 the proposal is considered with an investment of £ 50,000 is 18%, there will appear a positive NPV and the proposal needs to be accepted if the cost of capital remains lower than 18%. This will help in generating shareholder wealth however if the discount rate or cost is above 18% then the project needs to be rejected.
Higher uncertainty is linked to higher risk. Uncertainty might lead a race to invest to take a benefit of the potential high market prices in the upcoming future. While undergoing a decision making process, risk and uncertainty is inherent in the situation. The risk return tradeoff implies that the increment in the potential return increases with an increment in the risk. As per the risk return concept, higher return will be derived when the investor or the company is able to undertake higher risk and uncertainty. Thereby it is recommended that the company should = consider the investment when the NPV is positive and the risk level justified its appetite.
Potential merger and acquisition
The rationale to choose Sitari Pharmaceuticals
Sitari Pharmaceuticals is a renowned business that is trying to suppress the autoimmune response that is responsible for the pathogenesis of cells and intestinal inflammation. The Pharmaceutical program carried out by the organization will be helpful to a lot of prospective patients who are suffering from coeliac disease. The organization is stated to have a six-year relationship with Avalon ventures and GSK who will acquire the business and the two molecule program for celiac disease. The organization was formed under the GSK and Avalon venture collaboration in the year 2013 which was incubated at the COI Pharmaceuticals, The community of Innovation. The change in focus in the research and development program of GSK has helped to complement the autoimmune pharmaceutical sector and acquire firms that will help it to fulfil the operations. However, the firm should take care of the patients who still experience gastrointestinal symptoms and disease progression.
Sitari Pharmaceuticals was observed to target the TG2 pathway for the development of medicines and treatment of Celiac Diseases. The use of TG2 has been noticed to be multifactorial in various Celiac diseases. TG2 can be understood as a primary human protein that is helpful to create an autoimmune response for celiac diseases. This particular enzyme is also helpful for providing a catalyzing effect for the reaction of dietary gluten with peptides according to the data released by the firm (Keown 2019). Various target inhibitors using the TG2 enzyme are being created by Sitari Pharmaceuticals that will help the patients to fight the intestinal inflammatory problems and cell pathogenesis in celiac patients.
The synergistic gain of acquisition for the Sitari Pharmaceuticals It has been stated by the market and the theorists that the acquisition of the firm Sitari Pharmaceuticals will be very beneficial for improving the organizational revenue. A great deal of benefits will also be observed by the logistics department after gaining control over the firm. The acquisition of the firm will also enable GSK to gain control over the intangible assets of the firm which will further help to boost the goodwill of the organization in the industry. The staff requirement will also be fulfilled when the employees of Sitari Pharmaceuticals will work with the existing employees for completing the operations and achieving the targets (Adams 2019). Therefore, acquiring the firm will be profitable for GSK in every aspect which makes it best for the firm to utilize the opportunity and acquire control over the business of Sitari Pharmaceuticals.
Proposed Deal Value and Finance of the Acquisition
The acquisition of Sitari Pharmaceuticals will bring competition for GSK in the market segment as various other biotechs are racing towards diagnosing celiac patients with different medications. This will only increase the win ratio for the GSK and Avalon model as it will be a very big collaboration for the market. The GSK and Avalon model has also been profitable in terms of generating funds. They constitute to have the top-tier academic labs and the limitless discoveries which attract investors from different backgrounds to provide money for the operations carried out the business. The considerable increase in the funding platform will eventually be considered helpful for the increase in the overall profitability of the organization. The increased profitability of the firm will further help it to induce the funds in different other sectors of pharmaceuticals, which will further increase the long run capability of the business (Palepu et al 2014).
The potential implications of the specific acquisition on the performance of the organization
The above analysis helps us to ascertain that the firm will financially benefit after the acquisition deal. Further, the organization will also be gain diverted on the customer base. This will create a huge impact on the business of the firm and at the same time will be helpful to decrease the risk. All these factors will help the firm to implicate a huge increase in profitability in the future. Ergo, the expansion strategy of the firm will be helpful to increase the profitability at large and cater to the needs of its customer base.
Challenges and assessment of the risks related to the acquisition
The biggest risk for the firm is to analyze the fact that this acquisition will for sure help it to gain profit in the future because a large debt will be acquired by it for fulfilling the obligations of the deal (Hitchner 2016). Managing the integrity of the management structure and the finances of both the firms will also be a benefactor while assessing the risks. The acquisition also needs to have a full-proof legally abided contract that will help to cater to the laws of the respective countries. The differences present in the governing structures of the nations may arise various issues while fulfilling the legal obligations of the deal (Adams 2019). Hence, the firm should keep all the facts clear to avowing its presence in any unlawful activity.
Conclusion
Through the report, the financial performance of GSK is evaluated. The report sheds light on the financial performance and with the help of the ratio analysis; an analysis was made for the performance. However, ratio analysis has certain limitations which need to be considered in the case of evaluation and assessment. The result denotes a better and strong result for the company in terms of profitability and efficiency while liquidity and gearing are a major obstacle because the gearing is high followed by weak liquidity. Overall it can be recommended that the company should repay the debts and maintain a reasonable debt level that will help the company to remain free from the obligations. Such huge debts are eroding the profit of the company too and more interest payment is being outflowed. Over reliance on debt will lead to potential problem for the company in the long run hence the debt level should be reviewed and repaid. Further, the report even sheds light on the acquisition interest of the company. The acquisition of Sitari Pharmaceuticals indicates a potential win for GSK as it would lead to better market conditions and lead to major drug advancement in celiac disease.
References
Adams, B 2019, GSK buys Celiac startup Sitara 6 years after founding it with Avalon, viewed 1 May 2021, https://www.fiercebiotech.com/biotech/gsk-buys-celiac-startup-sitari-6-years-after-founding-it-avalon
Asiri, B. K 2015, ‘How investors perceive financial ratios at different growth opportunities and financial leverages’, Journal of Business Studies Quarterly, vol. 6. No. 3, pp. 1-12.
Atril, P 2014, Financial Ratios. In: Financial Management for Decision Makers, (7th Edition). Pearson Education Limited, p. 70.
Beaver, W.H., Correia, M., McNichols, M.F 2012, ‘Do differences in financial reporting attributes impair the predictive ability of financial ratios for bankruptcy?’, Review of Accounting Studies, vol. 17, no. 4, pp. 45-51
GlaxoSmithKline 2019, GlaxoSmithKline 2019 annual report & accounts. , viewed 1 May 2021, https://www.gsk.com/media/5894/annual-report.pdf
Hitchner, J. R 2016, Financial valuation, 4th edn. Somerset: John Wiley & Sons
Keown, A 2019, GSK to Acquire Celiac-Focused Sitari Pharmaceuticals, viewed 1 May 2021, https://www.biospace.com/article/gsk-snaps-up-celiac-focused-sitari-pharmaceuticals/
Myskova, R., & Hajek, P 2017, ‘Comprehensive assessment of firm financial performance using financial ratios and linguistic analysis of annual reports’, Journal of International Studies,vol. 10, no. 4, doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.14254/2071-8330.2017/10-4/7
Palepu, K. G., Lee, P., Palepu, Bradbury, & Healy 2014, Business analysis & valuation : using financial statements (Second Asia Pacific), Cengage Learning Australia.
Sherman, E 2015, A manager's guide to financial analysis : Powerful tools for analyzing the numbers and making the best decisions for your business (6th ed), Ama Self-Study
Vernimmen, P 2017, Corporate finance : theory and practice, Hoboken: Wiley.
Zainudin, E. F., & Hashim, H. A 2016, Detecting fraudulent financial reporting using financial ratio’, . Journal of Financial Reporting and Accounting, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 266-278. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/JFRA-05-2015-0053
Appendix
Appendix 1
Table 1
|
Scenario 1 |
Amount in '000 |
|
|
|
Initial Investment |
£ 42.00 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year |
Net Cash flow |
Discount rate 12 % |
Present Value |
|
0 |
-42 |
1.00 |
-42 |
|
1 |
10.5 |
0.89 |
9.38 |
|
2 |
12 |
0.80 |
9.57 |
|
3 |
13 |
0.71 |
9.25 |
|
4 |
14.5 |
0.64 |
9.22 |
|
5 |
15.5 |
0.57 |
8.80 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Present Value |
|
£ 4.20 |
|
The NPV is positive so the investment will create shareholder wealth |
|
|
|
|
Scenario 2 |
Amount in '000 |
|
|
|
Initial Investment |
£ 50.00 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year |
Net Cash flow |
Discount rate 12 % |
Present Value |
|
0 |
-50 |
1.00 |
-50 |
|
1 |
10.5 |
0.89 |
9.38 |
|
2 |
12.2 |
0.80 |
9.73 |
|
3 |
13.5 |
0.71 |
9.61 |
|
4 |
14.1 |
0.64 |
8.96 |
|
5 |
15.2 |
0.57 |
8.62 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Present Value |
|
-£ 3.70 |
|
The NPV is negative so the investment will destroy shareholder wealth |
|
|
|
|
Suppose discount rate changes from 12% to 11% |
|
|
|
TABLE 2
|
Revised NPV in Scenario 1 |
|
Amount in '000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year |
Net Cash flow |
Discount rate 11 % |
Present Value |
|
0 |
-42 |
1.00 |
-42 |
|
1 |
10.5 |
0.90 |
9.46 |
|
2 |
12 |
0.81 |
9.74 |
|
3 |
13 |
0.73 |
9.51 |
|
4 |
14.5 |
0.66 |
9.55 |
|
5 |
15.5 |
0.59 |
9.20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Present Value |
|
£ 5.45 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sensitivity analysis |
|
|
|
|
NPV= |
(5.45-4.2)/4.2= 30% |
30% |
|
|
Discount rate= |
1/12= 8.33% |
|
|
|
Therefore with 8.33% change in discount rate the NPV changes in 30% |
|
|
|
|
Revised NPV in Scenario 2 |
|
Amount in '000 |
|
|
Initial Investment |
£ 50.00 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year |
Net Cash flow |
Discount rate 11 % |
Present Value |
|
0 |
-50 |
1.00 |
-50 |
|
1 |
10.5 |
0.90 |
9.46 |
|
2 |
12.2 |
0.81 |
9.90 |
|
3 |
13.5 |
0.73 |
9.87 |
|
4 |
14.1 |
0.66 |
9.29 |
|
5 |
15.2 |
0.59 |
9.02 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Present Value |
|
-£ 2.46 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sensitivity analysis |
|
|
|
|
NPV= |
(3.70-2.46)/2.46= 18.16% |
50% |
|
|
Discount rate= |
1/12= 8.33% |
|
|
|
Therefore with 8.33% change in discount rate the NPV changes in 50% |
|
|
|
TABLE 3
Calculation of Internal Rate of Return
|
Calculation of Internal Rate of Return |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Scenario 1 |
Amount in '000 |
|
|
|
Initial Investment |
£ 42.00 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year |
Net Cash flow |
Discount rate 15 % |
Present Value |
|
0 |
-42 |
1.00 |
-42 |
|
1 |
10.5 |
0.87 |
9.13 |
|
2 |
12 |
0.76 |
9.07 |
|
3 |
13 |
0.66 |
8.55 |
|
4 |
14.5 |
0.57 |
8.29 |
|
5 |
15.5 |
0.50 |
7.71 |
|
6 |
5.5 |
0.43 |
2.38 |
|
7 |
6.1 |
0.38 |
2.29 |
|
8 |
6.3 |
0.33 |
2.06 |
|
9 |
5.1 |
0.28 |
1.45 |
|
10 |
5.5 |
0.25 |
1.36 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Considering 15% as IRR the NPV is 10.29 |
|
|
|
|
|
Net Present Value |
|
£ 10.29 |
|
Since NPV is not Zero so we need to increase discount rate |
|
|
|
|
Year |
Net Cash flow |
Discount rate 21 % |
Present Value |
|
0 |
-42 |
1.00 |
-42 |
|
1 |
10.5 |
0.83 |
8.68 |
|
2 |
14 |
0.68 |
9.56 |
|
3 |
13.8 |
0.56 |
7.79 |
|
4 |
14.5 |
0.47 |
6.76 |
|
5 |
15.8 |
0.39 |
6.09 |
|
6 |
5.5 |
0.32 |
1.75 |
|
7 |
6.1 |
0.26 |
1.61 |
|
8 |
6.3 |
0.22 |
1.37 |
|
9 |
5.6 |
0.18 |
1.01 |
|
10 |
4.5 |
0.15 |
0.67 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Considering 21% as IRR the NPV is |
|
|
|
|
|
Net Present Value |
|
£ 3.29 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Since NPV is 3.29 , therefore IRR is approx 21% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IRR is 21% |
|
|
|
|
Scenario 2 |
Amount in '000 |
|
|
|
Initial Investment |
£ 2.00 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year |
Net Cash flow |
Discount rate 15 % |
Present Value |
|
0 |
-50 |
1.00 |
-50 |
|
1 |
10.9 |
0.87 |
9.48 |
|
2 |
12.5 |
0.76 |
9.45 |
|
3 |
13.2 |
0.66 |
8.68 |
|
4 |
14.3 |
0.57 |
8.18 |
|
5 |
15.9 |
0.50 |
7.91 |
|
6 |
5.1 |
0.43 |
2.20 |
|
7 |
6.6 |
0.38 |
2.48 |
|
8 |
6.1 |
0.33 |
1.99 |
|
9 |
5.3 |
0.28 |
1.51 |
|
10 |
5.8 |
0.25 |
1.43 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Considering 15% as IRR the NPV is 1.31 |
|
|
|
|
|
Net Present Value |
|
£ 3.31 |
|
Since NPV is not Zero so we need to increase discount rate |
|
|
|
|
Year |
Net Cash flow |
Discount rate 17 % |
Present Value |
|
0 |
-52 |
1.00 |
-52 |
|
1 |
10.9 |
0.85 |
9.32 |
|
2 |
12.5 |
0.73 |
9.13 |
|
3 |
13.2 |
0.62 |
8.24 |
|
4 |
14.3 |
0.53 |
7.63 |
|
5 |
15.9 |
0.46 |
7.25 |
|
6 |
5.1 |
0.39 |
1.99 |
|
7 |
6.6 |
0.33 |
2.20 |
|
8 |
6.1 |
0.28 |
1.74 |
|
9 |
5.3 |
0.24 |
1.29 |
|
10 |
5.8 |
0.21 |
1.21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Considering 21% as IRR the NPV is |
|
|
|
|
|
Net Present Value |
|
-£ 2.01 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Since NPV is -0.02 , therefore IRR is approx 18% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IRR is 18% |
|
|
|
Appendix 2 Ratio analysis
|
Profitability |
|||||
|
|
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 |
2015 |
|
Net Profit |
5,268 |
4,046 |
2,169 |
1062 |
8372 |
|
Sales |
33754 |
30821 |
30186 |
27889 |
23923 |
|
Net Profit ratio |
16% |
13% |
7% |
4% |
35% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Efficiency |
|||||
|
|
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 |
2015 |
|
Net sales |
33754 |
30821 |
30186 |
27889 |
23923 |
|
Average total assets |
68879 |
57223.5 |
57731 |
56263.5 |
53446 |
|
Asset turnover |
0.490048 |
0.538607 |
0.522873 |
0.495685 |
0.447611 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Liquidity |
|||||
|
|
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 |
2015 |
|
Current assets |
19,491 |
16927 |
15907 |
16,711 |
16587 |
|
Current liabilities |
24050 |
22491 |
26569 |
19001 |
13417 |
|
Current ratio |
0.810437 |
0.752612 |
0.598705 |
0.87948 |
1.236267 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gearing |
|||||
|
|
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 |
2015 |
|
Debt |
61335 |
54394 |
52892 |
54118 |
44568 |
|
Equity |
18357 |
3672 |
3489 |
4963 |
8878 |
|
Debt to equity |
3.341232 |
14.81318 |
15.15964 |
10.90429 |
5.02005 |












